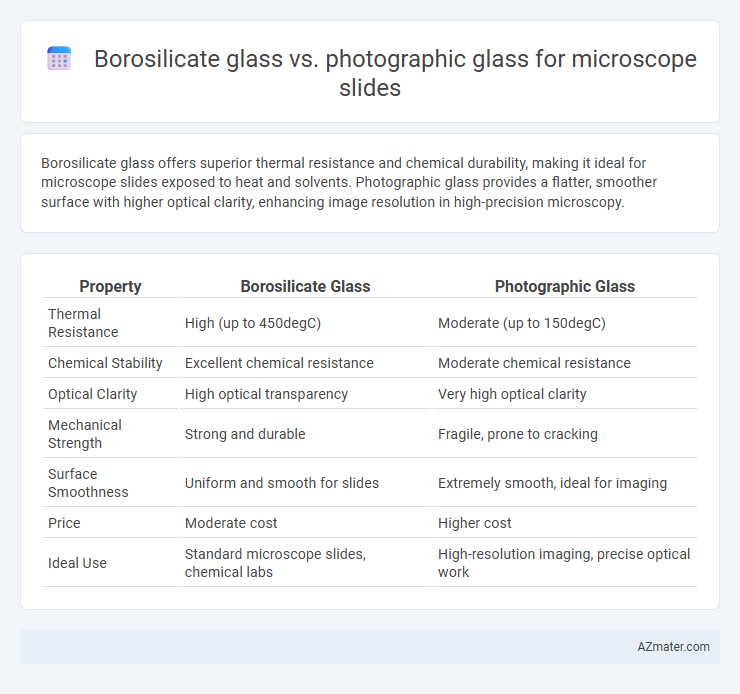
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for microscope slides exposed to heat and solvents. Photographic glass provides a flatter, smoother surface with higher optical clarity, enhancing image resolution in high-precision microscopy.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Photographic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Moderate (up to 150degC) |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent chemical resistance | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Optical Clarity | High optical transparency | Very high optical clarity |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong and durable | Fragile, prone to cracking |
| Surface Smoothness | Uniform and smooth for slides | Extremely smooth, ideal for imaging |
| Price | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
| Ideal Use | Standard microscope slides, chemical labs | High-resolution imaging, precise optical work |
Introduction: Understanding Microscope Slide Materials
Borosilicate glass for microscope slides offers high thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for repeated sterilization and long-term use in laboratory environments. Photographic glass, originally designed for imaging applications, provides exceptional optical clarity but lacks the chemical resistance and thermal stability required for rigorous biological specimen analysis. Choosing the appropriate microscope slide material depends on balancing optical quality with durability demands specific to scientific research and clinical diagnostics.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its low thermal expansion and high chemical resistance, making it ideal for microscope slides that require durability and resistance to thermal shock. Photographic glass, by contrast, is primarily designed for image clarity and surface smoothness but lacks the thermal stability and chemical inertness of borosilicate glass. Borosilicate glass slides provide superior performance in laboratory settings where precision and longevity under varying temperature conditions are critical.
What is Photographic Glass?
Photographic glass, commonly used for microscope slides, is a high-quality, flat, and optically clear glass designed to minimize distortion and maximize image clarity during microscopic examination. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is valued for its thermal and chemical resistance, photographic glass offers superior flatness and surface smoothness essential for precision imaging in microscopy. This specialized glass enhances the resolution and contrast of microscopic samples, making it suitable for detailed scientific analysis and high-resolution photography.
Key Differences in Glass Composition
Borosilicate glass contains silica and boron trioxide, providing high thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for microscope slides in laboratory settings. Photographic glass primarily consists of silica with coatings to enhance optical clarity and minimize reflections, optimized for imaging rather than thermal stability. The key difference lies in borosilicate's superior thermal shock resistance versus photographic glass's enhanced optical properties tailored for microscopy.
Optical Clarity: Borosilicate vs Photographic Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity with low thermal expansion and high chemical resistance, making it ideal for precise microscopy work. Photographic glass provides excellent flatness and minimal distortion, essential for high-resolution imaging, but may have slightly lower chemical durability compared to borosilicate. Both types ensure clear visibility, yet borosilicate glass is preferred for demanding optical applications requiring durability and stability.
Durability and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability with high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it ideal for microscope slides subjected to frequent handling and temperature changes. Photographic glass, typically soda-lime based, lacks the same level of chemical resistance and is more prone to scratching and breaking under harsh lab conditions. The exceptional chemical inertness of borosilicate glass ensures it withstands exposure to solvents and acids commonly used in microscopy sample preparation without degrading or leaching contaminants.
Price and Availability of Both Glass Types
Borosilicate glass microscope slides typically offer a balanced price point with widespread availability due to their durable chemical and thermal resistance, making them a popular choice for laboratories. Photographic glass slides usually come at a higher cost driven by their exceptional optical clarity and precision surface finish, but availability can be limited and often depends on specialty suppliers. Bulk purchasing options and supplier networks strongly influence price fluctuations and accessibility for both glass types in scientific research applications.
Suitability for Different Microscope Applications
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for applications involving high-temperature processes or harsh chemicals in microscopy. Photographic glass provides exceptional flatness and optical clarity, which is critical for high-precision imaging and digital microscopy. Choosing between these materials depends on the specific microscope application requirements such as thermal stability versus optical performance.
User Recommendations and Industry Standards
Borosilicate glass is highly recommended for microscope slides due to its superior thermal resistance, chemical durability, and minimal thermal expansion, aligning with industry standards such as ASTM E438 for optical glass. Photographic glass, while offering high clarity, lacks the durability and chemical resistance required for prolonged laboratory use, making it less favored among professional microscopists. Users in clinical and research settings prioritize borosilicate slides for consistent performance, ease of sterilization, and compliance with ISO 8037 standards in microscopy applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Microscope Slides
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance, chemical durability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for rigorous laboratory applications and long-term use. Photographic glass provides excellent optical clarity but lacks the robustness required for repeated handling and exposure to harsh chemicals. Choosing borosilicate glass ensures greater reliability and longevity for microscope slides in demanding research environments.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Photographic glass for Microscope slide
 azmater.com
azmater.com