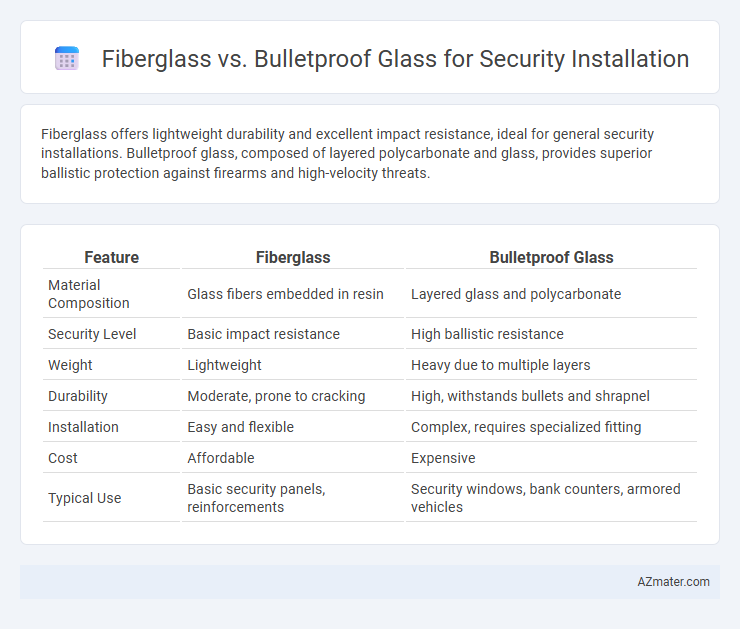
Fiberglass offers lightweight durability and excellent impact resistance, ideal for general security installations. Bulletproof glass, composed of layered polycarbonate and glass, provides superior ballistic protection against firearms and high-velocity threats.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fiberglass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers embedded in resin | Layered glass and polycarbonate |
| Security Level | Basic impact resistance | High ballistic resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy due to multiple layers |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, withstands bullets and shrapnel |
| Installation | Easy and flexible | Complex, requires specialized fitting |
| Cost | Affordable | Expensive |
| Typical Use | Basic security panels, reinforcements | Security windows, bank counters, armored vehicles |
Introduction to Security Glass Solutions
Security glass solutions balance protection and visibility by using specialized materials like fiberglass and bulletproof glass, each suited for different security needs. Fiberglass security glass offers lightweight impact resistance and is ideal for cost-effective reinforcement in less critical areas. Bulletproof glass combines multiple layers of polycarbonate and laminated glass to provide high-level ballistic protection for secure facilities and vulnerable points.
What is Fibre Glass?
Fiberglass is a composite material made from fine glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, known for its lightweight and high tensile strength properties. It is commonly used in security installations for its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for applications where impact resistance is required without excessive weight. Unlike bulletproof glass, fiberglass does not provide ballistic protection but offers an effective solution for reinforcing structures and enhancing safety against non-ballistic threats.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a laminated material composed of multiple layers of polycarbonate and glass designed to resist high-velocity impacts from firearms and explosives. It provides superior protection compared to fiberglass, which is primarily used for reinforcement and insulation but lacks ballistic resistance. Security installations favor bulletproof glass for its ability to absorb and disperse kinetic energy, preventing penetration and ensuring safety in high-risk environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bulletproof glass is typically composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, offering superior strength and impact resistance compared to fiberglass, which is a composite material made from woven glass fibers embedded in resin. While fiberglass is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion, it lacks the high-level ballistic protection that bulletproof glass provides, making it less suitable for security installations where resistance to gunfire and forced entry is critical. The durability of bulletproof glass under high-impact scenarios far exceeds that of fiberglass, ensuring enhanced protection and longevity in security applications.
Installation Process Differences
Fiberglass installation for security purposes involves layering woven glass fibers with resin, requiring curing time and skilled handling to ensure structural integrity and impact resistance. Bulletproof glass installation demands precise fitting of multiple laminated glass and polycarbonate layers, often necessitating professional alignment and specialized framing to maintain ballistic protection capabilities. The complexity of bulletproof glass installation generally leads to higher labor costs and longer setup times compared to fiberglass security panels.
Cost Analysis: Fibre Glass vs Bulletproof Glass
Fiberglass offers a cost-effective security solution with lower material and installation expenses compared to bulletproof glass, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple polycarbonate and glass layers, commands a significantly higher price due to its enhanced ballistic resistance and durability. Evaluating lifecycle costs, fiberglass may require more frequent maintenance and replacement, while bulletproof glass provides long-term investment value through superior protection and reduced need for repairs.
Applications in Security Installations
Fibre glass is commonly used for lightweight security panels, barriers, and protective enclosures due to its high tensile strength and resistance to environmental factors. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, is specifically designed for ballistic protection in security installations such as bank teller windows, armored vehicles, and secure entry points. While fibre glass offers cost-effective resistance against impact and intrusion, bulletproof glass provides certified levels of protection against firearm attacks and high-velocity projectiles in critical security environments.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Bulletproof glass offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to fiberglass, making it a preferred choice for long-term security installations where high-level protection is critical. Fiberglass, while easier and less expensive to maintain due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, may degrade faster under extreme weather conditions and frequent impact. Maintenance for bulletproof glass primarily involves routine cleaning and inspection for cracks, which can extend its lifespan significantly beyond fiberglass in high-threat environments.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Fibre glass and bulletproof glass differ significantly in safety standards and certifications for security installations. Bulletproof glass must comply with rigorous international standards such as UL 752 or NIJ Level IIIA to ensure resistance against high-velocity ballistic threats, while fibre glass primarily adheres to impact resistance and fire safety certifications like ASTM E84. Choosing materials with recognized certifications guarantees compliance with security protocols and optimal protection against specific threats in residential or commercial applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Security Needs
Fibre glass offers lightweight, cost-effective security solutions with moderate impact resistance, ideal for areas where shatter resistance and flexibility are priorities. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides superior protection against ballistic threats, making it essential for high-security installations such as banks, military facilities, and armored vehicles. Selecting the right glass depends on threat level assessment, budget constraints, and the balance between transparency, weight, and durability required for the specific security environment.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Bulletproof glass for Security installation
 azmater.com
azmater.com