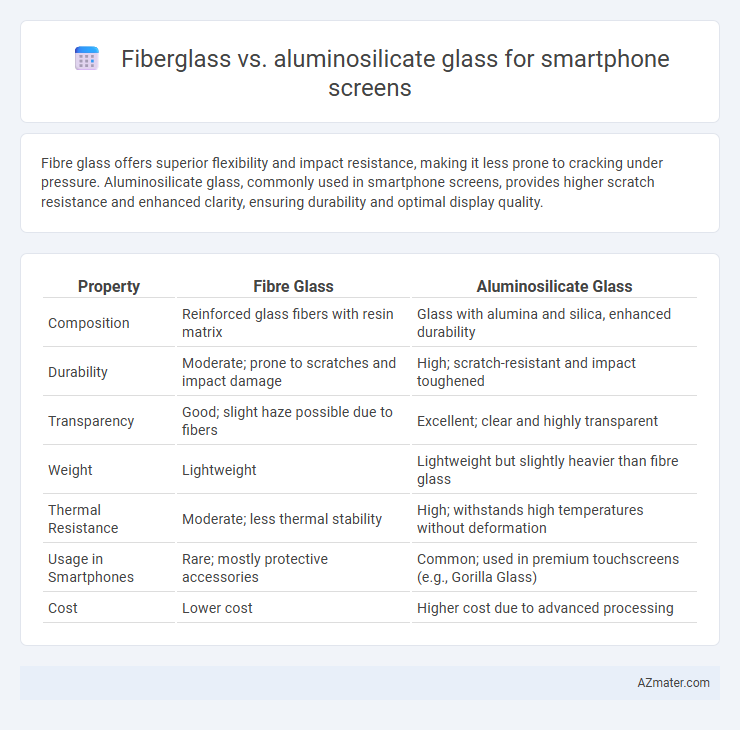
Fibre glass offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it less prone to cracking under pressure. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, provides higher scratch resistance and enhanced clarity, ensuring durability and optimal display quality.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fibre Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Reinforced glass fibers with resin matrix | Glass with alumina and silica, enhanced durability |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to scratches and impact damage | High; scratch-resistant and impact toughened |
| Transparency | Good; slight haze possible due to fibers | Excellent; clear and highly transparent |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but slightly heavier than fibre glass |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; less thermal stability | High; withstands high temperatures without deformation |
| Usage in Smartphones | Rare; mostly protective accessories | Common; used in premium touchscreens (e.g., Gorilla Glass) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Materials
Fibre glass and aluminosilicate glass are prominent materials used in smartphone screen manufacturing due to their distinct properties. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, provides superior durability and impact resistance compared to fibre glass. Fibre glass, while offering flexibility and lightweight characteristics, typically lacks the toughness and clarity found in aluminosilicate formulations like Corning Gorilla Glass utilized in many high-end smartphones.
What is Fibre Glass?
Fiberglass is a composite material made from fine fibers of glass woven into a fabric and bound with resin, offering high strength and flexibility. Unlike aluminosilicate glass used in smartphone screens, fiberglass is more impact-resistant but less transparent and scratch-resistant. It serves primarily in protective cases and structural components rather than direct screen surfaces due to its different optical and hardness properties.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of chemically strengthened glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offering exceptional durability and resistance to scratches, impacts, and thermal stress. Compared to traditional fiberglass, aluminosilicate glass provides superior hardness and clarity, making it ideal for smartphone screens that require thin, lightweight, and highly protective covers. This material's enhanced toughness helps prevent screen cracks and extends device longevity, setting it apart from other glass types in mobile technology applications.
Strength Comparison: Fibre Glass vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Fibre glass offers high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it effective in absorbing shocks, but it generally lacks the hardness required for scratch resistance in smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, specifically engineered for device displays like Corning Gorilla Glass, combines exceptional hardness (typically 6-7 on the Mohs scale) with enhanced toughness, providing superior protection against scratches and drops. The strength balance favors aluminosilicate glass due to its chemically strengthened composition, which outperforms fiber glass in durability and screen longevity.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers superior scratch resistance and high durability due to its chemical composition and ion-exchange strengthening process. Fiberglass, while strong in tensile strength and impact resistance, lacks the hardness required to prevent scratches effectively on smartphone displays. In terms of daily wear and tear, aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced protection against abrasions and cracks, making it the preferred choice for enduring smartphone screen performance.
Impact on Display Clarity and Touch Sensitivity
Fibre glass screens often compromise display clarity due to their lower transparency and higher light diffusion compared to aluminosilicate glass, which offers superior optical clarity and minimal distortion. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in premium smartphones, enhances touch sensitivity through its smooth surface and consistent conductive properties, ensuring precise and responsive interactions. The durable, scratch-resistant nature of aluminosilicate glass also maintains consistent touch performance over time, whereas fibre glass may degrade sensitivity and visual experience faster under frequent use.
Flexibility and Thickness Potential
Fibre glass offers superior flexibility compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it more resistant to bending and impact damage in smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass typically provides higher hardness and scratch resistance but at the cost of reduced flexibility and a generally thicker profile. The potential for ultra-thin smartphone screens is greater with fibre glass, as its flexible nature allows for thinner layers without sacrificing durability.
Cost and Manufacturing Challenges
Fiberglass offers cost advantages due to lower raw material and production expenses compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it attractive for budget smartphone screens. However, fiberglass faces manufacturing challenges such as lower scratch resistance and difficulties achieving the necessary thinness and clarity required in display technology. Aluminosilicate glass, although more expensive, provides superior durability and optical clarity but demands complex manufacturing processes like ion-exchange strengthening, increasing production costs and limiting scalability.
Environmental and Recycling Considerations
Fibre glass used in smartphone screens often contains resin and synthetic components, making recycling complex and less eco-friendly due to challenging separation processes. Aluminosilicate glass, like Gorilla Glass, offers enhanced durability and higher recyclability through established silica-based glass recycling methods, reducing environmental impact. The lower energy requirement for recycling aluminosilicate glass contributes to a more sustainable lifecycle compared to fibre glass, which generates more waste and emissions during disposal.
Which Glass is Best for Smartphones?
Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphones, offers superior scratch resistance, higher strength, and better clarity compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for touchscreen durability and visual performance. Fiberglass lacks the hardness and optical quality required for high-resolution displays and typically acts more as a reinforcement material rather than a primary protective screen. Considering impact resistance, screen sensitivity, and damage prevention, aluminosilicate glass remains the preferred choice for modern smartphone screens.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com