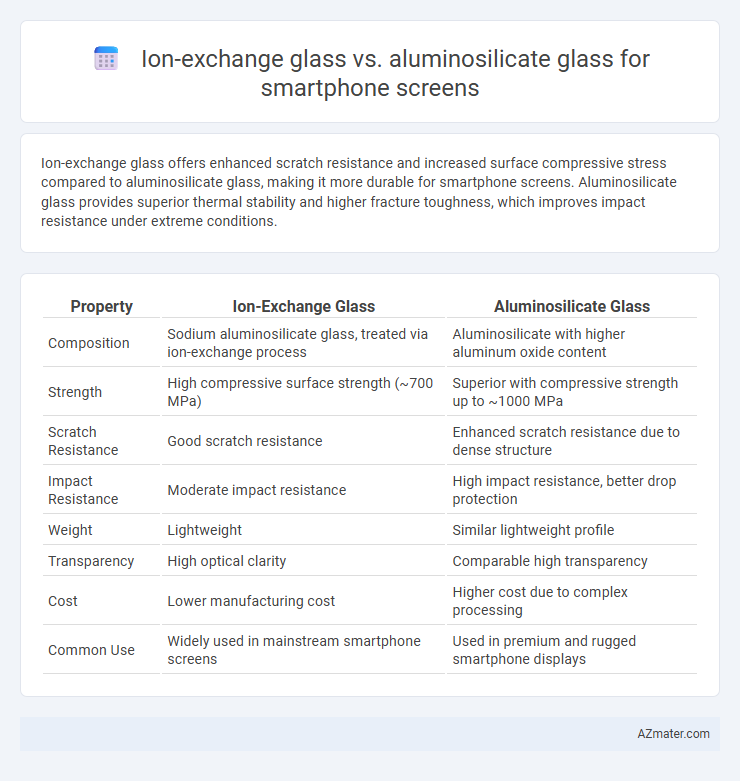
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced scratch resistance and increased surface compressive stress compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it more durable for smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass provides superior thermal stability and higher fracture toughness, which improves impact resistance under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium aluminosilicate glass, treated via ion-exchange process | Aluminosilicate with higher aluminum oxide content |
| Strength | High compressive surface strength (~700 MPa) | Superior with compressive strength up to ~1000 MPa |
| Scratch Resistance | Good scratch resistance | Enhanced scratch resistance due to dense structure |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact resistance | High impact resistance, better drop protection |
| Weight | Lightweight | Similar lightweight profile |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Comparable high transparency |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher cost due to complex processing |
| Common Use | Widely used in mainstream smartphone screens | Used in premium and rugged smartphone displays |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Materials
Ion-exchange glass enhances smartphone screen durability through a chemical strengthening process that replaces smaller ions with larger ones, creating compressive stress on the surface. Aluminosilicate glass, composed primarily of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen, delivers exceptional mechanical strength and scratch resistance ideal for high-impact environments. Both materials are essential in modern smartphones, balancing toughness, clarity, and responsiveness for optimal user experience.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a chemically strengthened material commonly used for smartphone screens, created by immersing glass in a molten salt bath to replace smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, increasing surface compression and enhancing scratch resistance. Compared to aluminosilicate glass, ion-exchange glass offers superior toughness, making it more resistant to impacts and everyday wear. The ion-exchange process creates a durable, high-strength surface ideal for protecting smartphones from drops and scratches.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, known for its exceptional strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for durable smartphone screens. Unlike traditional ion-exchange glass, aluminosilicate glass undergoes chemical strengthening through a high-temperature ion exchange process, enhancing its scratch resistance and impact durability. This combination of chemical composition and manufacturing process results in a tough, lightweight protective layer that significantly improves screen longevity and user experience.
Chemical Composition Differences
Ion-exchange glass for smartphone screens primarily consists of alkali aluminosilicate with a high concentration of sodium ions that are replaced by larger potassium ions during the ion-exchange process, enhancing surface compression and scratch resistance. Aluminosilicate glass, on the other hand, is characterized by a network of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3) with fewer alkali ions, resulting in inherent structural strength and thermal stability without the surface treatment. The chemical composition difference lies in the ion-exchange glass's surface-enriched potassium ion layer versus the aluminosilicate glass's bulk structure dominated by silica and alumina, which affects durability and resistance to impact.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ion-exchange glass, such as Gorilla Glass, achieves enhanced strength through a chemical tempering process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, creating compressive stress on the surface and significantly improving scratch resistance and impact durability. Aluminosilicate glass inherently possesses a robust molecular structure with high alumina content, which provides excellent fracture toughness and thermal stability but relies more on thickness and composition for strength. While ion-exchange glass excels in surface hardness and resistance to daily abrasion, aluminosilicate glass offers superior overall structural integrity under extreme mechanical stress, making the choice dependent on specific smartphone design priorities.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Ion-exchange glass provides superior scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened surface created through a potassium ion exchange process, resulting in a compressive stress layer that resists surface damage. Aluminosilicate glass, while also offering strong impact resistance, benefits from its durable aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide network, making it more capable of absorbing shock and resisting shattering upon impact. Overall, ion-exchange glass excels in preventing scratches, whereas aluminosilicate glass offers enhanced impact resistance, contributing to longer-lasting smartphone screen durability.
Manufacturing Processes
Ion-exchange glass undergoes a chemical strengthening process where smaller sodium ions on the surface are replaced by larger potassium ions, creating compressive stress that enhances scratch resistance and impact durability, commonly used in Gorilla Glass production. Aluminosilicate glass is typically produced through controlled melting and drawing processes with the addition of aluminum oxide, granting it superior thermal and mechanical properties, but often requires subsequent chemical or thermal tempering to achieve desired toughness. Manufacturing ion-exchange glass involves precise ion diffusion baths at elevated temperatures, whereas aluminosilicate glass relies more heavily on intrinsic material composition and post-processing to optimize hardness and flexibility for smartphone screen applications.
Cost Considerations
Ion-exchange glass typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to the complex chemical bath process required to enhance surface strength, impacting overall smartphone pricing. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in Gorilla Glass, offers a cost-effective balance between durability and production efficiency, making it a preferred choice for mass-market devices. Cost considerations also factor in the scalability of aluminosilicate glass production, which benefits from established industrial supply chains and lower raw material expenses.
Applications in Smartphone Brands
Ion-exchange glass, known for its superior scratch resistance and enhanced surface strength, is widely used in flagship smartphones such as Apple's iPhone and Samsung Galaxy series. Aluminosilicate glass offers excellent durability and impact resistance, making it a preferred choice for mid-range to high-end devices like Google Pixel and OnePlus. Both materials deliver critical protection, but ion-exchange glass often provides a higher level of toughness suited for premium smartphone displays.
Future Trends in Smartphone Glass Technology
Ion-exchange glass continues to dominate smartphone screens due to its superior scratch resistance and enhanced surface compression, yet aluminosilicate glass is gaining traction for its improved durability under impact and thermal stability. Future trends emphasize hybrid compositions combining ion-exchange and aluminosilicate properties to optimize toughness, flexibility, and transparency for foldable and wearable devices. Advances in chemical strengthening processes and nano-coatings further propel innovations, aiming to reduce screen damage and extend device longevity in increasingly compact smartphone designs.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com