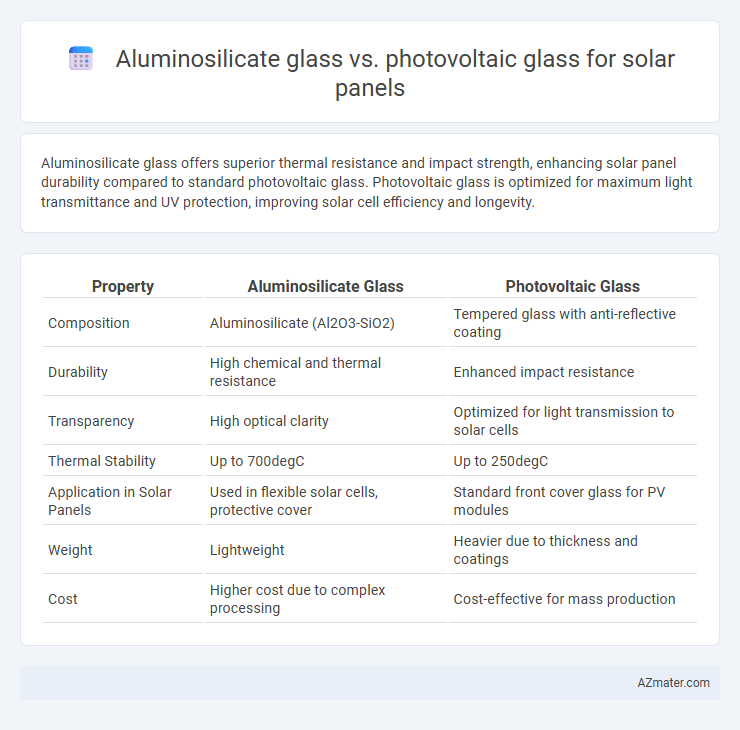
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and impact strength, enhancing solar panel durability compared to standard photovoltaic glass. Photovoltaic glass is optimized for maximum light transmittance and UV protection, improving solar cell efficiency and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Photovoltaic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate (Al2O3-SiO2) | Tempered glass with anti-reflective coating |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal resistance | Enhanced impact resistance |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Optimized for light transmission to solar cells |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 700degC | Up to 250degC |
| Application in Solar Panels | Used in flexible solar cells, protective cover | Standard front cover glass for PV modules |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to thickness and coatings |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex processing | Cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction to Solar Panel Glass Types
Aluminosilicate glass offers high mechanical strength and excellent thermal resistance, making it ideal for protecting solar cells in harsh environmental conditions. Photovoltaic glass, specifically designed for solar panels, provides superior light transmittance and durability to maximize energy conversion efficiency. The choice between aluminosilicate and photovoltaic glass depends on balancing toughness, optical clarity, and cost-effectiveness for optimal solar panel performance.
Overview of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass is a high-strength, chemically durable material widely used in solar panel applications due to its excellent thermal stability and resistance to mechanical stress. Compared to standard photovoltaic glass, aluminosilicate glass offers superior protection against environmental factors such as UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and humidity, enhancing the longevity and performance of solar panels. Its low thermal expansion coefficient reduces the risk of cracking under temperature fluctuations, making it an ideal choice for high-efficiency photovoltaic systems.
Overview of Photovoltaic Glass
Photovoltaic glass, designed specifically for solar panels, features high transparency and excellent light transmission to maximize energy conversion efficiency. Unlike standard aluminosilicate glass, photovoltaic glass incorporates anti-reflective coatings and enhanced durability to withstand environmental stress and reduce light loss. This specialized glass ensures optimal performance and longevity of solar modules in various climatic conditions.
Key Material Composition Differences
Aluminosilicate glass primarily consists of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and silicon dioxide (SiO2), offering high thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for protecting delicate photovoltaic cells. Photovoltaic glass, often tempered soda-lime glass with anti-reflective coatings, contains higher sodium oxide (Na2O) content to enhance transparency and light transmission crucial for solar efficiency. The key distinction lies in aluminosilicate glass's increased alumina content for robustness versus photovoltaic glass's optimized silica and soda lime composition tailored for maximum solar energy absorption.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits higher mechanical strength and improved resistance to impact and thermal shock compared to photovoltaic glass, making it more suitable for harsh environmental conditions. Its enhanced durability ensures prolonged lifespan and reduced risk of crack formation under mechanical stress, essential for maintaining solar panel efficiency. In contrast, standard photovoltaic glass offers adequate protection but generally has lower mechanical robustness and may degrade faster when exposed to extreme weather.
Optical Properties and Light Transmission Efficiency
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits high optical clarity and superior durability, enabling excellent light transmission efficiency crucial for solar panels. Photovoltaic glass, specifically engineered with anti-reflective coatings and controlled light absorption, optimizes the propagation of sunlight to photovoltaic cells, enhancing energy conversion rates. The balance of minimal light loss and robust environmental resistance in both glass types significantly influences overall solar panel performance.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior weather resistance due to its high chemical durability and excellent thermal stability, making it less prone to corrosion and degradation from prolonged sun exposure and harsh weather conditions. Photovoltaic glass, specifically engineered for solar panels, balances transmittance with durability but may be more susceptible to micro-cracks and potential aging effects under extreme environmental stress. The longevity of aluminosilicate glass typically exceeds that of standard photovoltaic glass, supporting more reliable long-term performance in solar panel applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Aluminosilicate glass offers enhanced durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it a cost-effective choice for solar panels in harsh environments due to its longer lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses. Photovoltaic glass, specifically designed for high light transmittance and energy efficiency, generally entails higher upfront costs but can improve solar panel performance and yield greater long-term energy savings. The economic impact of choosing aluminosilicate over photovoltaic glass depends on project scale, environmental conditions, and expected energy output, with aluminosilicate potentially lowering initial investment while photovoltaic glass maximizes energy revenue.
Performance in Real-World Applications
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits excellent mechanical strength and resistance to thermal stress, making it highly durable in harsh environmental conditions for solar panels. Photovoltaic glass, designed with enhanced light transmittance and anti-reflective coatings, maximizes solar energy absorption and improves overall panel efficiency in real-world applications. Performance-wise, aluminosilicate glass offers superior protection and longevity, while photovoltaic glass optimizes energy yield through better optical properties.
Choosing the Right Glass for Solar Panels
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for solar panels exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Photovoltaic glass, designed with high light transmittance and anti-reflective coatings, enhances solar cell efficiency and energy output. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing durability needs against optical performance to maximize solar panel longevity and power generation.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Photovoltaic glass for Solar panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com