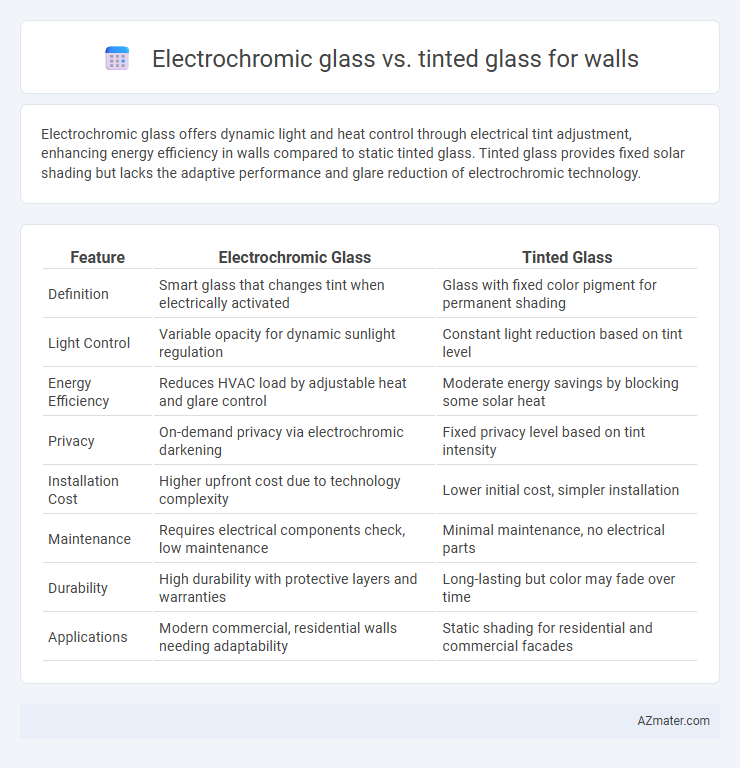
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light and heat control through electrical tint adjustment, enhancing energy efficiency in walls compared to static tinted glass. Tinted glass provides fixed solar shading but lacks the adaptive performance and glare reduction of electrochromic technology.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smart glass that changes tint when electrically activated | Glass with fixed color pigment for permanent shading |
| Light Control | Variable opacity for dynamic sunlight regulation | Constant light reduction based on tint level |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces HVAC load by adjustable heat and glare control | Moderate energy savings by blocking some solar heat |
| Privacy | On-demand privacy via electrochromic darkening | Fixed privacy level based on tint intensity |
| Installation Cost | Higher upfront cost due to technology complexity | Lower initial cost, simpler installation |
| Maintenance | Requires electrical components check, low maintenance | Minimal maintenance, no electrical parts |
| Durability | High durability with protective layers and warranties | Long-lasting but color may fade over time |
| Applications | Modern commercial, residential walls needing adaptability | Static shading for residential and commercial facades |
Introduction to Electrochromic and Tinted Glass
Electrochromic glass features a dynamic tinting capability allowing users to control light transmission and privacy through electrical voltage, making it highly energy-efficient and adaptable for walls in modern architecture. Tinted glass offers a fixed coloration that reduces glare and solar heat gain but lacks the flexibility and responsiveness of electrochromic technology. Both materials serve as functional wall solutions, with electrochromic glass providing advanced energy management and user control compared to the static performance of traditional tinted glass.
How Electrochromic Glass Works
Electrochromic glass changes its tint through an applied electrical voltage, which causes a reversible chemical reaction in the glass layers, modulating light and heat transmission dynamically. This smart glass technology allows users to control privacy and solar heat gain without compromising natural daylight, unlike traditional tinted glass which has a fixed shading level. By reducing reliance on blinds and air conditioning, electrochromic glass significantly enhances energy efficiency and occupant comfort in building walls.
Tinted Glass: Features and Functionality
Tinted glass for walls offers superior solar heat control by reducing glare and blocking harmful ultraviolet rays, improving indoor comfort while enhancing energy efficiency. It typically comes in various shades and colors, allowing customization of aesthetic appeal and light transmission based on specific architectural needs. Unlike electrochromic glass, tinted glass maintains a consistent tint without the need for electrical power or complex control systems, providing a passive and cost-effective solution for building facades.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Electrochromic glass offers superior energy efficiency compared to tinted glass by dynamically adjusting its tint in response to sunlight, reducing solar heat gain and lowering cooling costs. Tinted glass provides a fixed shading effect that limits visible light and heat transmission but cannot adapt to changing environmental conditions, potentially leading to higher energy consumption for heating or cooling. Studies show buildings with electrochromic glass can achieve up to 20%-30% greater HVAC energy savings than those using static tinted glass.
Daylight Control and Glare Reduction
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic daylight control by electronically adjusting its opacity to reduce glare and optimize indoor lighting throughout the day, unlike traditional tinted glass, which provides fixed shading. This adaptive feature enhances occupant comfort and energy efficiency by minimizing excessive solar heat gain and glare without compromising natural light. Tinted glass, while effective in reducing glare initially, cannot adapt to changing light conditions, often leading to under- or over-shading.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Design Options
Electrochromic glass offers superior aesthetic flexibility compared to tinted glass by allowing dynamic control over transparency and light transmission, enabling customization of ambiance and privacy on demand. Tinted glass provides a fixed color and light reduction, limiting design adaptability but enhancing consistent solar control. Designers benefit from electrochromic glass's ability to adjust shading in real-time, supporting innovative architectural concepts and maximizing natural light management.
Smart Technology Integration
Electrochromic glass offers advanced smart technology integration through its ability to dynamically control light and heat transmission via electrical signals, enhancing energy efficiency and user comfort in wall applications. Unlike static tinted glass, electrochromic glass can adapt to changing environmental conditions, reducing glare and UV exposure on demand while enabling seamless automation with building management systems. This smart functionality supports sustainable architecture by optimizing natural daylight use and lowering HVAC loads without compromising aesthetic appeal.
Cost Differences and Long-Term Value
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by changing transparency with an electrical charge, resulting in higher initial costs compared to traditional tinted glass, which provides fixed shading through embedded pigments. Over time, electrochromic glass delivers greater energy savings by reducing the need for artificial lighting and climate control, enhancing long-term value despite its upfront expense. Tinted glass, while more affordable initially, lacks adaptability and may increase energy consumption, limiting its cost-efficiency over the building's lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Electrochromic glass significantly reduces energy consumption by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and natural light, leading to lower HVAC emissions compared to traditional tinted glass fixed in opacity. Electrochromic technology enhances sustainability through its ability to adapt to environmental conditions, minimizing reliance on artificial lighting and climate control, whereas tinted glass offers limited energy efficiency benefits. Lifecycle analyses demonstrate electrochromic glass's potential to reduce carbon footprint, supporting green building certifications more effectively than conventional tinted solutions.
Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Wall
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and energy efficiency, making it ideal for smart building facades and privacy-sensitive spaces, while tinted glass provides consistent solar shading and glare reduction suitable for cost-effective, static applications. For walls requiring adjustable transparency and improved occupant comfort, electrochromic glass is preferred, particularly in office buildings and high-end residential projects. Tinted glass remains a practical choice for environments prioritizing uniform sunlight filtering and lower initial installation costs.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Tinted glass for Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com