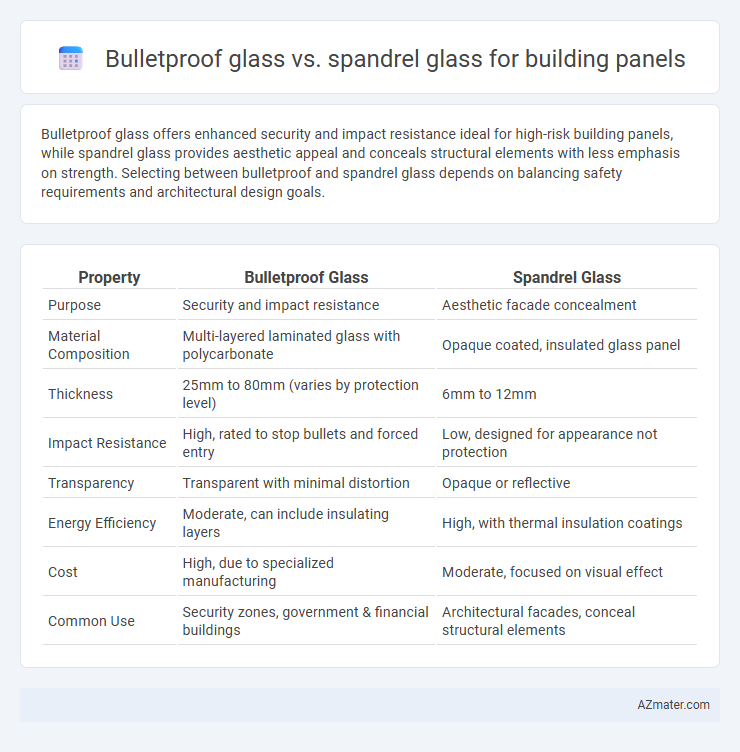
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security and impact resistance ideal for high-risk building panels, while spandrel glass provides aesthetic appeal and conceals structural elements with less emphasis on strength. Selecting between bulletproof and spandrel glass depends on balancing safety requirements and architectural design goals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bulletproof Glass | Spandrel Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Security and impact resistance | Aesthetic facade concealment |
| Material Composition | Multi-layered laminated glass with polycarbonate | Opaque coated, insulated glass panel |
| Thickness | 25mm to 80mm (varies by protection level) | 6mm to 12mm |
| Impact Resistance | High, rated to stop bullets and forced entry | Low, designed for appearance not protection |
| Transparency | Transparent with minimal distortion | Opaque or reflective |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate, can include insulating layers | High, with thermal insulation coatings |
| Cost | High, due to specialized manufacturing | Moderate, focused on visual effect |
| Common Use | Security zones, government & financial buildings | Architectural facades, conceal structural elements |
Introduction to Bulletproof and Spandrel Glass
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is engineered with multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials to resist high-velocity impacts, making it ideal for security-sensitive building panels. Spandrel glass, meanwhile, serves an architectural and aesthetic role, typically used to conceal structural elements and insulation between floors of commercial buildings while offering uniform exterior appearance. Both materials contribute distinct functional benefits in modern construction, with bulletproof glass prioritizing safety and spandrel glass emphasizing facade uniformity and thermal performance.
Key Differences Between Bulletproof and Spandrel Glass
Bulletproof glass, designed with multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, offers enhanced impact resistance to protect against ballistic threats, while spandrel glass primarily serves as an opaque architectural panel used to conceal structural elements and insulation in building facades. Bulletproof glass prioritizes security and durability under high-impact conditions, whereas spandrel glass focuses on aesthetic uniformity and energy efficiency without load-bearing capabilities. The distinct compositions and functional roles highlight the critical differences in safety performance and visual application between bulletproof and spandrel glass in building panel systems.
Structural Properties and Strength Comparison
Bulletproof glass offers exceptional resistance to impact and penetration due to its layered construction of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials, making it ideal for high-security building panels. Spandrel glass, while primarily designed for aesthetic concealment and solar shading, typically lacks the multi-layered reinforcement found in bulletproof glass, resulting in lower structural strength and limited impact resistance. In comparison, bulletproof glass exhibits superior tensile strength, shatter resistance, and durability under high stress, whereas spandrel glass primarily focuses on thermal performance and visual uniformity in facade applications.
Security Features: Bulletproof vs Spandrel Glass
Bulletproof glass offers superior security features by providing high resistance to ballistic impacts, making it ideal for protecting sensitive areas and preventing forced entry. Spandrel glass, primarily designed for aesthetic purposes and concealing building components, lacks the reinforced lamination and impact resistance found in bulletproof glass. When prioritizing security in building panels, bulletproof glass is the preferred choice due to its multi-layered construction engineered to withstand gunfire and physical attacks.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Bulletproof glass offers enhanced security with limited customization options, making it ideal for high-security areas but less adaptable to intricate architectural designs. Spandrel glass provides superior aesthetic versatility, available in various colors, finishes, and patterns, allowing seamless integration with curtain walls and facade designs. Architects prioritize spandrel glass for its ability to conceal building components while maintaining visual continuity and design flexibility in modern building panels.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Performance
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance but often has lower thermal insulation compared to spandrel glass, which is engineered with insulation materials to enhance energy efficiency in building panels. Spandrel glass typically incorporates insulating cores or coatings that reduce heat transfer, helping achieve better thermal performance and lower HVAC costs. Selecting spandrel glass improves building envelope efficiency, while bulletproof glass prioritizes security with moderate energy-saving properties.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Bulletproof glass typically incurs higher installation costs due to its weight and specialized framing requirements compared to spandrel glass, which is lighter and easier to handle. Maintenance expenses for bulletproof glass are generally greater because of the need for specialized cleaning techniques and potential damage repairs to its multi-layered structure. Spandrel glass offers a more cost-effective solution with lower upkeep demands, primarily used for aesthetic and opacity purposes rather than security.
Applications in Modern Building Panels
Bulletproof glass is primarily used in high-security applications such as government buildings, banks, and luxury residences to provide impact resistance and protection against forced entry. Spandrel glass is utilized for aesthetic purposes and to conceal structural elements or mechanical systems in building facades, contributing to a seamless, modern exterior. Both materials are integral in contemporary architectural designs, combining safety and visual appeal in building panels.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Bulletproof glass meets rigorous safety standards such as UL 752 and NIJ levels, providing certified ballistic protection critical for high-security building panels. Spandrel glass, commonly used to conceal structural components, adheres to ASTM E2190 and NFRC certifications for safety, thermal performance, and durability but lacks ballistic resistance. Choosing between bulletproof and spandrel glass depends on specific safety requirements, with bulletproof glass prioritized for impact resistance and spandrel glass optimized for architectural aesthetics and energy efficiency.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Bulletproof glass offers high-impact resistance and security, making it ideal for buildings requiring enhanced protection against forced entry or ballistic threats. Spandrel glass, typically used to conceal structural elements or insulation between floors, provides aesthetic uniformity without transparency, focusing on design rather than security. Choosing the right glass depends on project priorities: prioritize bulletproof glass for safety and security, while spandrel glass suits architectural aesthetics and facade continuity.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Spandrel glass for Building panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com