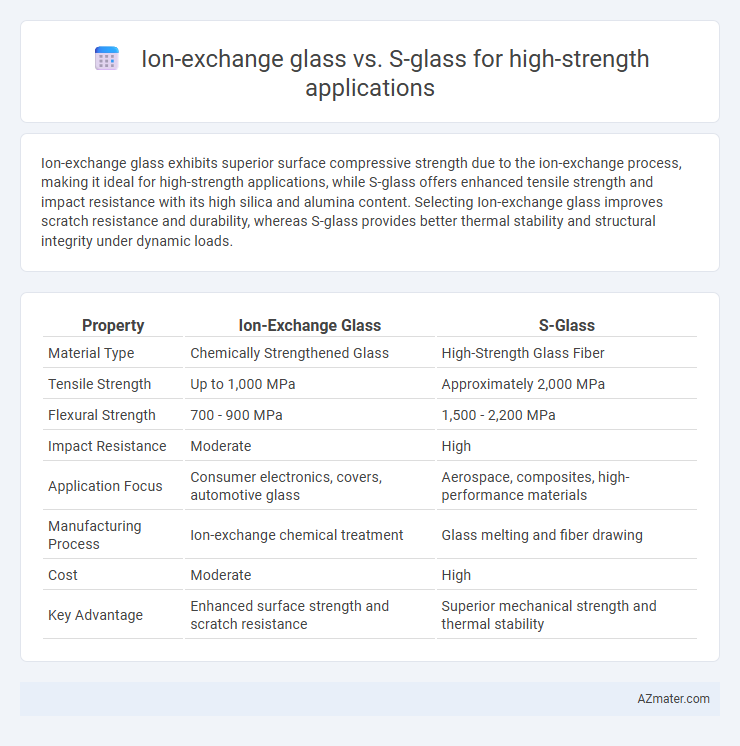
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior surface compressive strength due to the ion-exchange process, making it ideal for high-strength applications, while S-glass offers enhanced tensile strength and impact resistance with its high silica and alumina content. Selecting Ion-exchange glass improves scratch resistance and durability, whereas S-glass provides better thermal stability and structural integrity under dynamic loads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Chemically Strengthened Glass | High-Strength Glass Fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1,000 MPa | Approximately 2,000 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | 700 - 900 MPa | 1,500 - 2,200 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Application Focus | Consumer electronics, covers, automotive glass | Aerospace, composites, high-performance materials |
| Manufacturing Process | Ion-exchange chemical treatment | Glass melting and fiber drawing |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Key Advantage | Enhanced surface strength and scratch resistance | Superior mechanical strength and thermal stability |
Introduction to High-Strength Glass Applications
High-strength glass applications demand materials with exceptional mechanical properties and durability. Ion-exchange glass achieves superior strength through a chemical process that replaces smaller ions with larger ones, creating compressive stress on the surface and enhancing fracture resistance. S-glass, a high-strength fiberglass known for its excellent tensile strength and thermal stability, provides reliable performance in aerospace and industrial composites but typically exhibits lower surface compressive stress compared to ion-exchange glass.
Overview of Ion-Exchange Glass Technology
Ion-exchange glass technology enhances material strength by replacing smaller sodium ions in the glass surface with larger potassium ions, creating a compressive stress layer that significantly improves resistance to scratches and mechanical shocks. This method increases the surface strength and durability of the glass without compromising its optical clarity or thermal stability, making it ideal for high-strength applications compared to traditional S-glass fibers. Ion-exchange glass offers superior toughness and damage tolerance, thereby extending the lifespan and performance reliability in demanding environments.
Understanding S-Glass: Composition and Properties
S-Glass, a high-performance fiberglass, is composed primarily of alumino-silicate fibers with low calcium content, offering superior tensile strength and thermal stability compared to E-glass. Its enhanced composition results in improved mechanical properties such as higher modulus and better fatigue resistance, making it ideal for high-strength applications. Unlike ion-exchange glass, which relies on surface ion substitution to improve strength and scratch resistance, S-Glass delivers inherent structural robustness critical for aerospace, military, and advanced composite materials.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: Ion-Exchange Glass vs S-Glass
Ion-exchange glass exhibits enhanced surface compressive stress, significantly improving its mechanical strength and resistance to crack propagation compared to standard glass types. S-glass, a high-performance fiberglass, provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance due to its optimized silica-alumina composition and fiber reinforcement. While ion-exchange glass is preferred for applications requiring scratch resistance and durability in thin or transparent components, S-glass excels in structural and composite applications demanding high mechanical load capacity and toughness.
Toughness and Fracture Resistance Analysis
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior toughness and enhanced fracture resistance due to the compressive stress layer formed on its surface, which significantly improves its ability to absorb energy and resist crack propagation compared to S-glass. S-glass fibers, while boasting high tensile strength, demonstrate comparatively lower fracture toughness and are more susceptible to microcrack initiation under impact or cyclic loading. For high-strength applications requiring optimal durability and resistance to catastrophic failure, ion-exchange glass offers a more resilient performance profile than S-glass.
Chemical and Thermal Stability in High-Strength Scenarios
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior chemical stability due to its surface compressive stress layer, enhancing resistance to alkaline environments and reducing susceptibility to corrosion in high-strength applications. S-glass provides exceptional thermal stability with a high melting point and low thermal expansion coefficient, maintaining structural integrity under rapid temperature changes. The combination of ion-exchange treatment and S-glass composition optimizes performance by balancing enhanced surface strength and thermal resistance for demanding industrial uses.
Weight and Flexibility: Design Implications
Ion-exchange glass offers superior flexibility and reduced weight compared to S-glass, making it ideal for high-strength applications requiring lightweight yet durable materials. Its enhanced molecular structure through ion-exchange processes increases surface compression, resulting in greater impact resistance without compromising flexibility. In contrast, S-glass provides higher tensile strength but is generally heavier and less flexible, influencing design choices where weight savings and adaptability are critical.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Challenges
Ion-exchange glass offers superior surface compressive stress, enhancing strength and resistance to cracks, making it cost-effective for high-strength applications due to lower material waste and simplified production processes. S-glass provides high tensile strength and thermal stability but incurs higher manufacturing costs and complexity from specialized fiber production and handling requirements. Balancing ion-exchange glass's affordability with S-glass's performance depends on application-specific demands, where ion-exchange glass excels in cost efficiency and scalability while S-glass dominates in extreme durability scenarios.
Typical Use Cases in High-Strength Industries
Ion-exchange glass is predominantly used in high-strength smartphone screens and precision optical components, where scratch resistance and surface durability are critical. S-glass fibers are favored in aerospace and military applications due to their exceptional tensile strength and resistance to high temperatures and corrosive environments. Both materials enhance performance in industries demanding lightweight, high-strength solutions, but ion-exchange glass excels in surface protection while S-glass is preferred for structural reinforcement.
Future Trends and Innovations in High-Performance Glass
Ion-exchange glass enhances surface compressive stress through chemical strengthening, offering superior scratch resistance and durability for high-strength applications, while S-glass provides exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability due to its high silica and alumina content. Future trends include hybrid composites combining ion-exchange glass coatings with S-glass fibers to maximize mechanical performance and longevity. Innovations also focus on nano-engineered ion-exchange processes and environmentally friendly manufacturing techniques to improve strength-to-weight ratios and sustainability in aerospace and defense industries.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs S-glass for High-strength application
 azmater.com
azmater.com