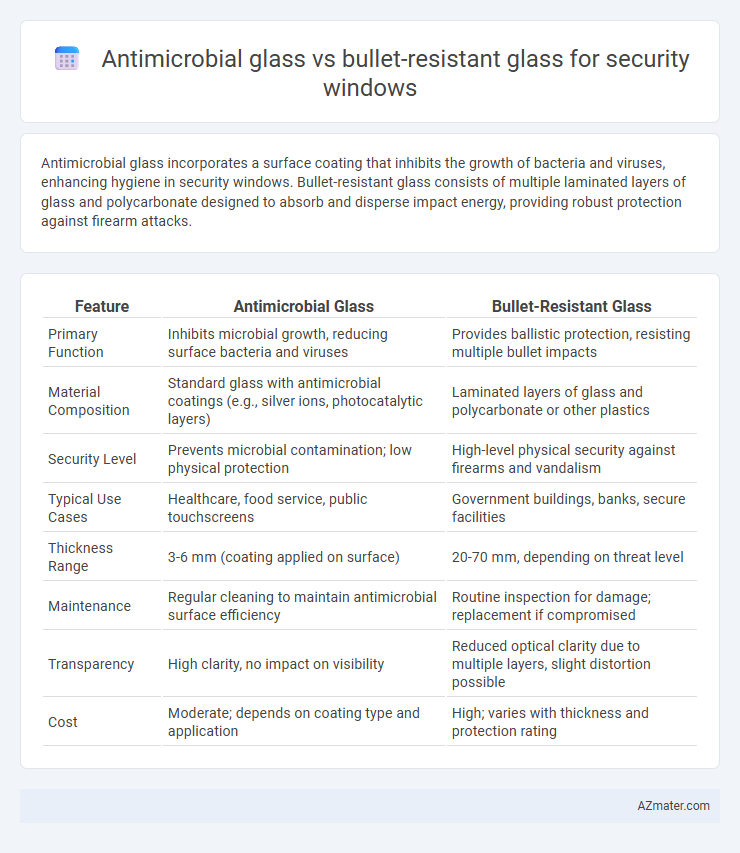
Antimicrobial glass incorporates a surface coating that inhibits the growth of bacteria and viruses, enhancing hygiene in security windows. Bullet-resistant glass consists of multiple laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate designed to absorb and disperse impact energy, providing robust protection against firearm attacks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Bullet-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Inhibits microbial growth, reducing surface bacteria and viruses | Provides ballistic protection, resisting multiple bullet impacts |
| Material Composition | Standard glass with antimicrobial coatings (e.g., silver ions, photocatalytic layers) | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate or other plastics |
| Security Level | Prevents microbial contamination; low physical protection | High-level physical security against firearms and vandalism |
| Typical Use Cases | Healthcare, food service, public touchscreens | Government buildings, banks, secure facilities |
| Thickness Range | 3-6 mm (coating applied on surface) | 20-70 mm, depending on threat level |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning to maintain antimicrobial surface efficiency | Routine inspection for damage; replacement if compromised |
| Transparency | High clarity, no impact on visibility | Reduced optical clarity due to multiple layers, slight distortion possible |
| Cost | Moderate; depends on coating type and application | High; varies with thickness and protection rating |
Introduction to Security Window Technologies
Antimicrobial glass incorporates silver ions or copper particles to inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses on window surfaces, enhancing hygiene in high-traffic or healthcare environments. Bullet-resistant glass, typically composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides critical ballistic protection by absorbing and dissipating the energy of gunfire to prevent penetration. Both technologies contribute to security windows by addressing different protective needs--antimicrobial glass enhances health safety, while bullet-resistant glass offers physical security against armed threats.
What is Antimicrobial Glass?
Antimicrobial glass incorporates a special coating containing metal ions such as silver or copper, which actively inhibit the growth and spread of bacteria, viruses, and fungi on its surface, enhancing hygiene in security windows. Unlike bullet-resistant glass designed primarily to withstand ballistic impacts through layered and laminated materials, antimicrobial glass offers protection by reducing microbial contamination while maintaining clarity and durability. This type of glass is ideal for security windows in healthcare, laboratories, and public spaces where cleanliness and infection control are critical factors.
What is Bullet-Resistant Glass?
Bullet-resistant glass is a specially engineered material designed to withstand high-velocity projectiles, providing critical protection in security windows against firearms attacks. Constructed from multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, it absorbs and disperses the energy from bullets to prevent penetration and minimize injury. This type of glass is essential for environments requiring enhanced safety measures, such as banks, government buildings, and armored vehicles.
Key Differences Between Antimicrobial and Bullet-Resistant Glass
Antimicrobial glass incorporates a coating or embedded ions such as silver or copper to inhibit microbial growth, making it ideal for hygiene-sensitive environments. Bullet-resistant glass consists of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate designed to absorb and disperse the energy of ballistic impacts, ensuring protection against firearm threats. The key difference lies in antimicrobial glass's focus on health safety through microbial reduction, whereas bullet-resistant glass prioritizes physical security by providing impact and penetration resistance.
Performance in Security and Safety Applications
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, making it ideal for healthcare and high-contact environments, while bullet-resistant glass provides critical ballistic protection by withstanding firearm impacts to prevent penetration. Bullet-resistant glass typically utilizes layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass to absorb and disperse energy, ensuring structural integrity during attacks, whereas antimicrobial coatings do not affect physical strength but improve safety by reducing microbial contamination. For security windows requiring both impact resistance and contamination control, integrating both technologies delivers comprehensive protection against physical threats and biological hazards.
Health and Hygiene Benefits of Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass incorporates ion-based coatings that inhibit bacteria and viral growth on surfaces, significantly reducing the risk of cross-contamination in high-traffic security windows. Unlike bullet-resistant glass, which primarily focuses on impact and ballistic protection, antimicrobial glass enhances health and hygiene by maintaining a cleaner surface environment. This makes antimicrobial glass especially valuable in healthcare, public transportation, and retail security settings where reducing microbial presence is crucial for occupant safety.
Protection Capabilities of Bullet-Resistant Glass
Bullet-resistant glass offers superior protection capabilities by effectively withstanding high-velocity projectiles and preventing penetration from bullets, making it ideal for high-security environments such as banks, military facilities, and government buildings. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which primarily focuses on reducing microbial contamination on surfaces, bullet-resistant glass is engineered with layers of polycarbonate and glass to absorb and disperse kinetic energy, ensuring the safety of occupants. This specialized composition enhances structural integrity and impact resistance, providing robust defense against ballistic threats.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Antimicrobial glass requires minimal maintenance, featuring coatings that inhibit microbial growth and remain effective without frequent cleaning, making it ideal for environments prioritizing hygiene. Bullet-resistant glass involves complex installation processes, including the need for reinforced framing and professional calibration to ensure impact resistance and safety standards are met. Maintenance for bullet-resistant glass often includes periodic inspections for surface integrity and recalibration of seals to maintain ballistic protection, contrasting with the relatively low upkeep of antimicrobial glass.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Value
Antimicrobial glass typically costs less upfront than bullet-resistant glass, making it a budget-friendly option for basic security and hygiene needs. Bullet-resistant glass involves higher initial investment due to its multi-layer construction and specialized materials designed to halt high-velocity projectiles. Over time, bullet-resistant glass provides greater long-term value by reducing vulnerability to forced entry and enhancing safety in high-risk environments, while antimicrobial glass offers enduring benefits by minimizing pathogen presence and maintenance requirements.
Choosing the Right Security Glass for Your Needs
Antimicrobial glass offers protection against bacteria and viruses, making it ideal for environments prioritizing hygiene, such as hospitals and food processing areas. Bullet-resistant glass provides enhanced security against forced entry and ballistic threats, suitable for banks, government buildings, and high-risk commercial sites. Choosing the right security glass depends on assessing the primary threat--pathogen control or physical protection--to ensure optimal safety and functionality for your specific environment.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Bullet-resistant glass for Security window
 azmater.com
azmater.com