Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced strength and chemical durability through surface ion replacement, making it ideal for durable display panels. Low-iron glass provides superior optical clarity and minimal color distortion, optimizing visual performance in high-end display applications.
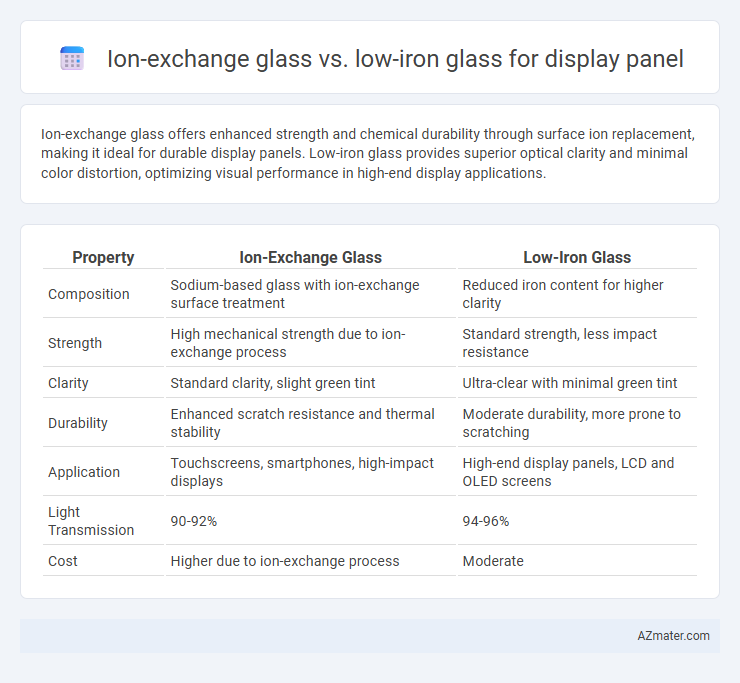
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | Low-Iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium-based glass with ion-exchange surface treatment | Reduced iron content for higher clarity |
| Strength | High mechanical strength due to ion-exchange process | Standard strength, less impact resistance |
| Clarity | Standard clarity, slight green tint | Ultra-clear with minimal green tint |
| Durability | Enhanced scratch resistance and thermal stability | Moderate durability, more prone to scratching |
| Application | Touchscreens, smartphones, high-impact displays | High-end display panels, LCD and OLED screens |
| Light Transmission | 90-92% | 94-96% |
| Cost | Higher due to ion-exchange process | Moderate |
Overview of Display Panel Glass Technologies
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced strength and damage resistance through a chemical strengthening process, making it ideal for high-durability display panels. Low-iron glass provides superior optical clarity and color accuracy by minimizing iron content, which reduces green tint and improves light transmission in displays. Both technologies are critical in optimizing display performance, with ion-exchange glass prioritizing mechanical durability and low-iron glass enhancing visual quality.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a type of chemically strengthened glass created by replacing smaller ions in the glass surface with larger ones through a controlled ion-exchange process, enhancing its mechanical strength and scratch resistance. It offers superior durability compared to standard glass, making it ideal for display panels that require high toughness and longevity. Low-iron glass, in contrast, prioritizes optical clarity and reduced green tint but does not undergo the same ion-exchange strengthening, making ion-exchange glass more suitable for rugged, impact-resistant display applications.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of glass with reduced iron content, resulting in higher clarity and improved light transmission compared to standard glass. This glass is commonly used in display panels to enhance brightness and color accuracy by minimizing the greenish tint caused by iron impurities. Unlike ion-exchange glass, which prioritizes surface strength through chemical treatment, low-iron glass focuses on optical performance, making it ideal for high-quality display applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Ion-Exchange vs Low-Iron Glass
Ion-exchange glass manufacturing involves a chemical strengthening process where sodium ions in the glass surface are replaced with larger potassium ions through immersion in a molten salt bath, enhancing durability and scratch resistance for display panels. Low-iron glass is produced by reducing iron oxide content during raw material selection and melting, resulting in higher light transmittance and color neutrality critical for high-clarity displays. The ion-exchange process focuses on mechanical strengthening post-production, while low-iron glass prioritizes raw material purity and melting conditions to optimize optical performance in display manufacturing.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission Comparison
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior optical clarity with fewer surface imperfections due to its enhanced surface compression, resulting in reduced light scattering compared to low-iron glass. Low-iron glass offers higher intrinsic light transmission, typically exceeding 91%, thanks to its reduced iron content, which minimizes greenish tint and improves overall transparency. In display panels, ion-exchange glass balances mechanical strength and clarity, while low-iron glass maximizes brightness and color accuracy, making both materials pivotal depending on specific display performance requirements.
Scratch and Impact Resistance: Which Glass Performs Better?
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior scratch resistance due to its surface compression layer created through a chemical strengthening process, making it highly durable against everyday abrasion. Low-iron glass, while offering enhanced clarity and light transmittance for display panels, generally lacks the same level of surface hardness and is more prone to scratches under impact. In terms of impact resistance, ion-exchange glass outperforms low-iron glass by absorbing and distributing force more effectively, resulting in fewer surface cracks and longer-lasting protection for display applications.
Cost Analysis: Ion-Exchange vs Low-Iron Glass
Ion-exchange glass typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to the complex chemical strengthening process that enhances durability and scratch resistance in display panels. Low-iron glass, while often cheaper to produce thanks to its reduced iron content that improves transparency and color accuracy, may require additional treatments to achieve similar strength levels. Cost analysis reveals ion-exchange glass as a premium option favored for high-performance displays, whereas low-iron glass balances cost and optical clarity for mid-range applications.
Applications in Modern Display Panels
Ion-exchange glass offers superior surface strength and scratch resistance, making it ideal for touch-sensitive modern display panels such as smartphones and tablets. Low-iron glass enhances light transmission and color accuracy, optimizing visual performance in high-end LCD and OLED displays used in monitors and televisions. Combining these glasses enables manufacturers to balance durability with visual clarity in advanced electronic display applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability through surface strengthening, extending display panel lifespan and reducing electronic waste compared to conventional glass types. Low-iron glass enables higher light transmission and energy efficiency in displays, which contributes to lower power consumption and diminished carbon footprint during use. Both materials present eco-friendly advantages, but ion-exchange glass's longevity supports sustainability by minimizing resource extraction for replacements, while low-iron glass prioritizes operational energy savings.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Display Panel Needs
Ion-exchange glass offers superior strength and scratch resistance, making it ideal for rugged display panels in smartphones and tablets, while low-iron glass provides exceptional clarity and high light transmission, enhancing color accuracy and brightness for premium displays. Selecting the right glass depends on prioritizing durability or optical performance in your display panel applications. For environments demanding both toughness and visual quality, combining ion-exchange strengthening with low-iron glass can deliver balanced performance.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Low-iron glass for Display panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com