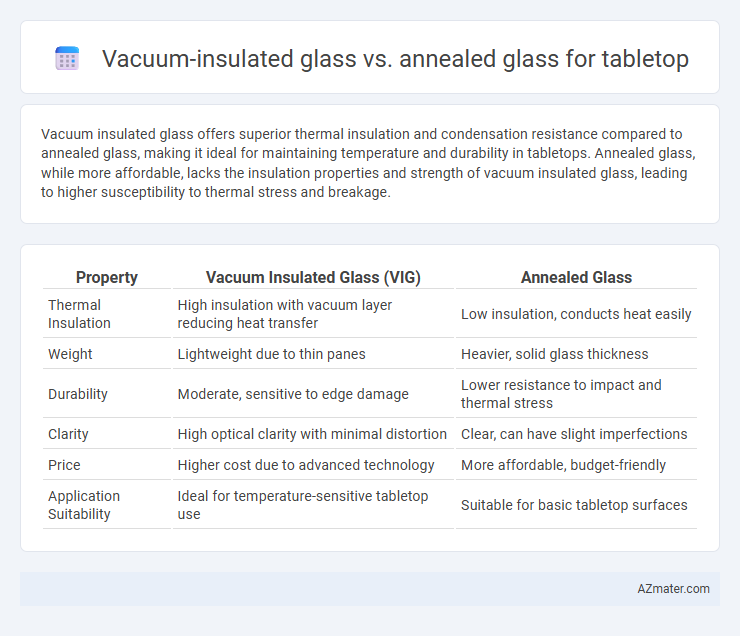
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance compared to annealed glass, making it ideal for maintaining temperature and durability in tabletops. Annealed glass, while more affordable, lacks the insulation properties and strength of vacuum insulated glass, leading to higher susceptibility to thermal stress and breakage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High insulation with vacuum layer reducing heat transfer | Low insulation, conducts heat easily |
| Weight | Lightweight due to thin panes | Heavier, solid glass thickness |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to edge damage | Lower resistance to impact and thermal stress |
| Clarity | High optical clarity with minimal distortion | Clear, can have slight imperfections |
| Price | Higher cost due to advanced technology | More affordable, budget-friendly |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for temperature-sensitive tabletop use | Suitable for basic tabletop surfaces |
Introduction to Glass Types for Tabletops
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) for tabletops features two glass panes separated by a vacuum, providing superior thermal insulation and resistance to condensation compared to traditional annealed glass. Annealed glass, a basic heat-treated glass, offers affordability and clarity but lacks the advanced energy efficiency and durability of vacuum insulated glass. Choosing between VIG and annealed glass involves balancing cost, thermal performance, and longevity for tabletop applications.
What Is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer, drastically reducing heat transfer and enhancing thermal insulation for tabletops. Unlike annealed glass, which is a single, solid pane treated to relieve internal stresses but offers limited insulation, VIG provides superior energy efficiency and resistance to temperature fluctuations. This makes vacuum insulated glass an ideal choice for tabletops requiring both durability and enhanced temperature control.
Understanding Annealed Glass
Annealed glass is a common choice for tabletops due to its clarity and ease of cutting or shaping, though it lacks the thermal insulation properties of vacuum insulated glass. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which features a sealed space between panes to reduce heat transfer, annealed glass provides minimal resistance to temperature changes, making it less effective in maintaining surface temperature. For tabletop applications where temperature insulation is not critical, annealed glass offers a cost-effective and durable solution.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) provides superior thermal insulation compared to annealed glass, significantly reducing heat transfer through its vacuum layer that eliminates conductive and convective heat loss. Annealed glass, lacking enhanced insulating properties, allows higher thermal conductivity, resulting in greater heat exchange and potential surface temperature fluctuations. For tabletops, VIG offers enhanced energy efficiency and temperature stability, making it a better choice for applications requiring thermal performance.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior strength and durability compared to annealed glass for tabletops due to its multi-layer construction and vacuum-sealed design, which minimizes thermal stress and prevents condensation. Annealed glass, while less expensive, is more prone to breakage and scratches as it lacks the enhanced structural integrity provided by vacuum insulation technology. The enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to temperature fluctuations in VIG significantly extend the lifespan of tabletops in both residential and commercial settings.
Safety Features and Risks
Vacuum insulated glass offers enhanced safety for tabletops by incorporating multiple glass layers with a vacuum gap, reducing the risk of shattering and providing superior impact resistance compared to annealed glass. Annealed glass is more prone to breakage and shattering into sharp, hazardous shards, posing a greater risk during accidents and everyday use. Its lack of strength and resistance to thermal stress makes annealed glass less suitable for high-traffic areas, while vacuum insulated glass combines durability with thermal insulation, making it a safer, longer-lasting choice.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass offers a sleek, minimalist aesthetic with its thinner profile and reduced fogging, enhancing clarity and modern design appeal for tabletops. Annealed glass, while more traditional, provides versatility with options for thickness and edge treatments, allowing for customized styles but may show more condensation and surface imperfections. Designers prioritize vacuum insulated glass for high-end, contemporary settings due to its seamless visual appeal and durability against thermal stress.
Cost and Value Assessment
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and durability for tabletops but comes at a higher initial cost compared to annealed glass, which is more affordable but less effective in temperature regulation. The long-term energy savings and enhanced comfort provided by vacuum insulated glass often justify the premium price in high-end or climate-sensitive applications. Annealed glass remains a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious projects where insulation performance is less critical.
Maintenance and Longevity
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability and minimal maintenance compared to annealed glass due to its advanced construction that resists moisture and temperature fluctuations, preventing fogging and condensation. Annealed glass, while more affordable, is more susceptible to scratches, chips, and thermal stress, leading to potential replacement and higher upkeep costs over time. Investing in vacuum insulated glass ensures longer-lasting clarity and structural integrity, reducing the frequency of cleaning and repairs for tabletops.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Tabletop
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance, making it ideal for tabletops exposed to temperature fluctuations or outdoor use. Annealed glass, known for its affordability and ease of cutting, suits indoor tabletops with minimal stress or heavy impact. Selecting the right glass depends on prioritizing thermal performance for outdoor environments or budget-friendly durability for controlled indoor settings.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Annealed glass for Tabletop
 azmater.com
azmater.com