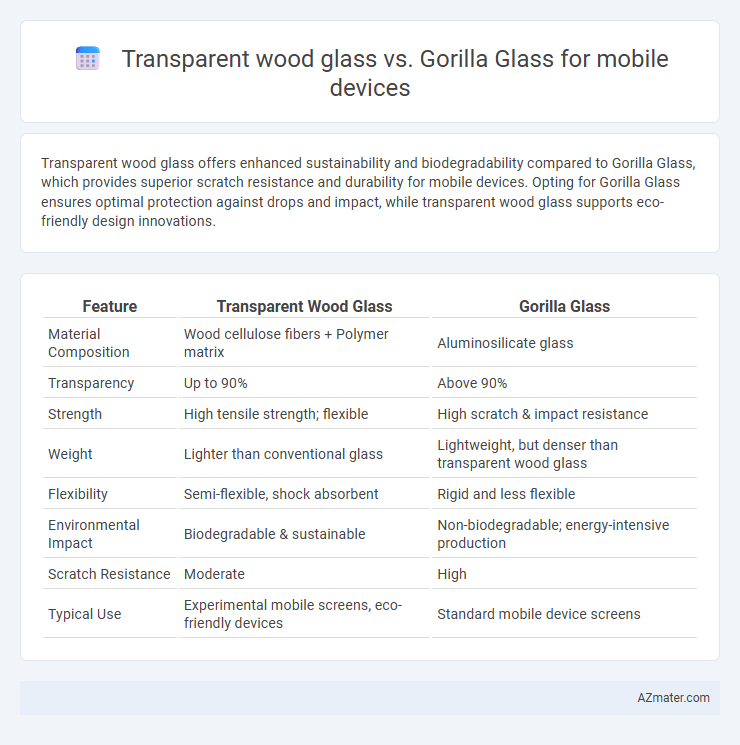
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced sustainability and biodegradability compared to Gorilla Glass, which provides superior scratch resistance and durability for mobile devices. Opting for Gorilla Glass ensures optimal protection against drops and impact, while transparent wood glass supports eco-friendly design innovations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Wood Glass | Gorilla Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood cellulose fibers + Polymer matrix | Aluminosilicate glass |
| Transparency | Up to 90% | Above 90% |
| Strength | High tensile strength; flexible | High scratch & impact resistance |
| Weight | Lighter than conventional glass | Lightweight, but denser than transparent wood glass |
| Flexibility | Semi-flexible, shock absorbent | Rigid and less flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable & sustainable | Non-biodegradable; energy-intensive production |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Typical Use | Experimental mobile screens, eco-friendly devices | Standard mobile device screens |
Overview of Transparent Wood Glass and Gorilla Glass
Transparent wood glass combines natural cellulose nanofibers with transparent polymers, offering lightweight, biodegradable, and impact-resistant protection for mobile devices. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is a chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass known for its high scratch resistance and durability against drops. Both materials aim to enhance device screen protection, with transparent wood glass emphasizing sustainability and Gorilla Glass focusing on hardness and clarity.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Transparent wood glass consists of cellulose nanofibers derived from the lignin-removed wood matrix, combined with polymer resins to create a lightweight, flexible, and eco-friendly material. Gorilla Glass, by contrast, is an aluminosilicate alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass chemically strengthened through ion-exchange processes, resulting in high scratch resistance and extreme hardness. The hierarchical nanostructure of transparent wood glass offers better impact resistance and biodegradability, while Gorilla Glass provides superior transparency and durability under high stress conditions.
Transparency and Visual Quality
Transparent wood glass exhibits high transparency with light transmittance rates up to 90%, offering excellent natural clarity and reduced glare for mobile device screens. Gorilla Glass provides superior visual quality through enhanced scratch resistance and durable strength while maintaining transparency levels typically above 85%. The choice between transparent wood and Gorilla Glass depends on balancing natural optical clarity against long-term durability and scratch resilience for display performance.
Strength and Durability Factors
Transparent wood glass offers high impact resistance and flexibility by combining wood's natural fibers with glass, resulting in enhanced fracture toughness compared to traditional glass. Gorilla Glass, engineered from aluminosilicate, provides superior scratch resistance and hardness through chemical strengthening, making it highly durable under daily wear. While Transparent wood glass excels in bending strength and shatter resistance, Gorilla Glass leads in scratch durability and thinness for mobile devices.
Flexibility and Weight Differences
Transparent wood glass offers significantly higher flexibility compared to Gorilla Glass, making it less prone to cracking under bending stress. It is also notably lighter due to its cellulose-based composition, reducing overall device weight while maintaining adequate transparency. Gorilla Glass, made from aluminosilicate, is more rigid and heavier but provides superior scratch resistance and durability.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Transparent wood glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to Gorilla Glass due to its natural fiber-reinforced structure that resists surface abrasions effectively. Gorilla Glass excels in impact resistance with its chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition, providing enhanced durability against drops and shocks. Mobile devices utilizing Gorilla Glass benefit from proven impact resilience, while transparent wood glass introduces a promising alternative for scratch protection with sustainable material advantages.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Transparent wood glass, derived from renewable wood fibers combined with transparent polymers, offers a biodegradable and lower-carbon-footprint alternative to conventional Gorilla Glass, which relies on energy-intensive manufacturing processes involving chemically strengthened aluminosilicate. The biodegradability and recyclability of transparent wood glass reduce long-term environmental waste, making it a sustainable option for mobile devices aiming to minimize e-waste. Conversely, Gorilla Glass, while highly durable and scratch-resistant, poses challenges in recycling due to its chemical composition and energy demands during production, impacting overall sustainability efforts.
Manufacturing Costs and Scalability
Transparent wood glass offers a promising eco-friendly alternative to Gorilla Glass by utilizing renewable wood fibers combined with polymer coatings, potentially reducing raw material expenses. Manufacturing transparent wood at scale involves challenges such as maintaining uniform transparency and mechanical strength, which can increase production complexity and costs compared to the well-established, highly optimized chemical vapor deposition and ion-exchange processes used in Gorilla Glass fabrication. While Gorilla Glass benefits from decades of scalable mass production with stable yields and cost efficiencies, transparent wood glass is still emerging, making it currently less economically viable for widespread mobile device adoption.
Potential Applications in Mobile Devices
Transparent wood glass offers lightweight and biodegradable alternatives for mobile device screens, enhancing sustainability and impact resistance compared to conventional Gorilla Glass. Gorilla Glass remains preferred for its exceptional toughness, scratch resistance, and established integration in high-end smartphones and tablets. Future mobile devices might leverage transparent wood glass in flexible displays and eco-friendly designs, while Gorilla Glass continues dominating in durability-critical applications.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Transparent wood glass offers a lightweight, sustainable alternative with superior impact resistance and biodegradability compared to Gorilla Glass, which dominates the market with exceptional scratch resistance and durability. Innovations in transparent wood nanocomposites aim to enhance optical clarity, flexibility, and thermal insulation, positioning it as a revolutionary material for flexible, eco-friendly mobile displays. Future research focuses on scalable production and integration of transparent wood with traditional glass technologies to create hybrid screens combining strength, transparency, and environmental benefits.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Gorilla glass for Mobile device
 azmater.com
azmater.com