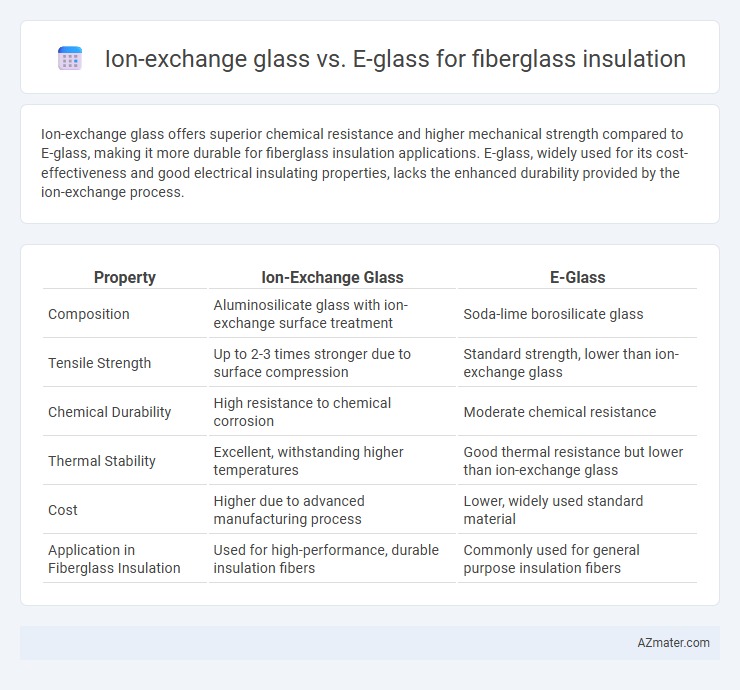
Ion-exchange glass offers superior chemical resistance and higher mechanical strength compared to E-glass, making it more durable for fiberglass insulation applications. E-glass, widely used for its cost-effectiveness and good electrical insulating properties, lacks the enhanced durability provided by the ion-exchange process.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate glass with ion-exchange surface treatment | Soda-lime borosilicate glass |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 2-3 times stronger due to surface compression | Standard strength, lower than ion-exchange glass |
| Chemical Durability | High resistance to chemical corrosion | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, withstanding higher temperatures | Good thermal resistance but lower than ion-exchange glass |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing process | Lower, widely used standard material |
| Application in Fiberglass Insulation | Used for high-performance, durable insulation fibers | Commonly used for general purpose insulation fibers |
Introduction to Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation primarily utilizes E-glass due to its high tensile strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, ensuring durable and efficient thermal performance. Ion-exchange glass, featuring enhanced chemical durability and ion-exchange strengthened surfaces, offers improved mechanical properties but remains less common in standard insulation applications. The choice between ion-exchange glass and E-glass impacts factors such as thermal conductivity, environmental resistance, and overall insulation lifespan in building construction.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a type of glass enhanced through a chemical process that replaces smaller ions in the glass with larger ones to improve strength and durability, making it highly resistant to mechanical stress and thermal shock. In fiberglass insulation, ion-exchange glass fibers offer superior corrosion resistance and long-term performance compared to traditional E-glass, which is primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate fibers with good electrical insulation properties. The ion-exchange treatment enhances the physical properties of glass fibers, leading to better structural integrity and increased lifespan for insulation applications.
What is E-Glass?
E-Glass, or electrical glass, is a type of fiberglass known for its excellent insulating properties and high tensile strength, commonly used in fiberglass insulation and composites. Unlike Ion-exchange glass, E-Glass is produced primarily from alumino-borosilicate materials, offering superior electrical insulation and resistance to chemical corrosion. This makes E-Glass particularly suitable for thermal insulation, electrical applications, and reinforcement in construction and automotive industries.
Chemical Composition Differences
Ion-exchange glass used in fiberglass insulation features a unique chemical composition where sodium ions in the glass matrix are replaced with larger potassium ions, enhancing chemical durability and thermal stability. E-glass, primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate with high silica content and low alkali levels, offers a well-balanced mix of mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties. The distinct ion-exchange process in ion-exchange glass imparts improved resistance to chemical attack compared to the correspondingly stable but less chemically durable E-glass formulation.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ion-exchange glass used in fiberglass insulation exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to traditional E-glass due to its enhanced ion-exchange process that creates a compressive surface layer. This improved strength translates to better resistance against mechanical stresses such as impact, bending, and tensile forces, making ion-exchange glass fibers more durable in demanding insulation applications. As a result, fiberglass products utilizing ion-exchange glass provide superior structural integrity and longevity compared to those made with conventional E-glass.
Thermal Performance and Insulation Efficiency
Ion-exchange glass fibers demonstrate superior thermal performance compared to E-glass due to their enhanced chemical durability and lower thermal conductivity, which contributes to better insulation efficiency in fiberglass applications. The ion-exchange process strengthens the glass matrix, reducing heat transfer and increasing resistance to thermal degradation under high temperatures. As a result, fiberglass insulation made with ion-exchange glass offers improved energy savings and prolonged material lifespan in both residential and industrial settings.
Durability and Lifespan
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and a longer lifespan than E-glass due to its improved chemical resistance and surface strength. The ion-exchange process strengthens the glass fibers, making Ion-exchange glass less prone to moisture degradation and mechanical wear in fiberglass insulation applications. This results in more sustained thermal performance and structural integrity over extended periods compared to standard E-glass insulation.
Cost Analysis: Ion-Exchange Glass vs E-Glass
Ion-exchange glass typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to its enhanced surface properties and increased durability, resulting in elevated material prices for fiberglass insulation production compared to E-glass. E-glass remains the preferred choice in insulation manufacturing because of its lower raw material and processing costs, enabling more economical bulk production. Cost analysis shows that while ion-exchange glass offers performance benefits, the substantial price premium limits its widespread adoption in cost-sensitive fiberglass insulation markets.
Applications in Building and Industry
Ion-exchange glass fibers offer enhanced chemical durability and higher mechanical strength compared to traditional E-glass, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications such as chemical processing plants and high-performance building facades. E-glass remains the standard choice for general fiberglass insulation due to its cost-effectiveness and balanced thermal and electrical properties, widely used in residential and commercial construction for wall, roof, and HVAC insulation. The superior alkali resistance of ion-exchange glass extends the lifespan of insulation in harsh environments, while E-glass provides reliable performance in typical building applications.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Insulation
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced alkali resistance and improved durability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for long-term fiberglass insulation performance in harsh environments. E-glass remains a cost-effective choice with good mechanical strength and thermal insulation properties suitable for general applications. Selecting between ion-exchange and E-glass depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for enhanced chemical resistance and longevity in specific insulation projects.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs E-glass for Fiberglass insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com