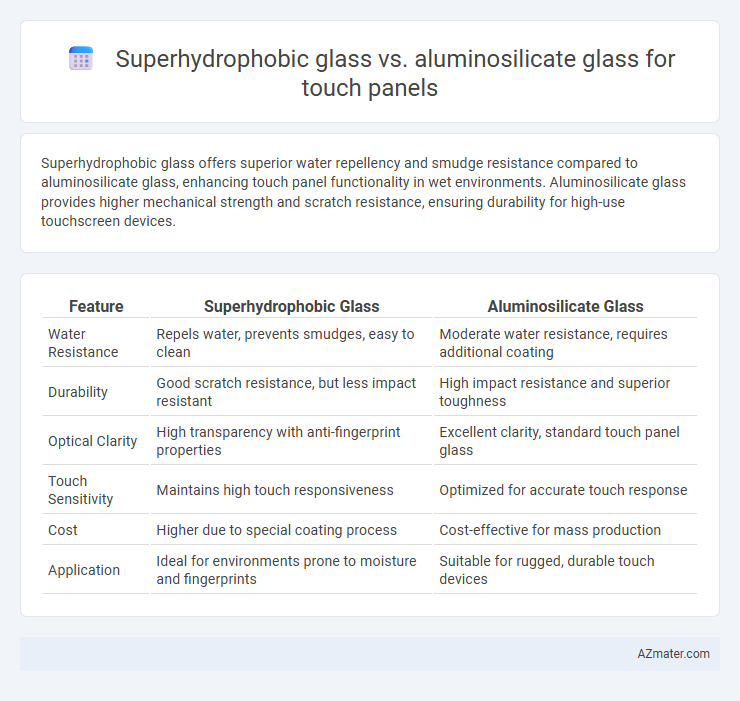
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and smudge resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing touch panel functionality in wet environments. Aluminosilicate glass provides higher mechanical strength and scratch resistance, ensuring durability for high-use touchscreen devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Repels water, prevents smudges, easy to clean | Moderate water resistance, requires additional coating |
| Durability | Good scratch resistance, but less impact resistant | High impact resistance and superior toughness |
| Optical Clarity | High transparency with anti-fingerprint properties | Excellent clarity, standard touch panel glass |
| Touch Sensitivity | Maintains high touch responsiveness | Optimized for accurate touch response |
| Cost | Higher due to special coating process | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Application | Ideal for environments prone to moisture and fingerprints | Suitable for rugged, durable touch devices |
Introduction to Touch Panel Glass Technologies
Superhydrophobic glass and aluminosilicate glass represent two advanced materials used in touch panel technologies, each offering distinct benefits for durability and user interaction. Aluminosilicate glass is renowned for its high strength, scratch resistance, and thermal stability, making it a preferred choice for protecting touchscreens in mobile devices and wearables. Superhydrophobic glass enhances touch panels by providing water and oil repellency, reducing smudges and fingerprints while maintaining clarity and responsiveness in various environmental conditions.
What is Superhydrophobic Glass?
Superhydrophobic glass is a specially coated surface designed to repel water by creating a high contact angle, often exceeding 150deg, which prevents water droplets from adhering and enhances touch panel visibility and cleanliness. It uses nanostructured coatings to achieve extreme water repellency, reducing fingerprints and smudges significantly compared to standard aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high strength and scratch resistance, does not inherently possess water-repellent properties, making superhydrophobic glass a superior choice for maintaining clarity and ease of use in touch panel applications under wet or oily conditions.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a high-strength, chemically resistant material commonly used for touch panels due to its enhanced durability and scratch resistance compared to traditional glass. It contains aluminum oxide (Al2O3) which improves mechanical properties and thermal stability, making it ideal for daily use in electronic devices. Compared to superhydrophobic glass, aluminosilicate glass prioritizes toughness and impact resistance, offering reliable performance under frequent contact and environmental stress.
Key Properties of Superhydrophobic Glass
Superhydrophobic glass for touch panels exhibits exceptional water repellency with contact angles exceeding 150deg, significantly reducing fingerprint smudges and enhancing clarity in wet conditions. It maintains high transparency and scratch resistance, ensuring durability and optimal user experience. Compared to aluminosilicate glass, superhydrophobic coatings offer superior self-cleaning properties and improved resistance to oil and moisture, making it ideal for high-performance touch interfaces.
Key Properties of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced durability compared to superhydrophobic glass, making it ideal for touch panels subjected to frequent use and impact. Its high hardness and resistance to thermal stress provide longer-lasting performance under environmental variations. Moreover, aluminosilicate glass maintains excellent optical clarity and touch sensitivity essential for interactive display technologies.
Durability Comparison: Superhydrophobic vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Superhydrophobic glass provides enhanced water and stain resistance, reducing the risk of surface damage and improving touch panel longevity. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength and scratch resistance, making it highly durable against impacts and abrasions. Compared to superhydrophobic coatings, aluminosilicate glass generally delivers greater overall durability under daily wear conditions for touch panels.
Scratch and Impact Resistance: Performance Insights
Superhydrophobic glass enhances touch panel durability by repelling water and reducing surface abrasion, but Aluminosilicate glass excels in scratch and impact resistance due to its robust chemical composition and thermal treatment processes. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphones, demonstrates superior hardness and toughness, making it more resistant to daily wear, scratches, and accidental drops. Performance tests highlight that while superhydrophobic coatings improve surface cleanliness and water resistance, Aluminosilicate glass offers a more reliable foundation for high-impact and scratch-prone environments.
Optical Clarity and Transparency Differences
Superhydrophobic glass features a nano-textured surface that repels water and smudges, enhancing touch panel visibility by maintaining a cleaner surface, but this texture can slightly reduce optical clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical transparency and clarity due to its smooth, uniform surface and high purity, minimizing light scattering and distortion for sharper display images. The trade-off lies in hydrophobic properties versus pristine optical performance, with aluminosilicate glass favored for maximum transparency while superhydrophobic glass balances cleanliness with minimal impact on clarity.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass coatings for touch panels often involve complex chemical treatments and nanostructuring processes, increasing manufacturing costs compared to aluminosilicate glass, which is produced through established, cost-efficient methods like ion exchange strengthening. Aluminosilicate glass offers robust scratch resistance and durability at a lower price point, making it a preferred choice for mass-market touch devices. Superhydrophobic surfaces enhance water repellency and fingerprint resistance but require additional steps in production, impacting scalability and overall cost-effectiveness.
Applications and Suitability for Modern Touch Panels
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and anti-fingerprint properties, making it ideal for touch panels in outdoor or high-moisture environments such as smartphones and rugged tablets. Aluminosilicate glass provides exceptional strength and scratch resistance, ensuring durability and longevity in everyday consumer electronics like smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The choice between superhydrophobic and aluminosilicate glass depends on application-specific requirements, balancing hydrophobic surface benefits against mechanical robustness for modern touch panels.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Touch panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com