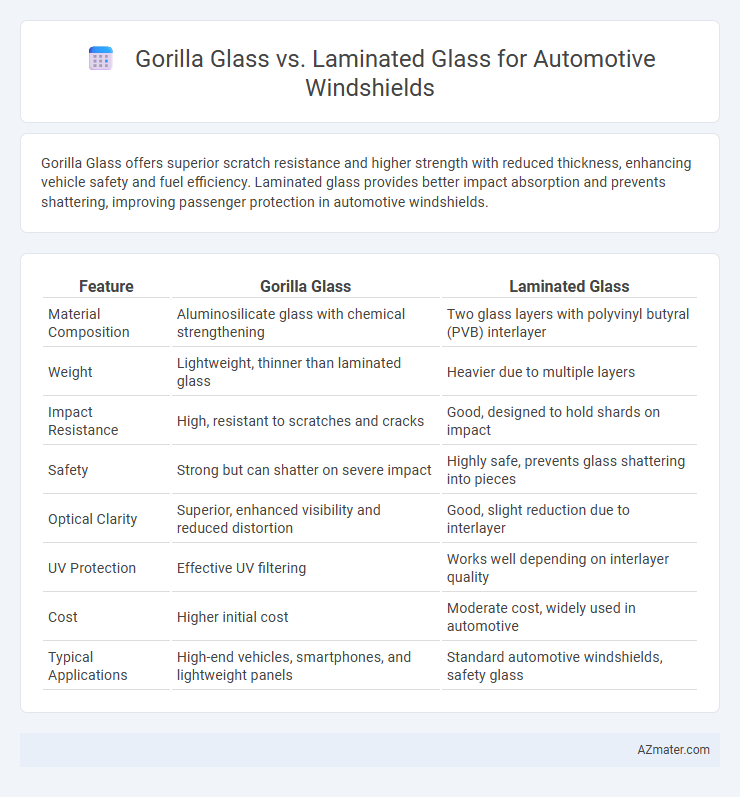
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher strength with reduced thickness, enhancing vehicle safety and fuel efficiency. Laminated glass provides better impact absorption and prevents shattering, improving passenger protection in automotive windshields.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gorilla Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate glass with chemical strengthening | Two glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Weight | Lightweight, thinner than laminated glass | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Impact Resistance | High, resistant to scratches and cracks | Good, designed to hold shards on impact |
| Safety | Strong but can shatter on severe impact | Highly safe, prevents glass shattering into pieces |
| Optical Clarity | Superior, enhanced visibility and reduced distortion | Good, slight reduction due to interlayer |
| UV Protection | Effective UV filtering | Works well depending on interlayer quality |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Moderate cost, widely used in automotive |
| Typical Applications | High-end vehicles, smartphones, and lightweight panels | Standard automotive windshields, safety glass |
Introduction to Automotive Windshield Materials
Automotive windshields primarily use laminated glass, consisting of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Gorilla Glass, a chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass, offers superior scratch resistance and reduced weight, making it an emerging alternative for next-generation automotive windshields. The choice between laminated glass and Gorilla Glass impacts vehicle durability, weight reduction, and passenger protection.
What is Gorilla Glass?
Gorilla Glass is an advanced chemically strengthened glass developed by Corning, designed for high durability and scratch resistance in automotive windshields. It offers superior impact resistance and lighter weight compared to traditional laminated glass, enhancing vehicle safety and fuel efficiency. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers including a plastic interlayer for shatter protection, Gorilla Glass is a single, ultra-thin sheet engineered to withstand significant stress without cracking.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and impact resistance. In automotive windshields, laminated glass prevents shattering upon impact by holding the fragments in place, reducing the risk of injury and maintaining structural integrity. Compared to Gorilla Glass, laminated glass offers superior resistance to penetration and maintains visibility even after minor damages, making it the industry standard for vehicle windshields.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher tensile strength compared to laminated glass, making it more durable against impacts and everyday wear in automotive windshields. Laminated glass, consisting of two glass layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, excels in shatter resistance by preventing glass fragments from dispersing upon impact, enhancing safety. While Gorilla Glass provides enhanced lightweight strength, laminated glass remains the preferred choice for its proven ability to maintain structural integrity under severe crash conditions.
Weight Differences: Impact on Vehicle Performance
Gorilla Glass weighs significantly less than laminated glass, reducing the overall vehicle weight by up to 30%. This weight reduction enhances fuel efficiency and improves acceleration and handling due to lower inertia. The lightweight nature of Gorilla Glass also contributes to better suspension performance and reduced carbon emissions in automotive applications.
Safety Features and Crash Protection
Gorilla Glass offers enhanced impact resistance and scratch durability, reducing the likelihood of windshield shattering during collisions, thereby improving occupant safety. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior fragmentation control by holding shards together upon impact to prevent ejection and injury. Both materials contribute to crash protection, but laminated glass remains the automotive industry standard for windshield safety due to its proven ability to maintain structural integrity and reduce occupant ejection during accidents.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to laminated glass due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it highly durable against everyday abrasions. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, excels in impact resistance by absorbing and distributing force to prevent shattering. While laminated glass provides excellent safety features by holding fragments together upon impact, Gorilla Glass balances scratch resistance with significant impact resilience, ideal for modern automotive windshields seeking both durability and safety.
Cost Analysis: Gorilla Glass vs Laminated Glass
Gorilla Glass offers higher durability and scratch resistance for automotive windshields but generally comes at a significantly higher cost compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass remains the industry standard due to its lower manufacturing expenses and effective impact absorption, resulting in a more budget-friendly replacement and repair process. Cost analysis reveals laminated glass as the more economical choice for mass-market vehicles, while Gorilla Glass suits premium models prioritizing longevity and weight reduction.
Industry Adoption and Real-World Applications
Gorilla Glass has seen growing adoption in automotive windshields by leading manufacturers due to its superior scratch resistance, lightweight properties, and enhanced safety features compared to traditional laminated glass. Laminated glass, consisting of multiple layers of glass and plastic interlayers, remains the industry standard for impact resistance and shatter protection, especially in heavy-duty vehicles and crash-prone environments. Real-world applications demonstrate Gorilla Glass's increasing use in electric and autonomous vehicles seeking weight reduction and durability, while laminated glass continues to dominate in cost-sensitive and regulatory-driven markets.
Choosing the Best Windshield Material for Your Car
Gorilla Glass offers exceptional scratch resistance, lightweight properties, and enhanced durability, making it a superior choice for automotive windshields aiming for improved fuel efficiency and safety. Laminated glass, commonly used in vehicles, provides excellent impact absorption and retains shards upon breakage, ensuring passenger protection during collisions. Selecting the best windshield material depends on prioritizing strength, weight reduction, clarity, and safety standards specific to your vehicle's design and driving conditions.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Laminated glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com