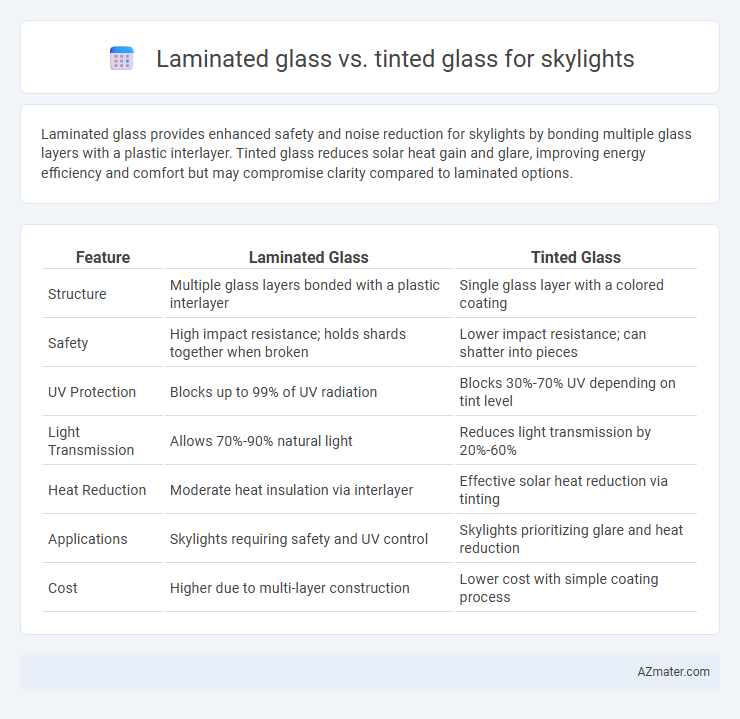
Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and noise reduction for skylights by bonding multiple glass layers with a plastic interlayer. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare, improving energy efficiency and comfort but may compromise clarity compared to laminated options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer | Single glass layer with a colored coating |
| Safety | High impact resistance; holds shards together when broken | Lower impact resistance; can shatter into pieces |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of UV radiation | Blocks 30%-70% UV depending on tint level |
| Light Transmission | Allows 70%-90% natural light | Reduces light transmission by 20%-60% |
| Heat Reduction | Moderate heat insulation via interlayer | Effective solar heat reduction via tinting |
| Applications | Skylights requiring safety and UV control | Skylights prioritizing glare and heat reduction |
| Cost | Higher due to multi-layer construction | Lower cost with simple coating process |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Skylight glass options primarily include laminated glass and tinted glass, each offering unique benefits in terms of safety, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. Laminated glass features a durable interlayer that enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering, making it ideal for skylights exposed to harsh weather or potential debris. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare by filtering sunlight, contributing to improved indoor comfort and energy savings in buildings with extensive skylight installations.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass for skylights consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and UV protection. It reduces the risk of shattering by holding broken glass fragments together, making it ideal for skylights exposed to impact or extreme weather. Laminated glass also offers superior sound insulation and energy efficiency compared to tinted glass, which primarily focuses on reducing solar heat gain and glare.
Understanding Tinted Glass
Tinted glass for skylights reduces solar heat gain by filtering sunlight, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing glare while maintaining natural light. It contains metal oxides or dyes that alter light transmission and solar reflectance, improving comfort in interior spaces. Compared to laminated glass, tinted glass offers passively controlled light and heat without compromising structural safety.
Safety and Security: Laminated vs Tinted
Laminated glass offers superior safety and security for skylights due to its interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury and intrusion. Tinted glass primarily provides UV protection and glare reduction but lacks the structural strength and shatter resistance found in laminated glass. Choosing laminated glass enhances protection against breakage and potential break-ins, making it the safer, more secure option for skylights.
Light Transmission and Glare Reduction
Laminated glass for skylights offers high light transmission while effectively reducing glare through its interlayer, enhancing visual comfort without compromising brightness. Tinted glass decreases light transmission by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, which reduces glare but results in a dimmer interior environment. Choosing between laminated and tinted glass depends on balancing the desired level of natural light with glare control needs in skylight applications.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Laminated glass for skylights offers superior UV protection by blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays while maintaining high energy efficiency through its insulating interlayer that reduces heat transfer. Tinted glass, however, primarily reduces solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, which lowers cooling costs but may diminish natural daylight penetration. Choosing laminated glass enhances building longevity and occupant comfort with better glare control and long-term UV shielding, whereas tinted glass provides immediate solar heat reduction but less overall UV defense.
Noise Reduction Capabilities
Laminated glass for skylights offers superior noise reduction capabilities by incorporating a specialized interlayer that dampens sound vibrations, effectively minimizing external noise infiltration. Tinted glass primarily focuses on controlling solar heat and glare, providing limited impact on acoustic insulation compared to laminated options. For enhanced soundproofing in skylights, laminated glass remains the preferred choice due to its multi-layered structure specifically designed to absorb and reduce noise pollution.
Durability and Maintenance
Laminated glass for skylights offers superior durability due to its tough interlayer, which holds shards together if broken, enhancing safety and reducing maintenance needs. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare but may require more frequent cleaning to maintain clarity and performance, especially in dusty or polluted environments. Choosing laminated glass ensures longer-lasting protection against impacts and weathering, while tinted glass focuses more on energy efficiency and comfort.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Laminated glass for skylights offers a sleek, clear appearance that enhances natural light while providing a subtle sheen, maintaining a modern and minimalist aesthetic. Tinted glass introduces color variation and reduces glare, contributing to a dynamic design element that can complement various architectural styles. Both options influence the indoor ambiance significantly, with laminated glass emphasizing clarity and safety, and tinted glass focusing on visual comfort and style customization.
Cost Comparison for Skylight Installation
Laminated glass for skylight installation generally incurs higher upfront costs due to its multi-layer construction and enhanced safety features compared to tinted glass. Tinted glass offers a more budget-friendly option by reducing solar heat gain and glare without the added expense of interlayers, resulting in lower material and installation expenses. Long-term savings with laminated glass can arise from its durability and noise reduction benefits, but initial installation typically favors tinted glass for cost efficiency.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Tinted glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com