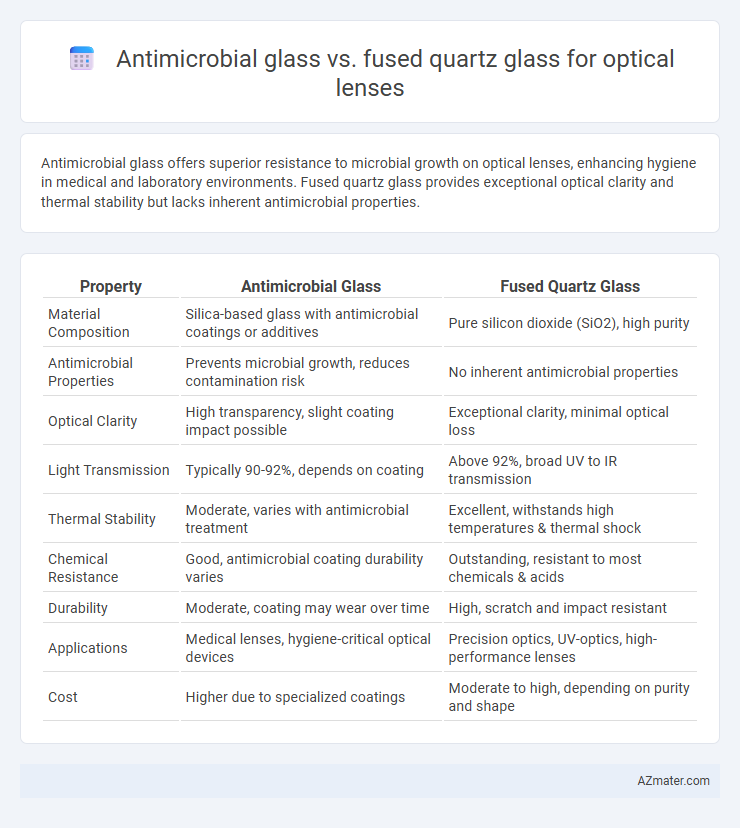
Antimicrobial glass offers superior resistance to microbial growth on optical lenses, enhancing hygiene in medical and laboratory environments. Fused quartz glass provides exceptional optical clarity and thermal stability but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Antimicrobial Glass | Fused Quartz Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica-based glass with antimicrobial coatings or additives | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), high purity |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Prevents microbial growth, reduces contamination risk | No inherent antimicrobial properties |
| Optical Clarity | High transparency, slight coating impact possible | Exceptional clarity, minimal optical loss |
| Light Transmission | Typically 90-92%, depends on coating | Above 92%, broad UV to IR transmission |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, varies with antimicrobial treatment | Excellent, withstands high temperatures & thermal shock |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, antimicrobial coating durability varies | Outstanding, resistant to most chemicals & acids |
| Durability | Moderate, coating may wear over time | High, scratch and impact resistant |
| Applications | Medical lenses, hygiene-critical optical devices | Precision optics, UV-optics, high-performance lenses |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coatings | Moderate to high, depending on purity and shape |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Optical lens materials are critical for achieving high clarity, durability, and resistance to environmental factors in various applications. Antimicrobial glass incorporates surface treatments or coatings that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing hygiene especially in medical and public environments, while fused quartz glass offers exceptional thermal stability, high transparency across ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths, and excellent chemical resistance. Both materials serve distinct purposes: antimicrobial glass prioritizes surface cleanliness and user safety, whereas fused quartz glass excels in optical precision and durability under extreme conditions.
Overview of Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass integrates metal ions like silver or copper to inhibit microbial growth, enhancing hygiene and durability in optical lenses. This glass type offers superior resistance to bacteria and fungi compared to fused quartz glass, which primarily excels in thermal and optical clarity but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. Its application in optical lenses improves lens longevity and reduces maintenance while maintaining high transparency and optical performance.
Overview of Fused Quartz Glass
Fused quartz glass is a high-purity, non-crystalline form of silica known for its exceptional optical clarity and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. Its low thermal expansion coefficient and high transmission across ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths enhance lens performance in demanding environments. Compared to antimicrobial glass, fused quartz glass offers superior mechanical strength and chemical durability but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Antimicrobial glass incorporates coatings or additives that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing lens hygiene without significantly altering optical clarity or refractive index, making it ideal for environments requiring sterilization. Fused quartz glass offers superior thermal stability, high purity, and excellent UV transmission with low thermal expansion, providing exceptional durability and optical performance but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. Key material properties comparison highlights antimicrobial glass's biocidal surface combined with typical optical metrics, whereas fused quartz excels in resistance to thermal shock and ultraviolet transparency essential for high-precision optical lens applications.
Optical Performance: Clarity and Transmission
Antimicrobial glass offers high optical clarity and excellent light transmission, maintaining surface integrity by reducing microbial contamination that can cause haze or discoloration. Fused quartz glass provides superior optical performance with exceptional clarity and near-UV to infrared transmission, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. While fused quartz excels in spectral uniformity and thermal stability, antimicrobial glass enhances long-term optical clarity in environments prone to microbial buildup.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Antimicrobial glass for optical lenses offers enhanced surface protection by incorporating antimicrobial agents that reduce bacterial growth, contributing to longer-lasting lens hygiene and surface integrity. Fused quartz glass excels in durability and scratch resistance due to its high hardness, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for precision optics under harsh conditions. Comparing both, fused quartz glass typically provides superior scratch resistance and mechanical robustness, while antimicrobial glass adds value through its self-sterilizing properties.
Antimicrobial Effectiveness and Applications
Antimicrobial glass incorporates biocidal agents such as silver ions to inhibit microbial growth on optical lenses, providing enhanced hygiene and reduced risk of contamination in medical and eyewear applications. Fused quartz glass, while offering superior optical clarity and thermal stability, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it less suitable for environments requiring stringent sanitary conditions. The antimicrobial effectiveness of treated glass makes it ideal for healthcare, laboratory, and personal protective equipment lenses where infection control is critical.
Cost Analysis: Antimicrobial vs Fused Quartz
Antimicrobial glass for optical lenses typically incurs higher initial costs due to embedded silver ions or copper coatings that provide infection control benefits, increasing material and manufacturing expenses compared to fused quartz glass. Fused quartz glass, known for its superior optical clarity and thermal resistance, is generally more cost-effective in mass production but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, potentially leading to added expenses in cleaning or replacement. Considering long-term use, antimicrobial glass may reduce maintenance and replacement costs in healthcare or laboratory settings, offsetting its premium, whereas fused quartz remains the economical choice for standard optical applications without infection control requirements.
Suitability for Medical and Industrial Use
Antimicrobial glass offers inherent resistance to microbial contamination, making it highly suitable for medical environments where hygiene and sterilization are critical, such as in surgical instruments and diagnostic devices. Fused quartz glass, known for its exceptional thermal stability, optical clarity, and resistance to chemical corrosion, is ideal for industrial applications requiring precision lenses exposed to high temperatures and harsh chemicals. While antimicrobial glass enhances safety by minimizing infection risks, fused quartz glass provides superior performance in extreme conditions, positioning each material based on the specific demands of medical and industrial optical lens uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Optical Lens Material
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced hygiene and durability for optical lenses, making it ideal for healthcare and personal use where contamination control is critical. Fused quartz glass excels in optical clarity, thermal stability, and resistance to UV radiation, suiting high-precision applications like scientific instruments and UV optics. Selecting the right optical lens material depends on balancing antimicrobial properties with optical performance requirements to meet specific application needs effectively.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Fused quartz glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com