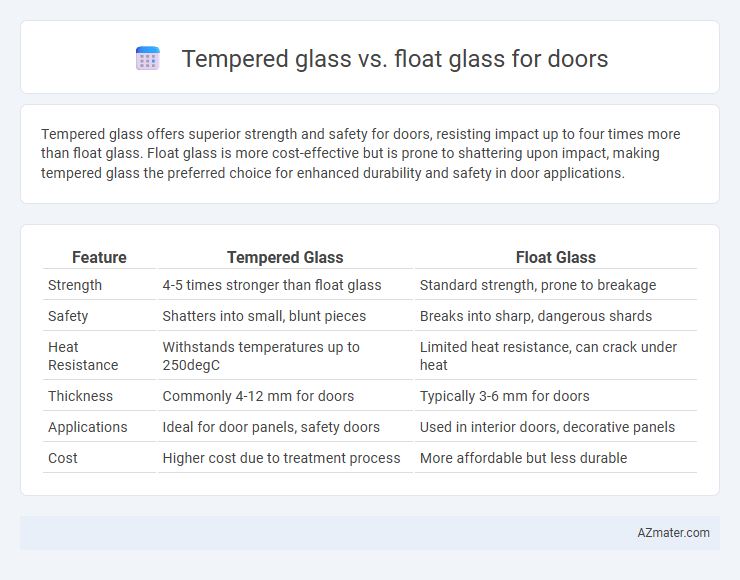
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for doors, resisting impact up to four times more than float glass. Float glass is more cost-effective but is prone to shattering upon impact, making tempered glass the preferred choice for enhanced durability and safety in door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than float glass | Standard strength, prone to breakage |
| Safety | Shatters into small, blunt pieces | Breaks into sharp, dangerous shards |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 250degC | Limited heat resistance, can crack under heat |
| Thickness | Commonly 4-12 mm for doors | Typically 3-6 mm for doors |
| Applications | Ideal for door panels, safety doors | Used in interior doors, decorative panels |
| Cost | Higher cost due to treatment process | More affordable but less durable |
Introduction to Glass Types for Doors
Tempered glass for doors offers enhanced strength and safety by undergoing a heat treatment process that increases its resistance to impact and thermal stress, making it less likely to shatter into sharp fragments. Float glass, commonly used for standard door panels, is produced by floating molten glass on molten metal, resulting in a smooth and uniform surface but with lower durability compared to tempered glass. Choosing between tempered and float glass depends on the required safety standards and performance characteristics for door applications.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to float glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces instead of sharp shards, reducing injury risk in door applications. This glass type offers enhanced durability, heat resistance, and impact strength, making it ideal for doors in residential and commercial buildings.
What is Float Glass?
Float glass is a type of flat glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten tin, resulting in uniform thickness and a smooth surface ideal for windows and doors. Unlike tempered glass, float glass is annealed, making it more prone to breaking into sharp shards rather than safe blunt fragments. Its clarity and cost-effectiveness make float glass a common choice for door panels where safety requirements are minimal.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength compared to float glass, as it is heat-treated to withstand impacts up to four to five times greater, making it ideal for door applications requiring enhanced safety. Its durability is significantly higher due to its resistance to thermal stress and scratches, preventing breakage under heavy use or temperature fluctuations. Float glass, while clearer and more cost-effective, lacks the robust structural integrity of tempered glass, making it less suitable for high-traffic or impact-prone door environments.
Safety Features of Tempered vs Float Glass
Tempered glass offers superior safety features compared to float glass due to its ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, minimizing injury risks in door applications. The heat-treatment process increases tempered glass strength to approximately four times that of float glass, making it more resistant to impact and thermal stress. Float glass, being untreated, is more prone to breakage and produces dangerous, sharp fragments, which poses a higher safety hazard in door installations.
Design and Aesthetic Differences
Tempered glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with enhanced clarity and a smooth, polished surface that complements contemporary door designs. Float glass, known for its uniform thickness and flatness, provides a classic, clear look but lacks the subtle brilliance and strength of tempered glass. The design advantage of tempered glass lies in its ability to withstand stress, allowing for larger, frameless door panels that enhance visual appeal and maximize natural light.
Cost Analysis: Tempered vs Float Glass
Tempered glass typically costs 2 to 3 times more than float glass due to its heat treatment process, enhancing strength and safety for door applications. Float glass is more affordable but lacks the durability and impact resistance required for high-traffic or safety-critical doors. The higher upfront investment in tempered glass often results in reduced replacement costs and enhanced safety, making it cost-effective over the door's lifecycle.
Installation Considerations
Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and safety, making it a preferred choice for door installations requiring higher impact resistance and compliance with building codes, but it demands precise cutting and handling before tempering to avoid defects. Float glass, being more fragile and prone to breakage, allows for easier cutting and customization during installation but requires additional treatments for safety and durability when used in doors. Proper framing and support are essential for tempered glass doors to accommodate thermal expansion, whereas float glass doors need careful sealing and protection to prevent breakage and weather damage.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tempered glass offers superior durability and resistance to scratches and impacts compared to float glass, making it easier to maintain and less prone to breakage over time for doors. Float glass, while more affordable, is more susceptible to scratches and can shatter easily, resulting in higher maintenance costs and shorter lifespan. Choosing tempered glass enhances door longevity by providing better structural integrity and reducing the frequency of repairs or replacements.
Which Glass is Best for Your Door?
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for doors due to its heat-treated process, making it resistant to impact and shattering into small, less harmful pieces. Float glass, while more affordable and clear, is more prone to breakage and lacks the durability required for high-traffic or exterior door applications. For optimal safety and longevity, tempered glass is the best choice for door installations.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Float glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com