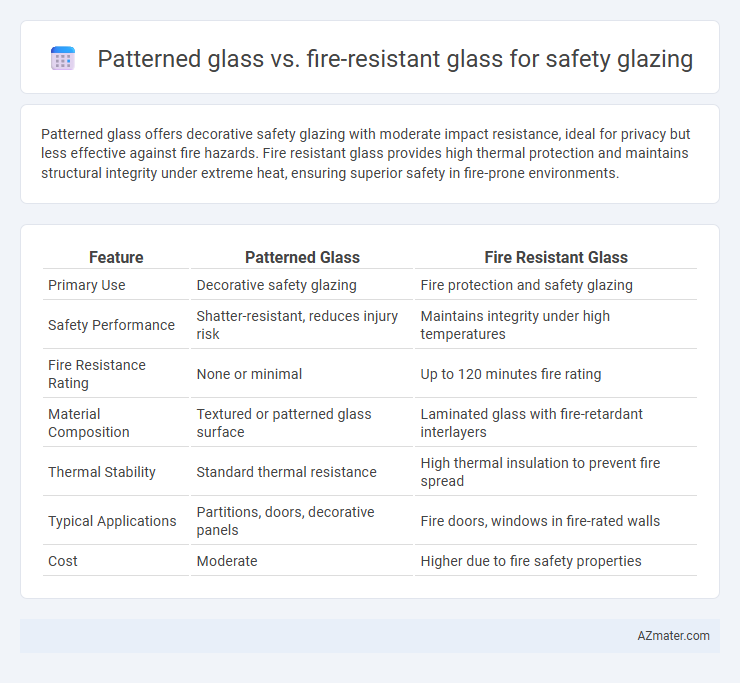
Patterned glass offers decorative safety glazing with moderate impact resistance, ideal for privacy but less effective against fire hazards. Fire resistant glass provides high thermal protection and maintains structural integrity under extreme heat, ensuring superior safety in fire-prone environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Patterned Glass | Fire Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Decorative safety glazing | Fire protection and safety glazing |
| Safety Performance | Shatter-resistant, reduces injury risk | Maintains integrity under high temperatures |
| Fire Resistance Rating | None or minimal | Up to 120 minutes fire rating |
| Material Composition | Textured or patterned glass surface | Laminated glass with fire-retardant interlayers |
| Thermal Stability | Standard thermal resistance | High thermal insulation to prevent fire spread |
| Typical Applications | Partitions, doors, decorative panels | Fire doors, windows in fire-rated walls |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to fire safety properties |
Introduction to Safety Glazing: Key Considerations
Safety glazing requires materials that balance visibility, impact resistance, and fire protection to ensure optimal user safety. Patterned glass offers enhanced privacy and aesthetic appeal while maintaining moderate strength, making it suitable for interior applications where obscured vision is beneficial. Fire resistant glass provides critical heat resistance and prevents flame spread, essential for areas demanding stringent fire safety compliance and protection.
Understanding Patterned Glass: Features and Uses
Patterned glass features textured surfaces created through rolling or casting processes, offering enhanced privacy and decorative appeal while allowing natural light to pass through. Commonly used in interior partitions, shower enclosures, and wardrobe doors, it helps obscure visibility without compromising brightness. Unlike fire resistant glass, patterned glass does not provide specialized protection against high temperatures or flames, making it suitable primarily for aesthetic and privacy purposes rather than safety glazing where fire resistance is critical.
Fire Resistant Glass: Core Properties and Applications
Fire resistant glass offers exceptional thermal insulation and integrity, preventing the passage of flames and smoke for up to several hours, making it crucial in fire-rated doors, partitions, and windows. Its core properties include high heat resistance, durability under extreme temperatures, and the ability to maintain visibility while providing life safety. Unlike patterned glass, which emphasizes privacy and aesthetic texture, fire resistant glass is engineered to meet stringent building codes and safety standards essential for protecting occupants and property during fire emergencies.
Safety Performance Comparison: Patterned vs Fire Resistant Glass
Fire resistant glass offers superior safety performance by providing a critical barrier against flames and smoke during fires, maintaining structural integrity and allowing safe evacuation. Patterned glass primarily enhances visual privacy and aesthetic appeal but lacks the specialized fire containment properties needed in high-risk environments. In safety glazing applications, fire resistant glass is essential for meeting stringent fire codes, whereas patterned glass serves more for decorative and minor impact resistance functions.
Impact Resistance: Which Glass Provides Better Protection?
Fire resistant glass offers superior impact resistance compared to patterned glass, making it the preferred choice for safety glazing in high-risk environments. Designed to withstand thermal shocks and physical impacts, fire resistant glass maintains structural integrity during fire emergencies, reducing the risk of breakage and injury. Patterned glass, while decorative and providing moderate impact resistance, lacks the specialized strengthening treatments that fire resistant glass undergoes, resulting in lower protection levels.
Fire Safety Standards and Building Codes
Fire resistant glass complies with stringent fire safety standards such as UL 305 or BS 476, ensuring it can withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread for designated durations, making it essential for safety glazing in fire-rated doors and windows. Patterned glass, while providing privacy and aesthetic appeal, typically does not meet fire resistance criteria outlined in building codes like NFPA 101 or the International Building Code (IBC). Selecting fire resistant glass ensures compliance with fire safety regulations, enhancing occupant protection and structural safety during fire incidents.
Design Flexibility: Aesthetic and Functional Differences
Patterned glass offers extensive design flexibility with its variety of textures and patterns that enhance privacy while allowing creative light diffusion, making it ideal for decorative applications. Fire resistant glass, while primarily engineered for safety, incorporates limited design options because its composition focuses on thermal resistance and integrity during fire exposure. Choosing between the two involves balancing aesthetic appeal against compliance with stringent safety standards and functional requirements in architectural glazing.
Cost Implications: Patterned Glass vs Fire Resistant Glass
Patterned glass generally offers a lower cost alternative compared to fire resistant glass, making it more budget-friendly for decorative safety glazing applications. Fire resistant glass, designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, commands a premium price due to its specialized materials and certification requirements. The higher initial investment in fire resistant glass can be offset by enhanced safety compliance and potential insurance savings in fire-sensitive environments.
Maintenance and Longevity in Safety Glazing
Patterned glass offers easy maintenance with its textured surface concealing minor scratches and dirt, reducing frequent cleaning needs, while fire-resistant glass requires specialized coatings that must be inspected regularly to ensure integrity. Fire-resistant glass demonstrates superior longevity as it withstands high temperatures and harsh conditions without compromising safety performance, whereas patterned glass may degrade faster under extreme environmental stress. Both materials contribute to safety glazing durability, but fire-resistant glass provides enhanced long-term protection and regulatory compliance in fire-prone environments.
Choosing the Right Glazing: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right safety glazing involves evaluating the specific requirements of the space, where patterned glass offers enhanced privacy and decorative appeal, while fire resistant glass prioritizes heat and flame protection through heat-absorbing layers and intumescent materials. Factors such as building codes, exposure to fire hazards, visual clarity demands, and intended use must guide the decision between these glazing types. Durability, thermal performance, and compliance with safety standards like ASTM E119 or EN 13501-2 are critical criteria when selecting patterned versus fire resistant glass.
Infographic: Patterned glass vs Fire resistant glass for Safety glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com