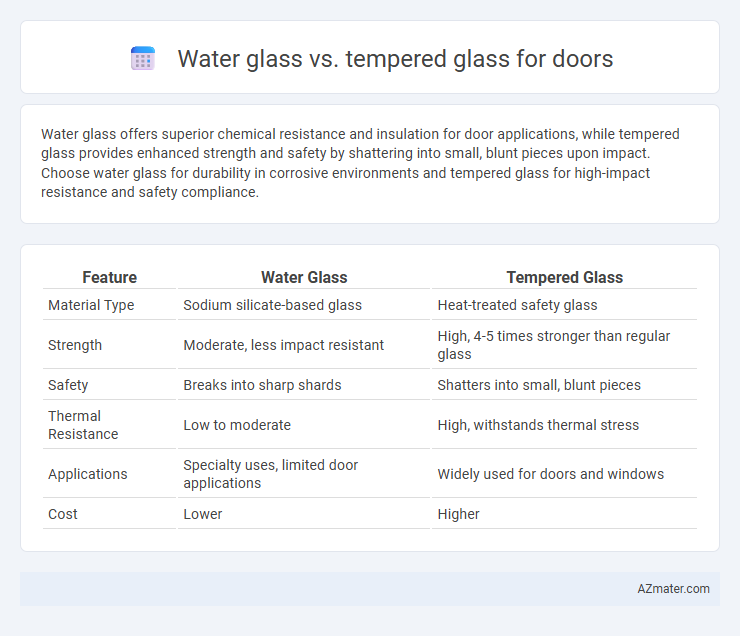
Water glass offers superior chemical resistance and insulation for door applications, while tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact. Choose water glass for durability in corrosive environments and tempered glass for high-impact resistance and safety compliance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Water Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Sodium silicate-based glass | Heat-treated safety glass |
| Strength | Moderate, less impact resistant | High, 4-5 times stronger than regular glass |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp shards | Shatters into small, blunt pieces |
| Thermal Resistance | Low to moderate | High, withstands thermal stress |
| Applications | Specialty uses, limited door applications | Widely used for doors and windows |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Water Glass and Tempered Glass
Water glass, also known as liquid glass or sodium silicate, is primarily used as a protective coating or adhesive in various applications but is not commonly utilized as a door material. Tempered glass, on the other hand, is a type of safety glass processed through controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for doors requiring durability and safety. The key difference lies in tempered glass's ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces upon breakage, enhancing safety, whereas water glass serves more specialized, non-structural roles in construction.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Water glass, primarily composed of sodium silicate, is produced through a solution process involving the fusion of silica sand with sodium carbonate; it forms a chemically treated, translucent panel often used for insulation or decorative doors. Tempered glass is manufactured by rapidly cooling heated annealed glass through a quenching process, creating a surface under compression that enhances strength and safety for door applications. The key distinction lies in water glass's chemical composition and solution-based fabrication versus tempered glass's thermal treatment and physical reinforcement.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength compared to water glass, as it undergoes a controlled thermal treatment that increases its resistance to impact and stress, making it ideal for high-traffic door applications. Water glass, also known as float glass, is less durable and more prone to breakage under pressure due to its unstrengthened nature. The enhanced durability of tempered glass ensures prolonged performance and safety in door installations, reducing the risk of shattering and maintenance costs.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Tempered glass offers superior safety features due to its heat-treated process, which increases its impact resistance and causes it to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risk in door applications. Water glass, or sodium silicate glass, is less impact-resistant and more prone to breakage under stress, making it less suitable for safety-critical door installations. The enhanced durability and compliance with safety standards make tempered glass the preferred choice for doors requiring high impact resistance and protection against accidental breakage.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Water glass doors offer a sleek, translucent aesthetic that enhances modern interiors while providing a smooth, glossy surface ideal for minimalist designs. Tempered glass doors combine durability with versatility, available in various finishes such as frosted, etched, or tinted, allowing for customized design options that complement both contemporary and traditional styles. Both materials ensure safety and visual appeal but differ in texture and range of decorative possibilities, influencing overall door design choices.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Tempered glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for energy-efficient doors. Water glass, or laminated glass, excels in acoustic insulation by dampening sound waves through its interlayer, significantly reducing noise transmission compared to tempered glass. Combining these properties, doors using tempered glass provide better thermal resistance, while water glass doors enhance soundproofing performance.
Cost Analysis: Water Glass vs Tempered Glass
Water glass doors typically cost 30-50% less than tempered glass doors due to lower manufacturing and material expenses. Tempered glass, known for its enhanced strength and safety features, commands a higher price but offers superior durability and impact resistance, potentially reducing long-term replacement costs. Choosing between water glass and tempered glass involves balancing upfront investment against longevity and safety requirements for door applications.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Water glass doors require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive, pH-neutral solutions to prevent damage and maintain clarity, while tempered glass doors are more resistant to scratches and can withstand stronger cleaners without deterioration. Tempered glass offers easier maintenance due to its durability and resistance to chemicals, reducing the frequency of cleaning and repairs compared to water glass. Both types benefit from regular wiping to prevent buildup of residues, but tempered glass's enhanced toughness ensures longer-lasting, low-maintenance performance in high-traffic areas.
Suitability for Various Door Applications
Water glass offers high transparency and is ideal for decorative interior doors where aesthetic appeal is prioritized, while tempered glass provides superior strength and safety, making it suitable for exterior doors and high-traffic areas. Tempered glass can withstand significant impact and temperature changes, ensuring durability and security in commercial and residential entrances. Water glass lacks the toughness of tempered glass, limiting its use to less demanding applications where safety and impact resistance are not critical factors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door
Water glass offers durability and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for exterior doors exposed to weather. Tempered glass provides enhanced safety due to its strength and shattering pattern, ideal for doors requiring impact resistance and security. Selecting the right glass depends on the balance between weather resistance and safety needs for your specific door application.
Infographic: Water glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com