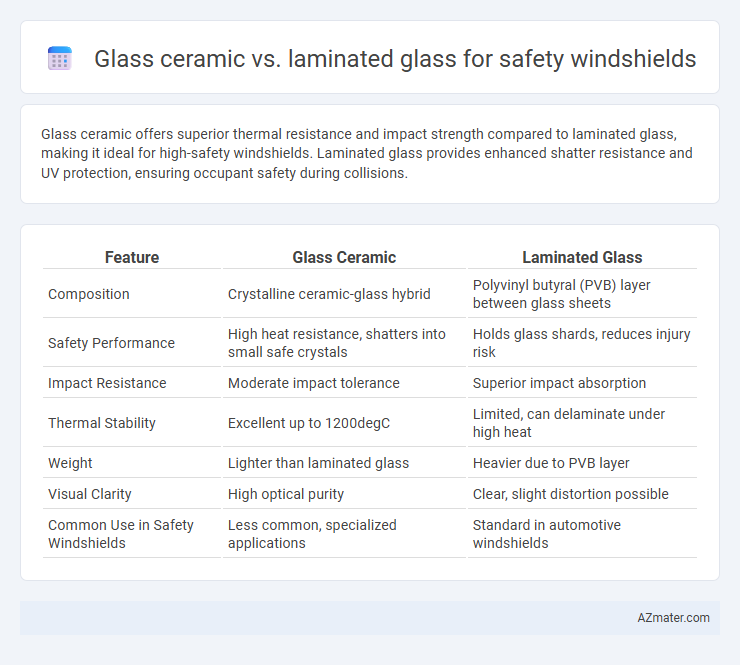
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal resistance and impact strength compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for high-safety windshields. Laminated glass provides enhanced shatter resistance and UV protection, ensuring occupant safety during collisions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Ceramic | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Crystalline ceramic-glass hybrid | Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer between glass sheets |
| Safety Performance | High heat resistance, shatters into small safe crystals | Holds glass shards, reduces injury risk |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact tolerance | Superior impact absorption |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent up to 1200degC | Limited, can delaminate under high heat |
| Weight | Lighter than laminated glass | Heavier due to PVB layer |
| Visual Clarity | High optical purity | Clear, slight distortion possible |
| Common Use in Safety Windshields | Less common, specialized applications | Standard in automotive windshields |
Introduction to Safety Windshields
Safety windshields primarily use laminated glass due to its superior impact resistance and shatter-retention properties that prevent injury during collisions. Glass ceramic, while offering high thermal stability and scratch resistance, is less commonly used in windshields because it lacks the flexible interlayer crucial for holding fragments together upon impact. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by a plastic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), ensuring enhanced safety by maintaining windshield integrity and protecting occupants during accidents.
Overview of Glass Ceramic Technology
Glass ceramic technology utilizes a unique process that crystallizes glass into a durable, fracture-resistant material with exceptional thermal stability and impact resistance, making it ideal for safety windshields. Unlike laminated glass, which relies on layers of glass and polymer interlayers to prevent shattering, glass ceramic offers superior structural integrity and enhanced optical clarity while maintaining lightweight properties. Its advanced composition enables better resistance to thermal stress and mechanical impacts, providing improved safety performance in automotive applications.
What Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together by an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon impact. Unlike glass ceramic, laminated glass is designed to hold fragments in place, significantly improving safety in windshield applications by reducing the risk of injury from broken glass. Its ability to absorb energy and maintain structural integrity makes laminated glass the preferred choice for automotive safety windshields.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Glass ceramic offers superior strength and higher thermal stability compared to laminated glass, making it more resistant to cracking under stress or temperature changes. Laminated glass comprises multiple layers of glass and PVB interlayers, which excel in impact resistance by holding shards together upon breakage, enhancing occupant safety. The choice between glass ceramic and laminated glass for safety windshields depends on balancing the need for structural integrity and effective impact absorption in automotive applications.
UV Protection and Heat Tolerance
Glass ceramic windshields offer superior UV protection and enhanced heat tolerance due to their crystalline structure, which effectively blocks harmful ultraviolet rays and withstands high temperature fluctuations without deformation. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides moderate UV filtering and heat resistance but is more prone to heat-induced stress and damage compared to glass ceramics. For safety windshields requiring maximum UV shielding and thermal durability, glass ceramic technology outperforms laminated glass in maintaining structural integrity and occupant protection under extreme environmental conditions.
Durability and Lifespan of Windshield Materials
Glass ceramic windshields offer exceptional durability due to their high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, resulting in a longer lifespan compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, composed of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, provides effective impact resistance and prevents shattering but is more prone to delamination and edge damage over time. For safety windshields, glass ceramic materials maintain optical clarity and structural integrity longer, making them preferable for environments demanding extended durability.
Safety Performance: Accidents and Shattering
Glass ceramic windshields exhibit superior resistance to shattering due to their high thermal stability and fracture toughness, enhancing occupant protection during collisions. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers fused with a plastic interlayer, prevents dangerous shards by holding broken pieces together, reducing injury risk in accidents. Both materials improve safety performance, but glass ceramic offers enhanced durability against impact and thermal stress, lowering the likelihood of windshield failure under extreme conditions.
Cost Analysis: Glass Ceramic vs Laminated Glass
Glass ceramic windshields typically incur higher upfront costs compared to laminated glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and enhanced thermal resistance features. Laminated glass remains more cost-effective with widespread availability and simpler production, offering a balance of safety and affordability for standard windshields. Maintenance and replacement expenses also favor laminated glass, as glass ceramic repairs often require specialized service and materials, increasing overall lifecycle costs.
Installation and Repair Considerations
Glass ceramic windshields require specialized installation techniques due to their unique thermal properties and precise fit requirements, making repairs more complex and often necessitating full panel replacement. Laminated glass windshields offer easier installation with more common tools and repair methods like resin injection, which can fix minor chips without full replacement. Repair costs for laminated glass tend to be lower and faster compared to glass ceramic, but laminated glass is more prone to delamination over time.
Choosing the Best Windshield for Your Vehicle
Glass ceramic windshields offer exceptional thermal resistance and durability, making them highly effective in withstanding extreme temperature changes and impact forces. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), excels in preventing shattering and maintaining windshield integrity during collisions. Choosing the best windshield depends on prioritizing impact resistance and safety performance, with laminated glass widely preferred for its superior ability to protect passengers by reducing the risk of injury from glass shards.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Laminated glass for Safety windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com