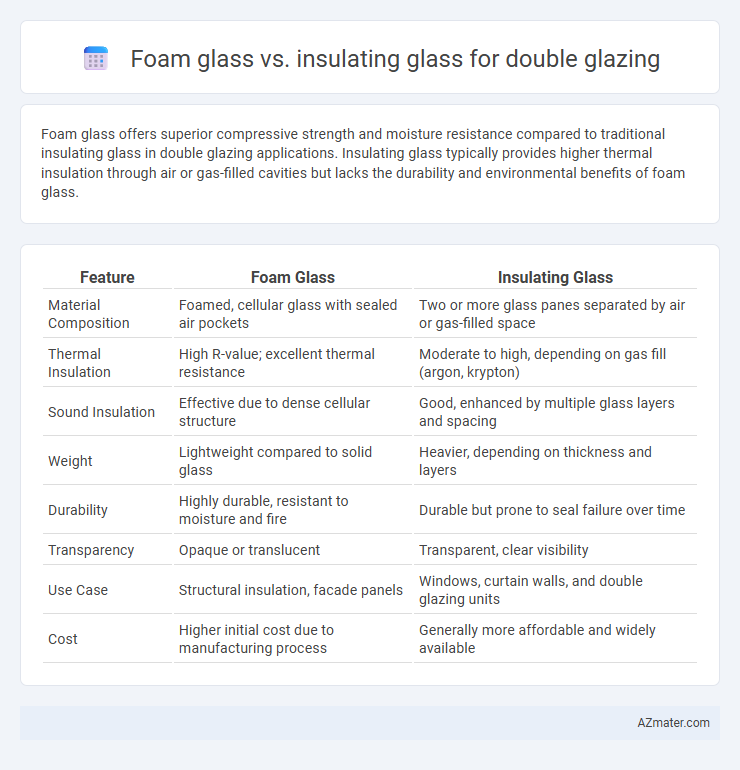
Foam glass offers superior compressive strength and moisture resistance compared to traditional insulating glass in double glazing applications. Insulating glass typically provides higher thermal insulation through air or gas-filled cavities but lacks the durability and environmental benefits of foam glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Glass | Insulating Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Foamed, cellular glass with sealed air pockets | Two or more glass panes separated by air or gas-filled space |
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value; excellent thermal resistance | Moderate to high, depending on gas fill (argon, krypton) |
| Sound Insulation | Effective due to dense cellular structure | Good, enhanced by multiple glass layers and spacing |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to solid glass | Heavier, depending on thickness and layers |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to moisture and fire | Durable but prone to seal failure over time |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Transparent, clear visibility |
| Use Case | Structural insulation, facade panels | Windows, curtain walls, and double glazing units |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to manufacturing process | Generally more affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Double Glazing Solutions
Double glazing solutions utilize a combination of materials to enhance thermal insulation and energy efficiency in windows. Foam glass offers superior insulation with its closed-cell structure and high compressive strength, ideal for minimizing heat transfer and improving durability. Insulating glass, composed of two or more glass panes separated by a gas-filled space, provides excellent soundproofing and thermal resistance, making it a widely used solution for modern energy-efficient buildings.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a highly insulating material made from crushed glass fused into a cellular structure, providing superior thermal resistance and moisture impermeability for double glazing applications. Unlike insulating glass, which consists of multiple glass panes separated by a gas-filled cavity to reduce heat transfer, foam glass offers structural strength along with excellent insulation properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient window systems. Its lightweight, durable composition enhances building insulation performance and minimizes thermal bridging in double-glazed units.
What is Insulating Glass?
Insulating glass, also known as double glazing, consists of two or more glass panes separated by a sealed air or gas-filled space to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in buildings. Foam glass, a lightweight cellular glass material used as insulation, differs by providing excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance without the transparency or sealing function of insulating glass. While insulating glass focuses on minimizing heat loss through glazing units, foam glass offers a rigid insulation solution ideal for walls, roofs, and floors with high compressive strength and durability.
Thermal Performance: Foam Glass vs Insulating Glass
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, minimizing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in double glazing applications. Insulating glass relies on gas-filled gaps between glass panes, which provide effective thermal resistance but may be less consistent in performance compared to the rigid foam glass layer. Both materials improve thermal performance, but foam glass provides long-term durability and stable insulation without degradation over time.
Sound Insulation Comparison
Foam glass offers superior sound insulation compared to insulating glass in double glazing due to its dense, closed-cell structure that effectively dampens sound waves and reduces noise transmission. Insulating glass primarily relies on air or gas-filled gaps between glass layers, which provide moderate noise reduction but are less effective against low-frequency sounds. Selecting foam glass can significantly enhance acoustic comfort in environments with high external noise levels, making it a preferred choice for optimal sound insulation in double-glazed windows.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Foam glass offers exceptional durability due to its rigid, non-porous structure, providing superior resistance to moisture, mold, and physical damage compared to insulating glass. Insulating glass units (IGUs) rely on sealed air or gas layers between glass panes, which can degrade over time, causing condensation and reduced thermal performance. Foam glass's resistance to environmental factors ensures longer lifespan and consistent insulation quality, making it a more durable option for double glazing applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam glass offers superior environmental benefits in double glazing through its use of recycled glass and long lifespan, reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon footprint compared to traditional insulating glass units. Insulating glass typically involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes and materials with limited recyclability, which can lead to higher embedded carbon emissions. Choosing foam glass enhances sustainability by improving thermal performance while supporting circular economy principles and minimizing resource consumption.
Installation Process and Challenges
Foam glass panels for double glazing require precise cutting and careful sealing due to their rigid, brittle nature, posing challenges during installation such as the need for specialized handling to prevent cracking. Insulating glass units (IGUs), constructed with sealed air or gas-filled spaces between glass panes, offer easier installation through standard glazing methods but demand meticulous sealing to avoid moisture ingress and gas leakage over time. Proper skill and attention are essential in both cases to ensure thermal efficiency and durability in double-glazed window systems.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Considerations
Foam glass offers higher durability and superior thermal insulation with a longer lifespan, resulting in lower long-term maintenance costs compared to traditional insulating glass used in double glazing. Initial costs for foam glass are significantly higher due to specialized manufacturing processes, while insulating glass panels have a more affordable upfront price but may require frequent replacement or repair. Considering energy savings and reduced lifecycle expenses, foam glass can provide better cost efficiency over time despite its elevated initial investment.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Project
Foam glass offers exceptional thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and durability for double glazing projects, making it ideal for energy-efficient and long-lasting installations. Insulating glass, typically consisting of multiple glass layers separated by air or gas, provides superior transparency and natural light while improving thermal performance. Selecting the best option depends on your project's priorities, such as enhanced insulation and structural strength for foam glass or increased daylight and aesthetic appeal with insulating glass.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Insulating glass for Double glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com