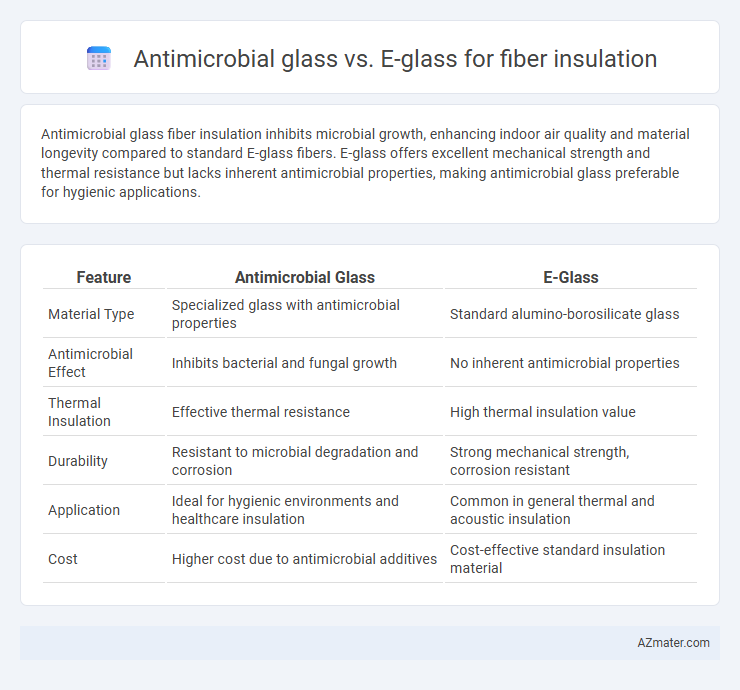
Antimicrobial glass fiber insulation inhibits microbial growth, enhancing indoor air quality and material longevity compared to standard E-glass fibers. E-glass offers excellent mechanical strength and thermal resistance but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making antimicrobial glass preferable for hygienic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Specialized glass with antimicrobial properties | Standard alumino-borosilicate glass |
| Antimicrobial Effect | Inhibits bacterial and fungal growth | No inherent antimicrobial properties |
| Thermal Insulation | Effective thermal resistance | High thermal insulation value |
| Durability | Resistant to microbial degradation and corrosion | Strong mechanical strength, corrosion resistant |
| Application | Ideal for hygienic environments and healthcare insulation | Common in general thermal and acoustic insulation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to antimicrobial additives | Cost-effective standard insulation material |
Introduction to Fiber Insulation Types
Fiber insulation includes various types such as antimicrobial glass and E-glass, each designed for specific performance characteristics. Antimicrobial glass fiber incorporates additives to inhibit microbial growth, enhancing durability in humid or bio-sensitive environments. E-glass fiber offers excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, making it a standard choice in general thermal and structural applications.
Understanding Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass used in fiber insulation incorporates specialized coatings or additives that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing hygiene and durability in environments prone to moisture and contamination. Unlike traditional E-glass, which primarily focuses on mechanical strength and thermal resistance, antimicrobial glass targets the prevention of mold, bacteria, and fungal proliferation on fiber surfaces. This innovation extends the lifespan of insulation materials while maintaining structural integrity and performance in various industrial and residential applications.
Defining E-Glass and Its Properties
E-glass, a type of fiberglass notable for its electrical insulation properties, is composed primarily of silica, alumina, and boron oxide, offering high tensile strength and excellent thermal resistance. This material is widely used in fiber insulation due to its durability, lightweight nature, and resistance to moisture and chemical degradation. In comparison, antimicrobial glass incorporates agents that inhibit microbial growth, providing enhanced hygiene benefits while maintaining similar structural attributes to standard E-glass.
Key Differences Between Antimicrobial Glass and E-Glass
Antimicrobial glass incorporates biocidal agents that inhibit microbial growth on the surface, enhancing hygiene and reducing contamination risks in fiber insulation applications. E-glass, composed primarily of silica, alumina, and boron oxide, offers exceptional mechanical strength and thermal resistance but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. The key differences include the antimicrobial functionality of treated glass versus the standard durability and electrical insulation characteristics of conventional E-glass fibers.
Insulation Performance Comparison
Antimicrobial glass fiber insulation offers enhanced resistance to microbial growth, contributing to sustained thermal and acoustic performance compared to standard E-glass fibers. E-glass insulation provides robust mechanical strength and excellent thermal stability but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, potentially leading to degradation in humid environments. Studies indicate that antimicrobial glass fibers maintain R-values longer under moisture exposure, improving overall insulation efficiency and durability in challenging conditions.
Durability and Longevity Aspects
Antimicrobial glass for fiber insulation offers enhanced durability by resisting microbial growth, which prevents material degradation and maintains structural integrity over time. E-glass, while providing excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, potentially leading to shorter service life in moist or biologically active environments. The longevity of antimicrobial glass surpasses that of standard E-glass by reducing biofilm formation and associated deterioration, ensuring prolonged insulation performance under challenging conditions.
Antimicrobial Benefits in Fiber Insulation
Antimicrobial glass in fiber insulation offers enhanced protection against bacterial and fungal growth, significantly reducing the risk of mold and mildew development compared to traditional E-glass. This property improves indoor air quality and extends the lifespan of insulation materials by preventing microbial degradation. Incorporating antimicrobial additives into glass fibers provides a hygienic advantage, making it ideal for applications in healthcare, residential, and commercial buildings where moisture and contamination concerns are prevalent.
Applications in Residential, Commercial, and Industrial Settings
Antimicrobial glass fiber insulation offers enhanced protection against mold and microbial growth, making it ideal for residential settings where air quality and health are priorities. E-glass fiber insulation provides high strength and thermal efficiency, commonly used in commercial building envelopes and industrial facilities requiring durable, fire-resistant materials. Both materials support energy savings and environmental sustainability but are selected based on specific performance needs such as hygiene control or structural integrity in different applications.
Cost Efficiency and Sustainability Considerations
Antimicrobial glass for fiber insulation often incurs higher upfront costs compared to traditional E-glass due to specialized coatings or additives but can reduce maintenance expenses by inhibiting microbial growth. E-glass remains cost-efficient with widely available manufacturing processes and lower raw material expenses, making it a common choice for large-scale insulation applications. Sustainability considerations favor antimicrobial glass when extended product lifespan and reduced chemical cleaning are factored, while E-glass benefits from established recycling streams and lower energy consumption in production.
Choosing the Right Fiber Insulation: Antimicrobial Glass vs E-Glass
Antimicrobial glass fiber insulation offers enhanced protection against mold, bacteria, and fungi, making it ideal for environments with high moisture or hygiene requirements. E-glass fiber insulation, known for its excellent mechanical strength and thermal resistance, is widely used for general applications where durability and cost-effectiveness are priorities. Selecting between antimicrobial glass and E-glass depends on specific environmental conditions, health safety needs, and desired performance characteristics in fiber insulation.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs E-glass for Fiber insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com