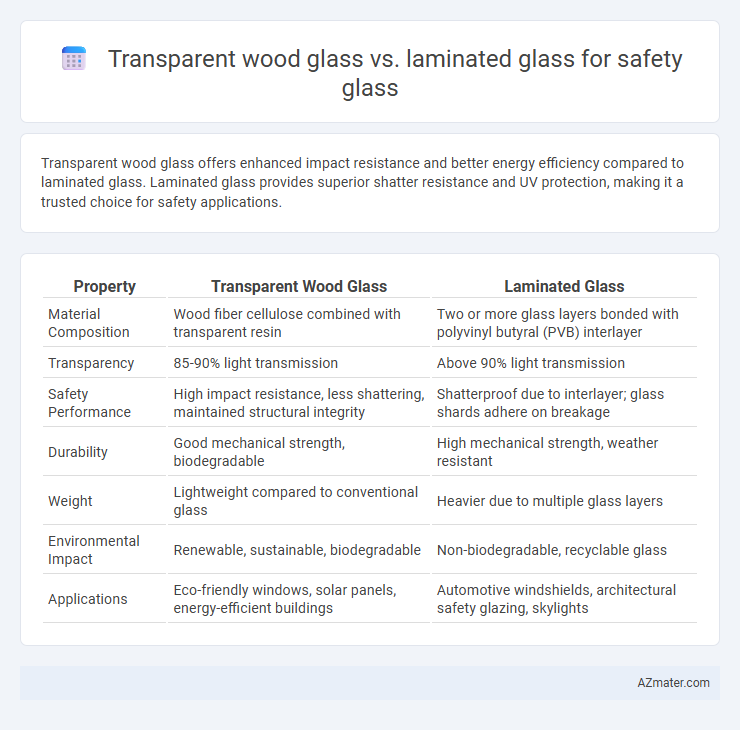
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced impact resistance and better energy efficiency compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides superior shatter resistance and UV protection, making it a trusted choice for safety applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Wood Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fiber cellulose combined with transparent resin | Two or more glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Transparency | 85-90% light transmission | Above 90% light transmission |
| Safety Performance | High impact resistance, less shattering, maintained structural integrity | Shatterproof due to interlayer; glass shards adhere on breakage |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, biodegradable | High mechanical strength, weather resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to conventional glass | Heavier due to multiple glass layers |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, sustainable, biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable glass |
| Applications | Eco-friendly windows, solar panels, energy-efficient buildings | Automotive windshields, architectural safety glazing, skylights |
Introduction to Safety Glass Solutions
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced impact resistance and superior energy efficiency compared to traditional laminated glass, making it an innovative choice for safety glass solutions. Laminated glass remains the industry standard with a proven ability to hold shards together upon impact, ensuring occupant protection and structural integrity. Both materials provide critical safety features, but transparent wood glass integrates sustainability and advanced mechanical properties that appeal to modern architectural applications.
What is Transparent Wood Glass?
Transparent wood glass is an innovative safety glass alternative made by removing lignin from natural wood and impregnating it with transparent polymers, resulting in a material that combines strength, flexibility, and optical clarity. This wood-based composite offers superior impact resistance and thermal insulation compared to traditional laminated glass while maintaining transparency and lightweight properties. Unlike laminated glass, which layers glass sheets with a plastic interlayer for safety, transparent wood glass enhances durability through its bio-based structure and sustainable manufacturing processes.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, often made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and impact resistance by holding the glass fragments in place upon breakage. In contrast, transparent wood glass, developed by infiltrating wood with transparent polymers, offers a sustainable alternative with high strength and optical clarity but is less commonly used in safety applications. Laminated glass remains the industry standard for safety glass due to its proven ability to prevent shattering and maintain structural integrity during impact or accidents.
Material Composition: Transparent Wood Glass vs Laminated Glass
Transparent wood glass consists of natural wood fibers infiltrated with a transparent polymer resin, combining the cellulose structure of wood with the clarity and strength of polymer for enhanced impact resistance and sustainability. Laminated glass is composed of two or more glass layers bonded by an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which holds the glass together upon impact to prevent shattering. The distinct material compositions provide transparent wood glass with superior biodegradability and flexibility, while laminated glass offers established safety performance with predictable fracture patterns and high stiffness.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Transparent wood glass exhibits higher impact resistance due to its unique cellulose nanofiber structure which enhances energy absorption and flexibility, outperforming laminated glass in shock absorption. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that provides exceptional strength and shatter resistance but can be more brittle under high impact forces. Strength testing reveals laminated glass offers superior rigidity and hardness, while transparent wood glass excels in durability and resilience against impact, making each suitable for different safety glass applications depending on specific performance requirements.
Transparency and Aesthetic Considerations
Transparent wood glass offers superior natural light diffusion with enhanced transparency compared to laminated glass, creating a warm, organic aesthetic ideal for modern interiors. Laminated glass provides high clarity and strength but can suffer from slight visual distortions or interlayer haziness, impacting overall transparency. Aesthetically, transparent wood glass introduces unique grain patterns and texture, blending safety with design innovation, while laminated glass emphasizes sleekness and uniformity in safety applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Transparent wood glass exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to laminated glass due to its low thermal conductivity and natural cellular structure, effectively reducing heat transfer. Laminated glass provides enhanced acoustic insulation through its interlayer materials that dampen sound vibrations, though transparent wood glass also offers competitive sound attenuation because of its porous matrix. Both materials contribute to safety glass applications, but transparent wood glass stands out for energy-efficient insulation, while laminated glass excels in noise reduction.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Transparent wood glass offers significant sustainability advantages over laminated glass by utilizing renewable wood fibers and reducing reliance on non-recyclable plastics and resins, thus lowering overall carbon footprint. Its production consumes less energy and generates fewer emissions, making it a more eco-friendly option for safety glass applications. Laminated glass, while providing robust impact resistance, often involves complex recycling processes and uses synthetic materials with higher environmental costs.
Cost and Applications in Industry
Transparent wood glass offers lower production costs due to sustainable raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes compared to laminated glass, which involves multiple glass layers and interlayers like PVB or EVA. Transparent wood glass finds increasing applications in energy-efficient building facades and decorative panels due to its lightweight and natural aesthetics, whereas laminated glass dominates in automotive windshields, protective barriers, and bullet-resistant windows for its proven durability and impact resistance. Cost efficiency and environmental benefits position transparent wood glass as promising for green architecture, while laminated glass remains the standard in high-safety industrial applications.
Future Prospects: Which Safety Glass Leads the Way?
Transparent wood glass offers innovative safety features by combining the natural strength of wood fibers with glass transparency, enhancing impact resistance and sustainability compared to traditional laminated glass. Laminated glass remains the industry standard due to its proven durability and ability to prevent shattering, but transparent wood glass shows promising future prospects with its eco-friendly attributes and potential for improved energy efficiency. Advances in material science and manufacturing techniques could position transparent wood glass as the leading safety glass for green building applications.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Laminated glass for Safety glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com