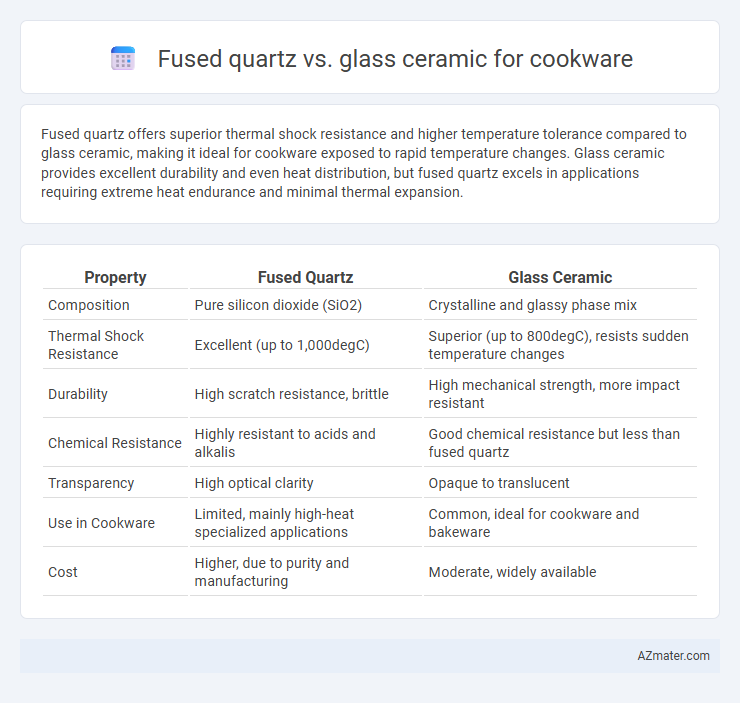
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to glass ceramic, making it ideal for cookware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic provides excellent durability and even heat distribution, but fused quartz excels in applications requiring extreme heat endurance and minimal thermal expansion.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Crystalline and glassy phase mix |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent (up to 1,000degC) | Superior (up to 800degC), resists sudden temperature changes |
| Durability | High scratch resistance, brittle | High mechanical strength, more impact resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to acids and alkalis | Good chemical resistance but less than fused quartz |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Opaque to translucent |
| Use in Cookware | Limited, mainly high-heat specialized applications | Common, ideal for cookware and bakeware |
| Cost | Higher, due to purity and manufacturing | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Fused Quartz and Glass Ceramic Cookware
Fused quartz cookware is made from high-purity silica with exceptional thermal shock resistance and minimal thermal expansion, making it ideal for rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic cookware, composed of crystalline and glass phases, offers superior heat retention, durability, and uniform heat distribution. Both materials provide non-porous surfaces resistant to chemical corrosion, enhancing cooking performance and durability in kitchen applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Fused quartz is composed nearly entirely of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), produced by melting high-purity quartz crystals, resulting in a material with extremely low thermal expansion and high thermal shock resistance. Glass ceramic cookware is created by controlled crystallization of specific glass formulations, containing crystalline phases like lithium disilicate that provide enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to traditional glass. Manufacturing fused quartz involves a melting and cooling process that preserves amorphous structure, while glass ceramics undergo a reheating step to induce crystallization, affecting their heat retention and resistance properties.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock Performance
Fused quartz offers exceptional heat resistance with a melting point around 1,650degC, significantly higher than typical glass ceramics, which generally withstand up to 800-1,200degC. This high heat resistance makes fused quartz ideal for cookware used in extreme temperature conditions. Additionally, fused quartz exhibits superior thermal shock performance due to its extremely low thermal expansion coefficient, minimizing the risk of cracking compared to glass ceramic cookware.
Durability and Longevity Comparisons
Fused quartz offers superior durability due to its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it less prone to cracking or staining over time compared to glass ceramic. Glass ceramic cookware excels in thermal stability and uniform heat distribution but is more susceptible to surface scratches and breakage under sudden temperature changes. Overall, fused quartz provides enhanced longevity, maintaining structural integrity and appearance longer under rigorous kitchen use.
Cooking Performance and Heat Distribution
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and uniform heat distribution, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking with minimal risk of cracking. Glass ceramic cookware provides excellent heat retention and even cooking due to its low thermal expansion but may heat less uniformly compared to fused quartz. Both materials ensure efficient energy use, yet fused quartz delivers more consistent cooking performance across various temperature ranges.
Chemical Stability and Reactivity with Food
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional chemical stability, resisting most acids, bases, and solvents, making it non-reactive and ideal for cookware exposed to varied food types and high temperatures. Glass ceramic also offers good chemical resistance but may contain trace elements that can slightly interact with highly acidic or alkaline foods over prolonged use. Both materials ensure minimal leaching and maintain food safety, but fused quartz provides superior inertness, enhancing durability and preserving flavor integrity.
Safety Aspects: Non-Toxicity and Health Considerations
Fused quartz cookware offers superior non-toxicity due to its inert chemical composition, eliminating the risk of harmful leaching during high-temperature cooking. Glass ceramic cookware is also safe, featuring low thermal expansion and resistance to thermal shock, but some varieties may contain trace elements that could pose health concerns under extreme conditions. Both materials prioritize health safety, with fused quartz providing an edge in chemical purity and biological inertness for cookware applications.
Maintenance, Cleaning, and Care Requirements
Fused quartz cookware offers exceptional resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it highly durable and easier to maintain with gentle, non-abrasive cleaning methods. Glass ceramic cookware, while also durable and suitable for stovetop use, requires careful handling to avoid scratches and is best cleaned with mild detergents and soft sponges to preserve its smooth surface. Both materials demand avoidance of sudden temperature changes to prevent damage, but fused quartz typically provides longer-lasting clarity and resilience with minimal upkeep.
Cost, Availability, and Brand Options
Fused quartz cookware typically comes at a higher cost due to its exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, while glass ceramic options are more affordable and widely available in various retail outlets. Glass ceramic cookware is offered by numerous mainstream brands, making it easier to find diverse styles and price ranges, whereas fused quartz cookware is manufactured by fewer specialized brands, often targeting premium markets. Availability of fused quartz cookware can be limited compared to the broad selection and mass-market distribution of glass ceramic cookware.
Final Considerations: Which Material is Right for You?
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and purity, making it ideal for precise cooking and laboratory-grade cookware. Glass ceramic excels in durability, heat retention, and versatility, suitable for everyday cooking and oven-safe applications. Choosing between fused quartz and glass ceramic depends on your priority for thermal stability versus general-purpose convenience and budget.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com