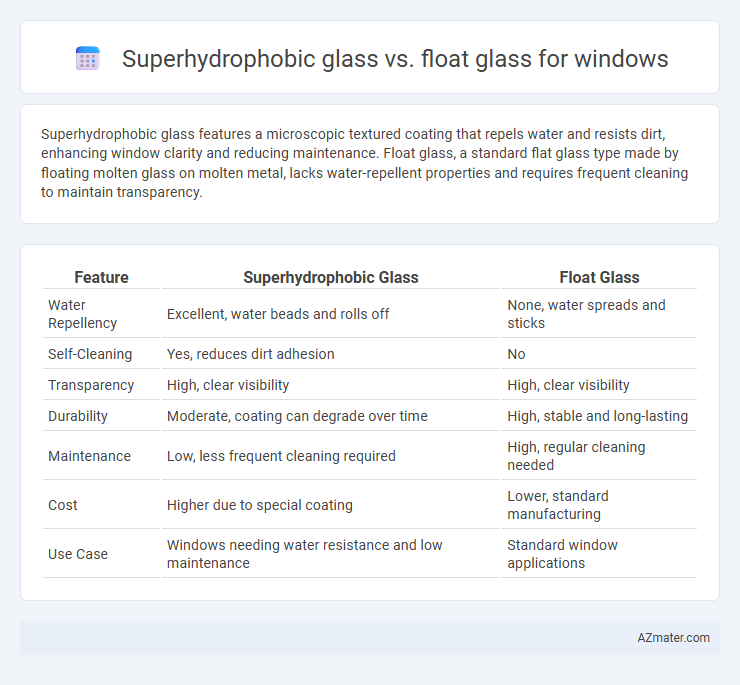
Superhydrophobic glass features a microscopic textured coating that repels water and resists dirt, enhancing window clarity and reducing maintenance. Float glass, a standard flat glass type made by floating molten glass on molten metal, lacks water-repellent properties and requires frequent cleaning to maintain transparency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Water Repellency | Excellent, water beads and rolls off | None, water spreads and sticks |
| Self-Cleaning | Yes, reduces dirt adhesion | No |
| Transparency | High, clear visibility | High, clear visibility |
| Durability | Moderate, coating can degrade over time | High, stable and long-lasting |
| Maintenance | Low, less frequent cleaning required | High, regular cleaning needed |
| Cost | Higher due to special coating | Lower, standard manufacturing |
| Use Case | Windows needing water resistance and low maintenance | Standard window applications |
Introduction to Superhydrophobic and Float Glass
Superhydrophobic glass features a highly water-repellent surface created by nanostructured coatings, enhancing self-cleaning properties and reducing maintenance. Float glass, produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, serves as the industry standard for windowpanes due to its smooth, flat surface and uniform thickness. The distinct manufacturing processes and surface characteristics of superhydrophobic and float glass determine their suitability for applications demanding water resistance versus basic transparency and durability.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Superhydrophobic glass is coated with nanoscale materials like silica or fluoropolymers applied through chemical vapor deposition or spray coating, creating a textured surface that repels water and dirt. Float glass is produced by pouring molten glass onto a bath of molten tin, forming a flat and smooth surface without additional coatings. The main difference lies in superhydrophobic glass's surface treatment for enhanced water resistance, while float glass remains untreated, offering basic transparency and durability.
Water Repellency and Self-Cleaning Properties
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits superior water repellency compared to float glass due to its micro- and nanoscale surface textures that cause water droplets to bead and roll off easily, preventing water accumulation and staining. The self-cleaning properties of superhydrophobic glass are enhanced by its ability to minimize adhesion of dust and dirt particles, allowing rainwater to wash contaminants away effortlessly. Float glass, while widely used for its clarity and affordability, lacks these advanced surface characteristics, resulting in more water retention and frequent manual cleaning requirements.
Durability and Longevity
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior durability compared to float glass due to its water-repellent coating that prevents moisture damage and reduces surface wear from environmental exposure. The longevity of superhydrophobic glass is enhanced by its self-cleaning properties, which minimize dirt accumulation and maintain clarity over time, unlike traditional float glass that is more prone to staining and degradation. This makes superhydrophobic glass a more resilient and long-lasting option for window applications in harsh weather conditions.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits superior thermal insulation capabilities compared to traditional float glass due to its advanced coating technology that minimizes heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency. The water-repellent surface not only reduces condensation but also contributes to maintaining indoor temperature stability by reflecting infrared radiation. Float glass, while cost-effective and widely used, lacks these thermal insulating properties, often resulting in higher energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces maintenance and cleaning efforts compared to float glass due to its water-repellent and self-cleaning properties that prevent dirt, dust, and water stains from adhering to the surface. Float glass requires frequent cleaning to maintain clarity as it readily accumulates grime and watermarks, often necessitating harsh chemicals and labor-intensive scrubbing. The long-term cost savings and enhanced durability of superhydrophobic glass make it a superior choice for windows in environments prone to heavy pollution or moisture.
Cost Comparison: Superhydrophobic vs Float Glass
Superhydrophobic glass typically costs significantly more than float glass due to advanced coating technologies that impart water-repellent properties, which increase manufacturing complexity and material expenses. Float glass remains the most cost-effective option for standard windows, providing clarity and strength at a lower price point but lacks the self-cleaning and anti-fogging benefits of superhydrophobic variants. The higher initial investment for superhydrophobic glass can be offset over time by reduced maintenance and cleaning costs, especially in environments prone to water and dirt accumulation.
Energy Efficiency in Window Applications
Superhydrophobic glass significantly improves energy efficiency in window applications by minimizing water retention and reducing surface contamination, which enhances natural light transmission and reduces the need for artificial lighting. Compared to float glass, superhydrophobic coatings provide better thermal insulation by repelling water and dirt that can degrade insulating properties over time. This leads to lower heating and cooling costs, making superhydrophobic glass a superior choice for sustainable building designs focused on energy conservation.
Suitability for Residential and Commercial Buildings
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties, making it highly suitable for residential and commercial buildings in regions with frequent rain or pollution, reducing maintenance costs. Float glass, known for its clarity and affordability, is widely used for standard window applications but lacks the advanced functional benefits needed in complex environmental conditions. Choosing superhydrophobic glass enhances durability and aesthetic appeal, while float glass remains a cost-effective option for basic glazing needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces water and dirt accumulation, lowering the frequency of cleaning and the use of harsh chemicals, which enhances environmental sustainability compared to traditional float glass. Float glass production is energy-intensive and generates higher carbon emissions, while superhydrophobic coatings extend window lifespan by protecting against corrosion and pollution. The durability and self-cleaning properties of superhydrophobic glass contribute to reduced maintenance costs and environmental footprint over its lifecycle.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Float glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com