Anti-reflective glass minimizes glare and enhances visibility, making it ideal for safety windows in high-light environments. Fire-resistant glass withstands high temperatures and prevents flame penetration, providing enhanced protection in fire-prone areas.
Table of Comparison
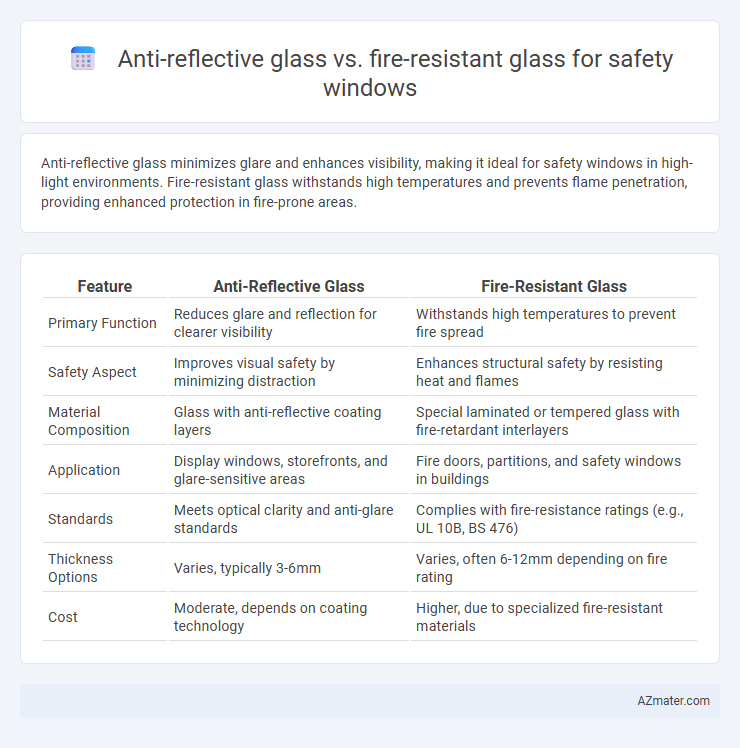
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Fire-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces glare and reflection for clearer visibility | Withstands high temperatures to prevent fire spread |
| Safety Aspect | Improves visual safety by minimizing distraction | Enhances structural safety by resisting heat and flames |
| Material Composition | Glass with anti-reflective coating layers | Special laminated or tempered glass with fire-retardant interlayers |
| Application | Display windows, storefronts, and glare-sensitive areas | Fire doors, partitions, and safety windows in buildings |
| Standards | Meets optical clarity and anti-glare standards | Complies with fire-resistance ratings (e.g., UL 10B, BS 476) |
| Thickness Options | Varies, typically 3-6mm | Varies, often 6-12mm depending on fire rating |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on coating technology | Higher, due to specialized fire-resistant materials |
Introduction to Safety Window Glass Types
Safety window glass types include anti-reflective glass, designed to minimize glare and enhance visibility by reducing surface reflections, and fire-resistant glass, engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames during a fire. Anti-reflective glass features advanced coatings that improve natural light transmission while maintaining clarity, making it ideal for environments requiring both safety and optimal visibility. Fire-resistant glass incorporates specialized materials and construction techniques to provide thermal insulation and structural integrity, ensuring occupant protection and compliance with fire safety regulations.
Understanding Anti-Reflective Glass
Anti-reflective glass enhances visibility and safety by minimizing glare and reflections, making it ideal for safety windows in high-visibility areas. This type of glass typically features specialized coatings that increase light transmission and reduce eye strain, improving surveillance and monitoring capabilities. Unlike fire-resistant glass, which prioritizes thermal insulation and fire containment, anti-reflective glass focuses on optical clarity and user comfort.
Key Properties of Fire-Resistant Glass
Fire-resistant glass is designed to maintain structural integrity and insulation during high-temperature fires, preventing heat and flames from passing through for specified durations such as 30, 60, or 90 minutes. This type of glass often includes intumescent interlayers or special coatings that expand when exposed to heat, providing a barrier against fire and smoke. Compared to anti-reflective glass, which primarily reduces glare and improves visibility, fire-resistant glass prioritizes safety by meeting strict fire safety standards like UL 9 or EN 13501-2.
Anti-Reflective Glass: Safety Benefits
Anti-reflective glass enhances safety windows by significantly reducing glare and improving visibility, which minimizes eye strain and enables clearer observation in various lighting conditions. This glass type maintains the structural integrity required for safety applications while allowing maximum light transmission without distortion, crucial for security monitoring and accident prevention. Compared to fire-resistant glass, anti-reflective glass prioritizes visual clarity and user comfort in safety-critical environments, making it ideal for surveillance, control rooms, and high-risk areas where clear sightlines are essential.
Fire-Resistant Glass: Protection Advantages
Fire-resistant glass provides superior protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, making it essential for safety windows in residential and commercial buildings. This glass type maintains structural integrity under intense heat, ensuring occupants have more time to evacuate safely while minimizing property damage. Unlike anti-reflective glass, which is designed primarily to reduce glare and improve visibility, fire-resistant glass prioritizes life safety and fire containment.
Comparing Durability: Anti-Reflective vs Fire-Resistant
Anti-reflective glass offers moderate durability with a coating resistant to scratches and environmental wear, ideal for maintaining clarity and visibility in safety windows. Fire-resistant glass, composed of multiple layers designed to withstand extreme heat and prevent fire penetration, provides superior structural integrity under high-temperature conditions. While anti-reflective glass enhances visual performance, fire-resistant glass excels in durability for fire safety applications, making each suited to different protective priorities.
Visual Clarity and Light Transmission Differences
Anti-reflective glass enhances visual clarity by minimizing glare and reflections, allowing for maximum light transmission of up to 99%, making it ideal for safety windows requiring clear visibility. Fire-resistant glass, while designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame penetration, typically has a slightly reduced light transmission rate, usually ranging between 60% and 85%, due to its multiple layers and intumescent interlayers. The trade-off between safety and transparency means that fire-resistant glass prioritizes thermal protection over optical performance, whereas anti-reflective glass emphasizes optical clarity and natural lighting.
Security Considerations for Each Glass Type
Anti-reflective glass enhances visibility and reduces glare, improving occupant safety by allowing clear surveillance through windows without compromising structural strength. Fire-resistant glass provides critical protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, making it essential for maintaining building integrity during fire emergencies. Security considerations favor fire-resistant glass for environments requiring both fire containment and impact resistance, while anti-reflective glass suits areas prioritizing visual clarity and daily security monitoring.
Cost Efficiency and Installation Factors
Anti-reflective glass offers cost efficiency through reduced energy consumption by minimizing glare and enhancing natural light transmission, leading to lower utility bills over time, while its installation requires precise handling to maintain coating integrity but is generally straightforward. Fire-resistant glass incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and engineering designed to withstand high temperatures, and installation demands strict compliance with safety codes and skilled labor to ensure proper sealing and structural support. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment with long-term savings and considering the specific safety requirements and installation complexities of the building project.
Choosing the Right Safety Window Glass: Recommendations
Anti-reflective glass enhances visibility and reduces glare, making it ideal for environments where clear vision is crucial, while fire-resistant glass prioritizes heat insulation and protects against flames, suitable for fire safety requirements. Selecting the right safety window glass depends on the primary hazard--choose anti-reflective glass for areas requiring maximum light transmission and minimal reflection, or fire-resistant glass for spaces needing stringent fire protection standards like those meeting ASTM E119 or EN 13501-2 certifications. For optimal safety and performance, evaluate building codes, exposure risks, and functional needs before installation to ensure compliance and occupant protection.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Fire-resistant glass for Safety window
 azmater.com
azmater.com