Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for decorative glazing, resisting impact and thermal stress, while acid-etched glass provides a matte, translucent surface ideal for privacy and aesthetic diffusion without compromising durability. Choosing between tempered and acid-etched glass depends on balancing safety requirements and desired visual texture in decorative applications.
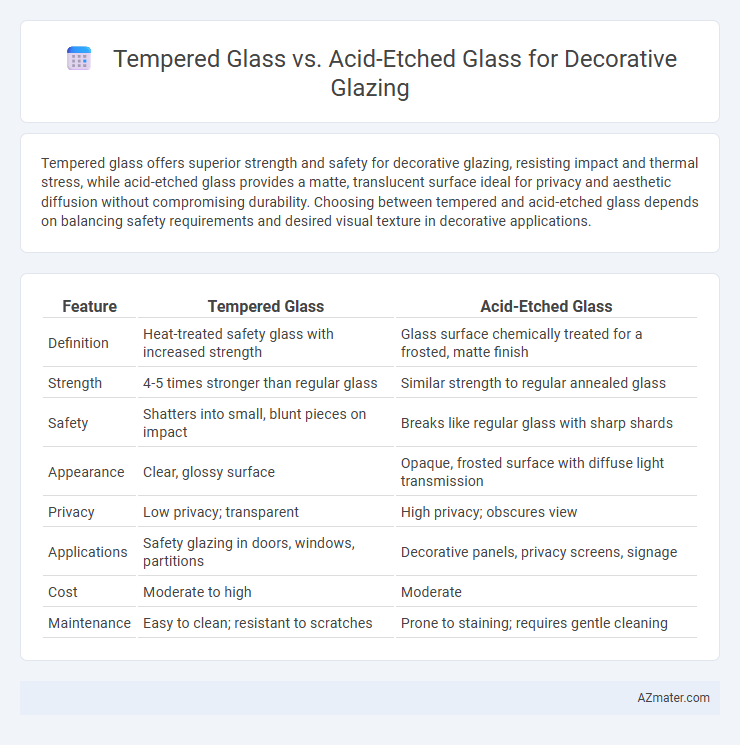
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Acid-Etched Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat-treated safety glass with increased strength | Glass surface chemically treated for a frosted, matte finish |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass | Similar strength to regular annealed glass |
| Safety | Shatters into small, blunt pieces on impact | Breaks like regular glass with sharp shards |
| Appearance | Clear, glossy surface | Opaque, frosted surface with diffuse light transmission |
| Privacy | Low privacy; transparent | High privacy; obscures view |
| Applications | Safety glazing in doors, windows, partitions | Decorative panels, privacy screens, signage |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean; resistant to scratches | Prone to staining; requires gentle cleaning |
Introduction to Decorative Glazing
Decorative glazing enhances architectural aesthetics and functionality by incorporating unique glass treatments such as tempered glass and acid-etched glass. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety, making it ideal for high-traffic areas requiring impact resistance and thermal durability. Acid-etched glass provides a frosted, translucent appearance, enhancing privacy while allowing natural light, commonly used in office partitions, shower enclosures, and decorative panels.
Overview: Tempered Glass vs Acid-Etched Glass
Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and safety by undergoing a heat treatment process that increases its resistance to breakage, making it ideal for decorative glazing requiring durability. Acid-etched glass provides a smooth, frosted finish achieved through chemical treatment, delivering a high level of privacy and aesthetic appeal without compromising light transmission. Both materials serve distinct functional and visual purposes, with tempered glass excelling in impact resistance and acid-etched glass favored for its elegant, translucent surface.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Tempered glass is produced through a thermal or chemical treatment process that increases its strength by rapidly cooling the surface after heating, resulting in a durable, impact-resistant material ideal for safety applications. Acid-etched glass undergoes a chemical treatment using hydrofluoric acid to create a frosted, translucent surface that provides privacy and aesthetic appeal without compromising the glass's inherent strength. While tempered glass manufacturing emphasizes enhancing mechanical strength through controlled cooling, acid-etched glass focuses on surface modification for texture and light diffusion through precise acid exposure.
Strength and Durability Differences
Tempered glass offers significantly higher strength and impact resistance due to its heat treatment process, making it less prone to breakage compared to acid-etched glass. Acid-etched glass, while providing a matte, frosted appearance, has reduced structural integrity since the surface is chemically corroded rather than reinforced. For decorative glazing applications requiring robust durability and safety, tempered glass is the superior choice, whereas acid-etched glass prioritizes aesthetic texture over strength.
Aesthetic Options and Customization
Tempered glass offers sleek clarity and durability, making it ideal for designs requiring high strength and a modern, polished finish. Acid-etched glass provides a soft, frosted texture that diffuses light and enhances privacy while allowing intricate patterns and custom artwork through sandblasting techniques. Both materials enable customization through coatings, treatments, and shapes, but acid-etched glass excels in creating unique, artistic textures, whereas tempered glass emphasizes structural integrity and vibrant color tinting options.
Light Diffusion and Privacy Features
Tempered glass provides strong durability and enhanced safety but offers limited light diffusion, maintaining a clearer view with moderate privacy. Acid-etched glass excels in privacy by creating a frosted, textured surface that diffuses light evenly, reducing glare and obscuring visibility without sacrificing brightness. For decorative glazing, acid-etched glass is ideal when balancing light diffusion with superior privacy, while tempered glass suits applications requiring impact resistance and safety.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Tempered glass offers high durability and resistance to scratches, requiring only regular cleaning with mild soap and water to maintain its clarity and strength. Acid-etched glass features a matte, textured surface that can trap dust and fingerprints, necessitating gentle cleaning with non-abrasive, pH-neutral cleaners to prevent surface damage. Both types benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive tools to preserve their decorative finishes and prolong lifespan.
Safety and Security Considerations
Tempered glass offers superior safety through its shatter-resistant properties, breaking into small, blunt pieces that minimize injury risk, making it ideal for high-traffic decorative glazing applications requiring enhanced security. Acid-etched glass provides aesthetic appeal with a frosted, translucent look but lacks the impact resistance and strength of tempered glass, posing higher vulnerability to breakage and less effective protection against forced entry. For environments prioritizing safety and security, tempered glass remains the preferred choice due to its compliance with rigorous building codes and durability under stress.
Cost Analysis: Tempered vs Acid-Etched Glass
Tempered glass typically costs more than acid-etched glass due to its heat-treatment process that enhances durability and safety, making it a preferred choice for high-traffic or impact-prone areas. Acid-etched glass, while less expensive, offers a more customizable matte finish and intricate decorative patterns, which can increase costs if complex designs are required. Considering long-term value, tempered glass provides greater resistance to damage and maintenance costs, whereas acid-etched glass may need more frequent replacement or repair in certain environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Decorative Applications
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety, making it ideal for decorative glazing in high-traffic or impact-prone areas. Acid-etched glass provides a smooth, frosted appearance that enhances privacy and artistic design without compromising light diffusion. Selecting between tempered and acid-etched glass depends on balancing durability needs with aesthetic preferences for decorative applications.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Acid-etched glass for Decorative glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com