Lead glass offers superior clarity and thermal conductivity for cookware but poses health risks due to lead content. Glass ceramic cookware provides excellent thermal shock resistance and durability without toxic elements, making it safer for cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
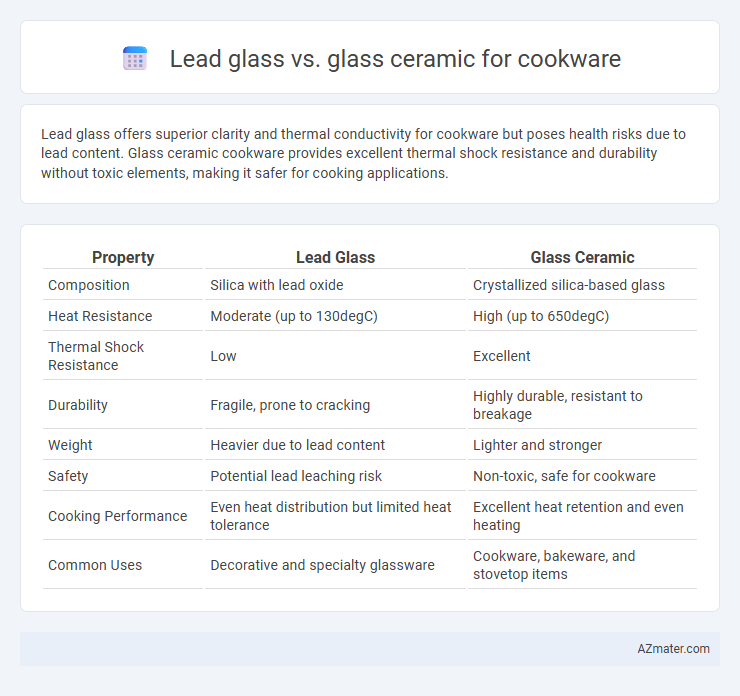
| Property | Lead Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica with lead oxide | Crystallized silica-based glass |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 130degC) | High (up to 650degC) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | Excellent |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to cracking | Highly durable, resistant to breakage |
| Weight | Heavier due to lead content | Lighter and stronger |
| Safety | Potential lead leaching risk | Non-toxic, safe for cookware |
| Cooking Performance | Even heat distribution but limited heat tolerance | Excellent heat retention and even heating |
| Common Uses | Decorative and specialty glassware | Cookware, bakeware, and stovetop items |
Introduction to Cookware Materials
Lead glass and glass ceramic represent two key materials in cookware, each with distinct thermal properties and safety considerations. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, offers excellent clarity and ease of shaping but poses health risks if used improperly in foodware. Glass ceramic, composed of crystalline phases within a glass matrix, exhibits superior heat resistance and thermal shock durability, making it a safer and more efficient choice for cookware applications.
What is Lead Glass?
Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains a significant percentage of lead oxide, typically between 18% and 40%, which increases its weight, brilliance, and refractive index. It is primarily used in decorative cookware due to its clarity and ability to be finely cut, but it is not recommended for high-temperature cooking as lead can leach into food under heat. Glass ceramic cookware, by contrast, is engineered for thermal stability and durability, making it safer and more practical for cooking applications.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a highly durable material engineered by controlled crystallization of glass, resulting in exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Unlike lead glass, which contains lead oxide for clarity and weight, glass ceramic cookware withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for stovetop and oven use. Its non-porous surface also resists staining and chemical corrosion, providing long-lasting cookware performance.
Key Differences Between Lead Glass and Glass Ceramic
Lead glass contains lead oxide, enhancing its weight, brilliance, and thermal expansion, but it can pose health risks if used improperly in cookware. Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance, high durability, and consistent heat distribution, making it ideal for direct stovetop cooking. Unlike lead glass, glass ceramic is non-toxic and designed to withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking or breaking.
Durability and Heat Resistance Comparison
Lead glass offers moderate durability but lower heat resistance compared to glass ceramic cookware, which is engineered for superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Glass ceramic materials exhibit enhanced toughness and structural integrity under high heat, making them more durable for stovetop and oven use. The thermal stability of glass ceramics extends the lifespan of cookware by resisting warping and breakage during intensive cooking.
Safety and Health Concerns
Lead glass cookware often contains lead oxide, which can leach into food, posing significant health risks such as lead poisoning and neurological damage, especially when exposed to acidic or hot foods. In contrast, glass ceramic cookware is free from harmful heavy metals and is engineered to withstand high temperatures without releasing toxic substances, making it a safer choice for health-conscious consumers. Selecting glass ceramic over lead glass minimizes exposure to toxic compounds, ensuring safer cooking practices and better long-term health outcomes.
Performance in Cooking Applications
Lead glass offers excellent thermal clarity and even heat distribution, making it suitable for precise cooking tasks and visually monitoring food. Glass ceramic cookware excels with superior thermal shock resistance and rapid heat transfer, allowing for high-temperature cooking and quick temperature changes without cracking. Both materials provide durability, but glass ceramic's enhanced performance under direct heat makes it more versatile for stovetop and oven use.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Lead glass offers superior clarity and brilliance, making it ideal for cookware where a sleek, elegant appearance is desired, enhancing visual appeal on the countertop. Glass ceramic cookware boasts a matte or slightly textured finish, providing a contemporary, minimalist aesthetic favored in modern kitchen designs. Both materials allow for unique design elements, but lead glass emphasizes transparency and shine, while glass ceramic prioritizes durability with a stylish, understated look.
Cost and Availability
Lead glass cookware tends to be more expensive due to the complex manufacturing process and limited suppliers, while glass ceramic cookware is generally more affordable and widely available in retail stores. Glass ceramic cookware offers better resistance to thermal shock and is commonly found in both budget and premium ranges, making it accessible to a broader audience. Cost efficiency and easier procurement make glass ceramic a preferred choice for everyday cooking needs compared to the pricier lead glass options.
Which is Better for Your Kitchen?
Lead glass offers excellent clarity and is commonly used for decorative cookware but contains lead, which can pose health risks if used for cooking. Glass ceramic cookware, such as Pyroceram, provides superior thermal shock resistance, durability, and safety, making it more suitable for everyday kitchen use. Choosing glass ceramic cookware ensures better performance and safety, especially for stovetop and oven cooking applications.
Infographic: Lead glass vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com