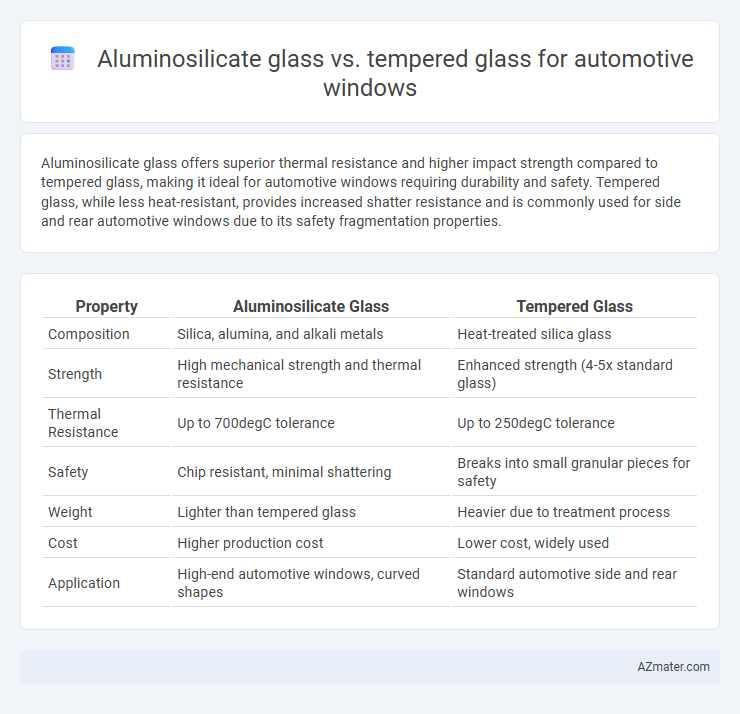
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and higher impact strength compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for automotive windows requiring durability and safety. Tempered glass, while less heat-resistant, provides increased shatter resistance and is commonly used for side and rear automotive windows due to its safety fragmentation properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, alumina, and alkali metals | Heat-treated silica glass |
| Strength | High mechanical strength and thermal resistance | Enhanced strength (4-5x standard glass) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 700degC tolerance | Up to 250degC tolerance |
| Safety | Chip resistant, minimal shattering | Breaks into small granular pieces for safety |
| Weight | Lighter than tempered glass | Heavier due to treatment process |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, widely used |
| Application | High-end automotive windows, curved shapes | Standard automotive side and rear windows |
Introduction to Automotive Window Glass Types
Automotive windows primarily use aluminosilicate glass and tempered glass for their distinct properties. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for laminated windshields that enhance safety by preventing shattering. Tempered glass, known for its high strength and ability to break into small, blunt pieces, is typically used in side and rear windows to reduce injury risk during impact.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in automotive windows, is a high-strength, chemically toughened material composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offering enhanced resistance to thermal shock and mechanical impact compared to traditional glasses. Unlike tempered glass, which is heat-treated to improve strength but can shatter into small blunt pieces, aluminosilicate glass combines both chemical durability and thermal stability, making it ideal for advanced automotive applications requiring lightweight and safer window solutions. Its superior resistance to scratches and environmental degradation ensures longer lifespan and improved safety standards in vehicles.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. In automotive windows, tempered glass is manufactured using rapid heating followed by sudden cooling, creating balanced internal stresses that make it resistant to impact and thermal stress. Upon breaking, it shatters into small, granular chunks rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury to passengers.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass offers enhanced strength and heat resistance due to its aluminum and silicon oxide composition, making it highly durable under thermal stress and impact. Tempered glass, produced by rapid cooling, achieves superior mechanical strength and shatters into small, less harmful pieces, providing better safety in automotive windows. While aluminosilicate glass excels in thermal durability, tempered glass is preferred for its impact resistance and fracture behavior in automotive applications.
Impact Resistance and Safety Features
Aluminosilicate glass in automotive windows offers superior impact resistance due to its enhanced chemical composition that increases tensile strength and thermal stability, reducing the likelihood of shattering upon collision. Tempered glass undergoes a thermal or chemical treatment process to improve strength and, when broken, fractures into small, blunt pieces that minimize injury risk. The combination of aluminosilicate's high durability and tempered glass's safety fragmentation characteristics makes them critical for ensuring passenger protection and structural integrity in automotive applications.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Aluminosilicate glass used in automotive windows is typically thinner and lighter than tempered glass, offering improved fuel efficiency due to reduced vehicle weight. Tempered glass requires increased thickness to achieve comparable strength and safety, which contributes to higher weight. This difference in material structure impacts overall vehicle performance, with aluminosilicate glass providing better weight optimization without compromising durability.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Aluminosilicate glass offers higher durability and enhanced thermal resistance compared to tempered glass, but it typically incurs greater production costs due to specialized raw materials and manufacturing processes. Tempered glass is more cost-effective and widely used in automotive windows because it can be manufactured quickly through thermal or chemical toughening, reducing overall production time and expenses. Manufacturers must balance the higher expense of aluminosilicate glass with its superior performance benefits against the affordability and manufacturing efficiency of tempered glass for automotive applications.
UV Protection and Optical Clarity
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior UV protection due to its inherent chemical composition, effectively blocking harmful ultraviolet rays and reducing interior fading in automotive windows. Tempered glass provides high impact resistance and safety but generally lacks the same level of UV filtration, making it less effective for protecting car interiors from sun damage. Optical clarity in aluminosilicate glass remains excellent, with minimal light distortion, whereas tempered glass can sometimes exhibit slight optical distortions caused by the tempering process.
Industry Standards and Automotive Adoption
Aluminosilicate glass, with its superior chemical durability and resistance to thermal shock, meets automotive industry standards such as ANSI Z26.1 and ECE R43, making it suitable for high-performance and safety-critical applications. Tempered glass, widely adopted for automotive side and rear windows, complies with impact resistance and fragmentation standards by shattering into small, blunt pieces to minimize injury. The automotive industry favors aluminosilicate glass for lightweight, durable windshield solutions, while tempered glass remains the standard for side and rear windows due to cost-effectiveness and safety regulations.
Choosing the Right Glass for Automotive Windows
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior resistance to thermal shock and scratches, making it ideal for automotive windows exposed to varying temperatures and harsh conditions. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing injury risks in accidents. Choosing between aluminosilicate and tempered glass depends on balancing durability, safety standards, and specific vehicle design requirements.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Tempered glass for Automotive window
 azmater.com
azmater.com