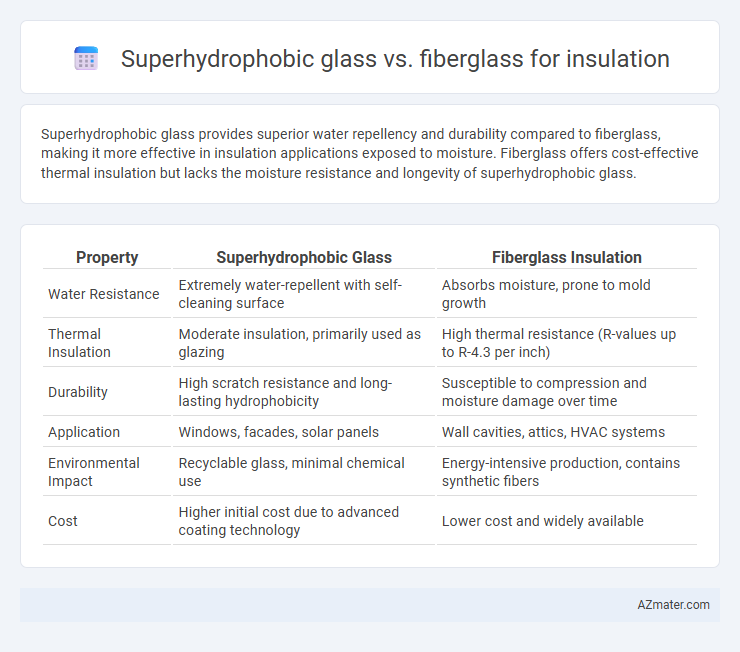
Superhydrophobic glass provides superior water repellency and durability compared to fiberglass, making it more effective in insulation applications exposed to moisture. Fiberglass offers cost-effective thermal insulation but lacks the moisture resistance and longevity of superhydrophobic glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superhydrophobic Glass | Fiberglass Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Extremely water-repellent with self-cleaning surface | Absorbs moisture, prone to mold growth |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation, primarily used as glazing | High thermal resistance (R-values up to R-4.3 per inch) |
| Durability | High scratch resistance and long-lasting hydrophobicity | Susceptible to compression and moisture damage over time |
| Application | Windows, facades, solar panels | Wall cavities, attics, HVAC systems |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable glass, minimal chemical use | Energy-intensive production, contains synthetic fibers |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced coating technology | Lower cost and widely available |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Superhydrophobic glass and fiberglass represent two advanced insulation materials with distinct properties tailored for thermal efficiency and moisture resistance. Superhydrophobic glass offers enhanced water repellency and durability, making it ideal for environments prone to condensation and humidity. Fiberglass insulation excels in thermal performance and cost-effectiveness, widely used for its ability to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass is a type of glass treated with nanoscale coatings that create an ultra-water-repellent surface, preventing water droplets from adhering and reducing corrosion or staining. Unlike fiberglass insulation, which is a fibrous material designed primarily for thermal resistance, superhydrophobic glass offers both insulation benefits and exceptional durability against moisture and contaminants. This makes superhydrophobic glass ideal for applications requiring transparency, weather resistance, and ease of maintenance in building insulation.
Key Properties of Fiberglass
Fiberglass insulation is characterized by its excellent thermal resistance, typically having an R-value ranging from 2.2 to 2.7 per inch, which effectively reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency. Its porous structure provides soundproofing benefits and resists moisture absorption, preventing mold growth and maintaining durability over time. Fiberglass also offers fire resistance, non-combustibility, and affordability, making it a widely used material for thermal insulation in residential and commercial buildings.
Thermal Insulation Efficiency: Glass vs Fiberglass
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits enhanced thermal insulation efficiency due to its ability to repel water, reducing heat transfer caused by moisture accumulation. Fiberglass insulation provides excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging between R-2.9 and R-3.8 per inch, making it a widely used material for maintaining indoor temperatures. While superhydrophobic glass offers added durability and moisture control, fiberglass remains more effective in consistent thermal insulation performance across various temperatures.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Superhydrophobic glass offers exceptional moisture resistance due to its water-repellent coating that prevents water absorption, making it highly effective in humid or wet environments. Fiberglass insulation, while commonly used, tends to absorb moisture which can reduce its thermal efficiency and promote mold growth over time. In terms of durability, superhydrophobic glass maintains structural integrity and clarity without degradation from moisture exposure, whereas fiberglass can deteriorate and lose insulating properties when consistently exposed to damp conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass offers a streamlined installation process due to its lightweight, rigid panels that fit seamlessly into modern framing systems, requiring minimal sealing compared to fiberglass. Maintenance of superhydrophobic glass is simplified by its self-cleaning surface that repels water and dirt, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and prolonging durability. In contrast, fiberglass insulation demands careful handling during installation to avoid irritation and requires periodic inspection for moisture and mold buildup, increasing long-term maintenance efforts.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Superhydrophobic glass typically commands a higher upfront cost than fiberglass insulation due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized coatings that enhance water repellency. Fiberglass remains widely available and cost-effective, benefiting from mass production and established supply chains across construction markets. Budget-conscious projects often favor fiberglass for its affordability and accessibility, while superhydrophobic glass is selected for niche applications requiring superior moisture resistance despite higher expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior environmental benefits compared to fiberglass by reducing energy consumption through enhanced thermal insulation and durability, which decreases the frequency of replacements and waste generation. Fiberglass insulation, while widely used, often involves energy-intensive production processes and poses disposal challenges due to non-biodegradable materials and potential health risks from airborne fibers. Sustainable choices favor superhydrophobic glass as it supports energy efficiency, longevity, and recyclability, aligning with green building standards and reducing overall environmental footprints.
Practical Applications in Construction
Superhydrophobic glass offers exceptional water repellency and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for exterior building facades and windows that require high durability and low maintenance. Fiberglass insulation excels in thermal resistance and soundproofing, widely used in walls and ceilings to improve energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Combining superhydrophobic coatings on glass with fiberglass insulation enhances overall building performance by reducing moisture-related damage and maximizing thermal protection.
Choosing the Best Insulation: Factors to Consider
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for environments prone to moisture exposure, while fiberglass provides excellent thermal insulation at a lower cost. When choosing the best insulation, factors such as moisture control, thermal performance, fire resistance, and cost-effectiveness must be evaluated. Consider the specific application, climate conditions, and long-term maintenance requirements to determine whether the advanced properties of superhydrophobic glass or the widespread practicality of fiberglass better meet project needs.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com