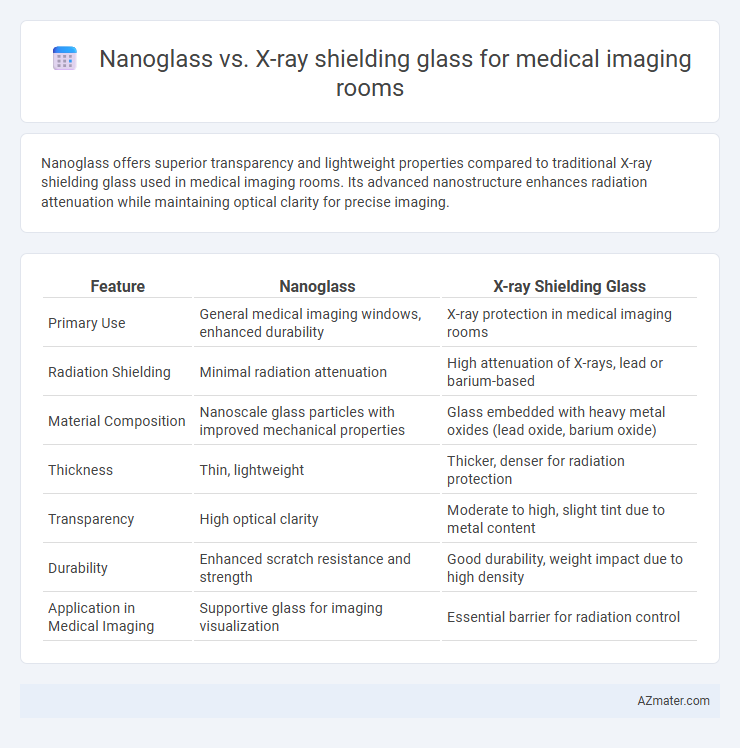
Nanoglass offers superior transparency and lightweight properties compared to traditional X-ray shielding glass used in medical imaging rooms. Its advanced nanostructure enhances radiation attenuation while maintaining optical clarity for precise imaging.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanoglass | X-ray Shielding Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General medical imaging windows, enhanced durability | X-ray protection in medical imaging rooms |
| Radiation Shielding | Minimal radiation attenuation | High attenuation of X-rays, lead or barium-based |
| Material Composition | Nanoscale glass particles with improved mechanical properties | Glass embedded with heavy metal oxides (lead oxide, barium oxide) |
| Thickness | Thin, lightweight | Thicker, denser for radiation protection |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Moderate to high, slight tint due to metal content |
| Durability | Enhanced scratch resistance and strength | Good durability, weight impact due to high density |
| Application in Medical Imaging | Supportive glass for imaging visualization | Essential barrier for radiation control |
Introduction to Glass Types in Medical Imaging Rooms
Nanoglass and X-ray shielding glass serve crucial roles in medical imaging rooms by balancing visibility and radiation protection. Nanoglass features embedded nanoparticles that enhance transparency while maintaining effective radiation attenuation, making it suitable for control windows and observation areas. X-ray shielding glass typically incorporates heavy metal oxides like lead or barium, providing high-density barriers that reduce scatter and protect staff from ionizing radiation exposure.
Defining Nanoglass: Composition and Properties
Nanoglass used in medical imaging rooms is an advanced composite material composed primarily of silica nanoparticles embedded in a polymer matrix, offering exceptional clarity and lightweight properties. Its unique nano-scale structure enhances radiation attenuation while maintaining superior transparency compared to traditional X-ray shielding glass. The high atomic number nanomaterials within nanoglass contribute to efficient X-ray absorption, making it an innovative solution for radiation protection in healthcare environments.
Understanding X-Ray Shielding Glass
X-ray shielding glass is engineered with high-density materials like lead oxide or barium oxide to effectively absorb and block harmful ionizing radiation in medical imaging rooms. Nanoglass, featuring nanotechnology-enhanced composites, offers improved clarity and reduced thickness while maintaining comparable radiation attenuation properties. Choosing between nanoglass and traditional X-ray shielding glass depends on balancing visual transparency, radiation protection standards, and installation requirements specific to medical environments.
Key Differences Between Nanoglass and X-Ray Shielding Glass
Nanoglass offers superior transparency and lighter weight compared to traditional X-ray shielding glass, enhancing visibility and reducing structural load in medical imaging rooms. X-ray shielding glass contains metal oxides or lead compounds that provide high-density radiation protection, while nanoglass utilizes nanotechnology to achieve comparable shielding with thinner, more durable layers. The key differences lie in nanoglass's advanced material composition enabling enhanced optical clarity and environmental safety, versus the conventional glass's heavier, less eco-friendly properties.
Radiation Protection Efficiency: Nanoglass vs X-Ray Shielding Glass
Nanoglass offers superior radiation protection efficiency compared to traditional X-ray shielding glass due to its advanced nanocomposite structure that enhances X-ray absorption while maintaining optical clarity. While conventional X-ray shielding glass relies heavily on lead content, nanoglass integrates nano-sized particles to achieve equivalent or better attenuation at reduced thickness and weight. This results in more effective protection against ionizing radiation in medical imaging rooms, optimizing safety without compromising visibility.
Optical Clarity and Visual Performance
Nanoglass used in medical imaging rooms offers superior optical clarity with high light transmittance and minimal distortion, ensuring precise visual performance crucial for accurate diagnosis. X-ray shielding glass, while effective in radiation protection, typically exhibits lower transparency due to embedded lead or barium content, which can reduce image sharpness and viewer comfort. Selecting Nanoglass enhances image quality and operational efficiency by providing clearer visuals without compromising safety in medical environments.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Nanoglass offers superior durability for medical imaging rooms due to its resistance to scratches, chemicals, and thermal stress, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-use environments. X-ray shielding glass requires periodic inspections for lead content integrity and can be more susceptible to damage from impacts or surface wear, increasing maintenance demands. Choosing Nanoglass reduces maintenance frequency and costs while maintaining consistent radiation protection, making it ideal for long-term healthcare applications.
Installation and Cost Considerations
Nanoglass offers easier installation due to its lightweight and thinner profile, reducing structural support requirements compared to traditional X-ray shielding glass, which is typically heavier and thicker. Cost considerations favor Nanoglass as it often requires less framing and labor, though initial material expenses can be higher. X-ray shielding glass may have a lower upfront price but increased installation complexity and time, potentially raising the total project cost.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Nanoglass offers superior radiation attenuation properties that meet stringent safety standards such as ANSI N43.3 and IEC 61331 for X-ray shielding in medical imaging rooms, ensuring regulatory compliance and enhanced patient and staff protection. X-ray shielding glass, while effective, may require increased thickness or lead content to achieve comparable radiation protection, potentially impacting room design and environmental sustainability. Compliance with FDA and NRC guidelines is critical for both materials, but Nanoglass's advanced composition often allows for lighter, more ergonomic solutions without compromising certified radiation shielding efficacy.
Choosing the Right Glass for Medical Imaging Applications
Nanoglass offers superior clarity and enhanced radiation shielding properties compared to traditional X-ray shielding glass, making it ideal for medical imaging rooms where image quality and patient safety are paramount. Its advanced nanomaterial composition ensures optimal protection against harmful radiation while maintaining excellent transparency for clear diagnostic imaging. Choosing Nanoglass improves operational efficiency and safety in medical environments by combining high radiation attenuation with durable, lightweight construction.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs X-ray shielding glass for Medical imaging room
 azmater.com
azmater.com