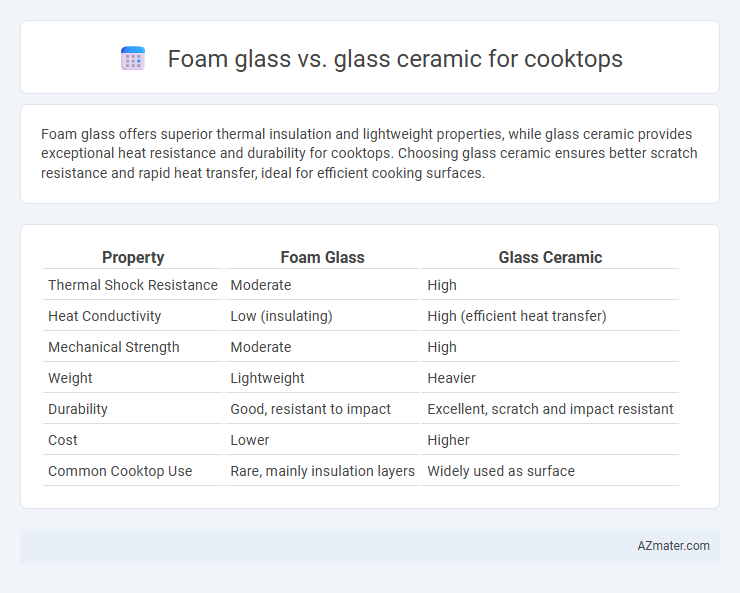
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, while glass ceramic provides exceptional heat resistance and durability for cooktops. Choosing glass ceramic ensures better scratch resistance and rapid heat transfer, ideal for efficient cooking surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Foam Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Heat Conductivity | Low (insulating) | High (efficient heat transfer) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Durability | Good, resistant to impact | Excellent, scratch and impact resistant |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Cooktop Use | Rare, mainly insulation layers | Widely used as surface |
Introduction to Cooktop Materials
Foam glass and glass ceramic are innovative materials used in modern cooktops, each offering distinct thermal properties and durability advantages. Foam glass provides excellent insulation and lightweight strength, making it ideal for heat retention and efficiency. Glass ceramic features superior heat resistance and smooth surface aesthetics, commonly used for its rapid heating capabilities and easy cleaning.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a lightweight, insulating material made from recycled glass that has been crushed, powdered, and heated to create a porous structure filled with tiny air bubbles. Its excellent thermal insulation and resistance to heat shock make foam glass a suitable choice for cooktops requiring efficient heat distribution and durability. Unlike glass ceramic, which is engineered for direct heat contact and rapid temperature changes, foam glass primarily serves as an insulating layer, enhancing energy efficiency and safety in cooktop design.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a durable, heat-resistant material made by controlled crystallization of certain glasses, offering excellent thermal shock resistance and stability at high temperatures. It is commonly used in cooktops due to its smooth surface, scratch resistance, and ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Unlike foam glass, which is porous and insulating, glass ceramic combines glass-like aesthetics with ceramic strength, making it ideal for efficient and safe cooking surfaces.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Foam glass is produced through a foaming process where crushed glass is heated with a foaming agent, creating a lightweight, porous structure ideal for thermal insulation. Glass ceramic cooktops undergo controlled crystallization via heat treatment of glass, forming a dense, durable surface with high thermal shock resistance and strength. This manufacturing contrast results in foam glass being optimized for insulation, while glass ceramic offers superior mechanical and thermal properties for cooking applications.
Thermal Properties: Heat Resistance and Conductivity
Foam glass exhibits excellent heat resistance with a melting point above 1100degC, making it suitable for high-temperature applications, but its low thermal conductivity around 0.1 W/m*K limits rapid heat transfer on cooktops. Glass ceramic cooktops, such as those made from lithium aluminosilicate, offer superior thermal shock resistance and higher thermal conductivity typically between 1.5 and 2.5 W/m*K, enabling efficient heat distribution and quick temperature changes. The combination of high heat resistance and moderate thermal conductivity in glass ceramics results in enhanced cooktop performance compared to foam glass.
Durability and Lifespan
Foam glass cooktops are highly durable due to their cellular structure, which provides excellent thermal insulation and resistance to cracking under temperature fluctuations, extending their lifespan significantly. Glass ceramic cooktops offer superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making them resilient to daily kitchen wear and tear, often lasting over a decade with proper care. Both materials deliver long-lasting performance, but glass ceramics typically excel in durability in high-use cooking environments due to their enhanced toughness and scratch resistance.
Safety Considerations
Foam glass cooktops offer excellent thermal insulation, reducing the risk of heat transfer and minimizing burns, while glass ceramic cooktops provide superior heat resistance and uniform temperature distribution that prevent cracking under rapid temperature changes. Foam glass's porous structure enhances shock absorption but may be more prone to surface scratches compared to the dense, non-porous surface of glass ceramic, which is easier to clean and more resistant to stains. Both materials require careful handling, but glass ceramic's engineered strength and smooth finish generally offer higher safety standards in everyday cooktop use.
Aesthetic Differences
Foam glass cooktops deliver a sleek, matte finish with a subtle texture that complements minimalist kitchen designs. Glass ceramic cooktops feature a smooth, high-gloss surface that enhances light reflection and offers a modern, polished appearance. The aesthetic difference lies in foam glass's muted elegance versus glass ceramic's vibrant, mirror-like shine.
Cost Analysis
Foam glass cooktops typically offer a lower initial cost compared to glass ceramic options, making them an economical choice for budget-conscious consumers. Glass ceramic cooktops, while more expensive upfront, provide greater durability and better heat resistance, potentially reducing replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Cost analysis should factor in long-term performance, energy efficiency, and repair frequency to determine the most cost-effective option for specific kitchen uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Your Cooktop
Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation and durability but lacks the high heat resistance and scratch resistance found in glass ceramic cooktops. Glass ceramic cooktops provide superior heat tolerance, rapid heating, and a smooth surface ideal for cooking efficiency and easy cleaning. For optimal performance and longevity in kitchens, glass ceramic remains the preferred choice for cooktop material.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com