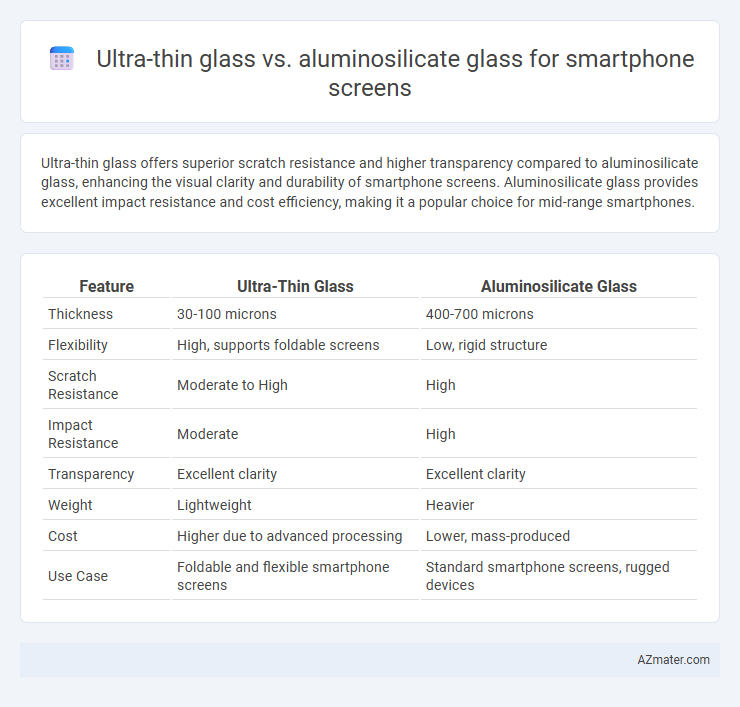
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher transparency compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing the visual clarity and durability of smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass provides excellent impact resistance and cost efficiency, making it a popular choice for mid-range smartphones.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Thin Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 30-100 microns | 400-700 microns |
| Flexibility | High, supports foldable screens | Low, rigid structure |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate to High | High |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Transparency | Excellent clarity | Excellent clarity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced processing | Lower, mass-produced |
| Use Case | Foldable and flexible smartphone screens | Standard smartphone screens, rugged devices |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Materials
Smartphone screens commonly use ultra-thin glass and aluminosilicate glass, both engineered for durability and clarity. Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced flexibility and scratch resistance, making it ideal for foldable devices and curved displays. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high hardness and impact resistance, is widely adopted in traditional smartphone screens to protect against drops and abrasions.
What is Ultra-thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) is a specially engineered glass material designed for flexible displays in smartphones, typically measuring between 30 to 100 microns in thickness. It offers superior scratch resistance and clarity compared to conventional polymers used in flexible screens, enabling foldable devices to maintain a smooth, durable surface. UTG provides enhanced durability and a premium touch experience while allowing for innovative smartphone designs such as foldable and rollable screens, distinguishing it from the hard, rigid Aluminosilicate glass used in traditional flat displays.
Understanding Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced durability compared to ultra-thin glass, making it ideal for smartphone screens exposed to daily wear and tear. Its chemical composition, rich in aluminum and silicon oxides, provides high thermal stability and impact resistance, ensuring better protection against drops and temperature fluctuations. Manufacturers favor aluminosilicate glass due to its excellent balance of strength and lightweight properties, contributing to slimmer yet robust smartphone designs.
Key Differences in Composition
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) primarily consists of highly purified silica with minimal additives, offering exceptional thinness and flexibility tailored for foldable smartphones. Aluminosilicate glass incorporates aluminum oxide and silicon oxide, enhancing its hardness, chemical durability, and scratch resistance, commonly used in rigid smartphone screens. The fundamental compositional difference lies in UTG's ultra-pure silica base optimized for flexibility versus aluminosilicate's aluminum-enriched matrix designed for rigidity and impact resistance.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced durability compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it highly suitable for modern smartphone screens. Its thinner composition increases flexibility while maintaining hardness, reducing the risk of cracks and abrasions during everyday use. Aluminosilicate glass, though durable, is generally thicker and less resistant to fine scratches, which can affect long-term screen clarity and device longevity.
Flexibility and Bendability
Ultra-thin glass exhibits superior flexibility and bendability compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it highly suitable for foldable smartphone screens and devices requiring curved designs. Its molecular structure allows for greater elasticity without compromising durability, whereas aluminosilicate glass, while strong and scratch-resistant, tends to be more rigid and prone to cracking under stress. This enhanced pliability of ultra-thin glass supports advanced smartphone innovations in seamless and flexible displays.
Impact on Display Quality
Ultra-thin glass offers superior optical clarity and enhanced touch sensitivity, resulting in vibrant color reproduction and sharper image resolution compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and scratch-resistant, may slightly reduce display brightness and color accuracy due to its thicker composition and coating variations. The improved light transmission properties of ultra-thin glass contribute to a more immersive and responsive visual experience on smartphone screens.
Production Costs and Scalability
Ultra-thin glass offers lower production costs due to its compatibility with existing OLED manufacturing lines, enabling easier integration and higher scalability in smartphone screen production. Aluminosilicate glass requires more intensive chemical strengthening processes and specialized equipment, leading to higher overall costs and challenges in scaling for mass production. The cost efficiency and scalability of ultra-thin glass make it a preferred choice for high-volume smartphone displays.
Current Smartphone Applications
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) is predominantly used in flagship foldable smartphones due to its exceptional flexibility and scratch resistance, offering a smooth, durable surface that enhances touch sensitivity and visual clarity. Aluminosilicate glass like Corning Gorilla Glass remains the industry standard for most non-foldable smartphones, providing hardened protection against drops and scratches through its chemically strengthened composition. Current smartphone designs often combine UTG for foldable displays with aluminosilicate glass for rigid areas, optimizing durability and user experience across multiple device models.
Future Trends in Smartphone Glass Technology
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and enhanced scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass, driving its adoption in foldable and wearable smartphones. Advances in chemical strengthening and coating technologies are expected to further improve ultra-thin glass durability and optical clarity. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid glass-polymer composites that combine the robustness of aluminosilicate and the sleekness of ultra-thin glass for next-generation smartphone displays.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com