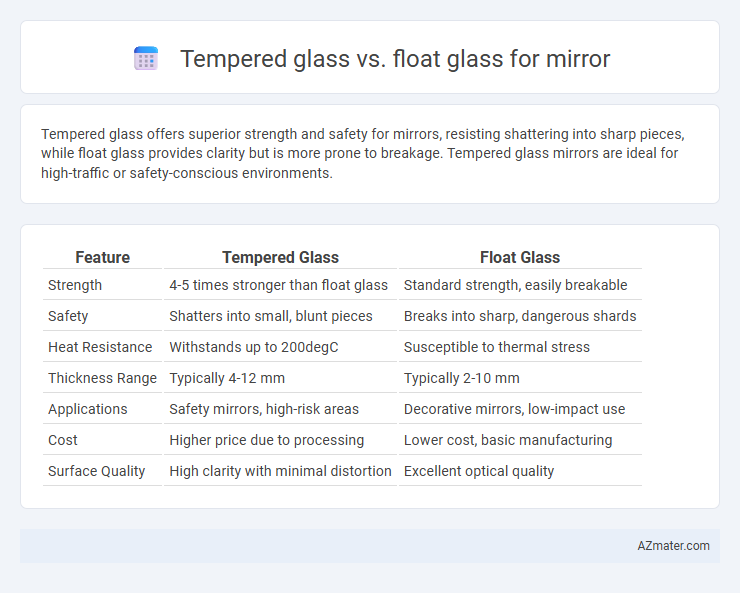
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for mirrors, resisting shattering into sharp pieces, while float glass provides clarity but is more prone to breakage. Tempered glass mirrors are ideal for high-traffic or safety-conscious environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than float glass | Standard strength, easily breakable |
| Safety | Shatters into small, blunt pieces | Breaks into sharp, dangerous shards |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands up to 200degC | Susceptible to thermal stress |
| Thickness Range | Typically 4-12 mm | Typically 2-10 mm |
| Applications | Safety mirrors, high-risk areas | Decorative mirrors, low-impact use |
| Cost | Higher price due to processing | Lower cost, basic manufacturing |
| Surface Quality | High clarity with minimal distortion | Excellent optical quality |
Introduction to Tempered Glass and Float Glass
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass, making it ideal for mirrors exposed to impact or high temperatures. Float glass, also known as annealed glass, is produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, resulting in a smooth, uniform surface commonly used for standard mirror manufacturing. The choice between tempered and float glass mirrors depends on the application's safety requirements and durability needs.
Key Differences Between Tempered Glass and Float Glass
Tempered glass undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment to increase its strength, making it about four to five times stronger than float glass, which is standard annealed glass formed by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal. Float glass breaks into small, blunt pieces when shattered, reducing injury risk, while tempered glass shatters into tiny granular chunks, enhancing safety in mirrors. The superior thermal resistance and mechanical durability of tempered glass make it ideal for high-traffic or impact-prone mirror applications, whereas float glass is more suitable for decorative or low-stress uses.
Manufacturing Process: Tempered vs Float Glass
Tempered glass mirrors are produced by heating float glass to approximately 620degC and rapidly cooling it, inducing compressive stress that enhances strength and safety. Float glass mirrors are manufactured using a continuous ribbon process where molten glass floats on molten tin, producing a smooth, flat surface but without thermal treatment. The tempering process significantly increases resistance to impact and thermal stress compared to untreated float glass mirrors.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength compared to float glass, being up to five times stronger due to its heat treatment process, which enhances its resistance to impact and thermal stress. Its durability makes it ideal for mirrors in high-traffic or safety-sensitive environments, as it reduces the risk of shattering into sharp pieces, unlike float glass that breaks into large, dangerous shards. Float glass, while more cost-effective and suitable for standard mirror applications, lacks the reinforced durability and resilience against mechanical and thermal damage that tempered glass provides.
Safety Features of Both Glass Types
Tempered glass offers superior safety features for mirrors due to its enhanced strength and ability to crumble into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing the risk of injury. Float glass, while common and cost-effective, breaks into large, sharp shards that pose greater hazards during accidents or breakage. The inherent safety benefits of tempered glass make it the preferred choice in environments requiring stringent safety standards.
Optical Clarity and Surface Quality
Tempered glass offers enhanced surface strength but may exhibit slight distortions affecting optical clarity compared to float glass, which provides superior flatness and optical transparency ideal for high-quality mirrors. The uniform surface quality of float glass ensures minimal light refraction and distortion, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring precise reflection. However, tempered glass's safety features make it suitable where durability is critical despite a marginal compromise in mirror clarity.
Suitability for Mirror Applications
Tempered glass is ideal for mirror applications requiring enhanced safety and durability due to its impact resistance and slip-resistant properties, making it suitable for high-traffic areas like gyms and bathrooms. Float glass, while cost-effective and providing excellent optical clarity, is more prone to breakage and lacks the strength needed for environments subject to frequent impact or thermal stress. Choosing tempered glass enhances the longevity and safety of mirrors in commercial and residential spaces where durability is critical.
Cost Analysis: Tempered Glass vs Float Glass
Tempered glass for mirrors typically costs 20-30% more than float glass due to the additional heat treatment process enhancing strength and safety. Float glass offers a more affordable option but lacks the durability and impact resistance of tempered glass, making it less suitable for high-risk environments. Evaluating long-term value, tempered glass reduces replacement and maintenance expenses, potentially offsetting its initial higher price.
Installation Considerations for Mirrors
Tempered glass offers enhanced safety and durability, making it ideal for mirror installations in high-traffic or humid areas, as it reduces the risk of shattering into sharp pieces. Float glass, while more cost-effective, requires careful handling and secure mounting to prevent breakage during installation, limiting its use in environments prone to impact or stress. The choice between tempered and float glass for mirrors hinges on balancing installation complexity with safety requirements and environmental conditions.
Which Glass Type is Best for Your Mirror?
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for mirrors, as it shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risk. Float glass, while more affordable and easier to cut, lacks the impact resistance and thermal durability of tempered glass, making it less ideal for high-traffic or humid environments. For optimal mirror performance and safety, especially in bathrooms or public spaces, tempered glass is the best choice.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Float glass for Mirror
 azmater.com
azmater.com