Superhydrophobic glass features a nanocoating that repels water and dirt, enhancing facade self-cleaning and durability. Solar control glass reduces solar heat gain by reflecting infrared radiation, improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort in building facades.
Table of Comparison
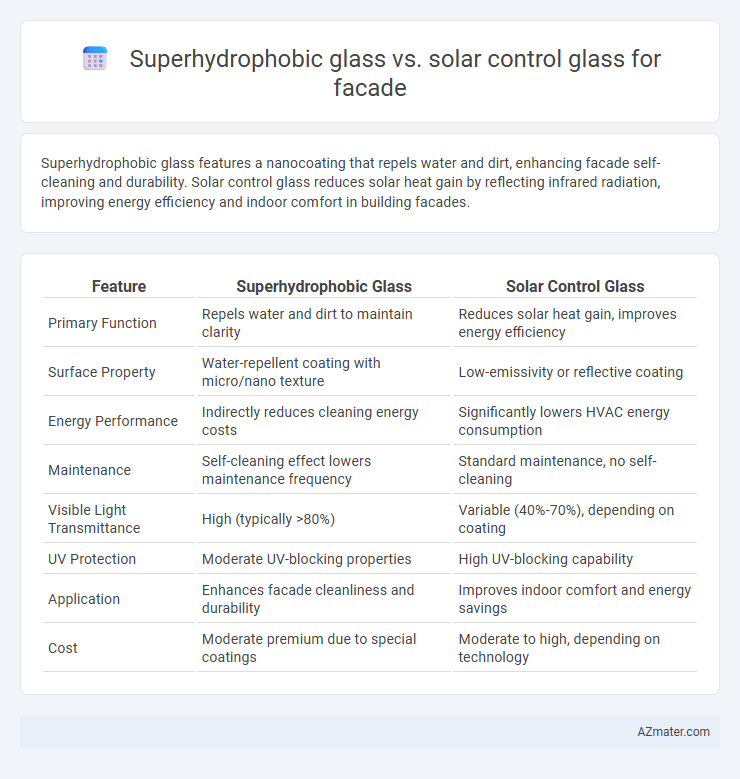
| Feature | Superhydrophobic Glass | Solar Control Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Repels water and dirt to maintain clarity | Reduces solar heat gain, improves energy efficiency |
| Surface Property | Water-repellent coating with micro/nano texture | Low-emissivity or reflective coating |
| Energy Performance | Indirectly reduces cleaning energy costs | Significantly lowers HVAC energy consumption |
| Maintenance | Self-cleaning effect lowers maintenance frequency | Standard maintenance, no self-cleaning |
| Visible Light Transmittance | High (typically >80%) | Variable (40%-70%), depending on coating |
| UV Protection | Moderate UV-blocking properties | High UV-blocking capability |
| Application | Enhances facade cleanliness and durability | Improves indoor comfort and energy savings |
| Cost | Moderate premium due to special coatings | Moderate to high, depending on technology |
Introduction to Advanced Glass Technologies for Facades
Superhydrophobic glass features nanostructured surfaces that repel water and dirt, enhancing facade self-cleaning and reducing maintenance costs. Solar control glass incorporates selective coatings that reflect infrared radiation while allowing visible light transmission, improving building energy efficiency by minimizing heat gain. Both advanced glass technologies revolutionize facade performance by combining durability, aesthetic appeal, and sustainable functionality.
Defining Superhydrophobic Glass: Properties and Functions
Superhydrophobic glass features a surface coated with nanostructures that create extreme water repellency, promoting self-cleaning by causing water droplets to bead up and roll off, removing dirt and contaminants. This property significantly reduces maintenance and improves transparency over time, making it ideal for building facades exposed to environmental elements. In contrast to solar control glass, which primarily focuses on reducing solar heat gain through reflective coatings, superhydrophobic glass enhances durability and clarity by preventing water accumulation and surface soiling.
Understanding Solar Control Glass: Key Benefits and Applications
Solar control glass enhances building energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare, thereby lowering air conditioning costs and improving indoor comfort. This glass type incorporates coatings or films that reflect or absorb infrared and ultraviolet rays while allowing visible light transmission, making it ideal for facades in commercial and residential buildings. Its applications include high-rise office towers, shopping malls, and urban housing where controlling solar radiation is critical for sustainable design and occupant wellbeing.
Performance Comparison: Water Repellence vs. Solar Efficiency
Superhydrophobic glass exhibits exceptional water repellence due to its nano-structured surface, which minimizes adhesion and promotes self-cleaning properties, ideal for rain-prone facades. Solar control glass, designed with low-emissivity coatings, enhances solar efficiency by selectively filtering infrared radiation, reducing heat gain while maintaining visible light transmission. When comparing performance, superhydrophobic glass excels in maintaining facade cleanliness and durability against water but offers limited solar heat reduction, whereas solar control glass significantly improves energy efficiency by mitigating solar heat without compromising natural illumination.
Energy Efficiency Impact of Superhydrophobic vs. Solar Control Glass
Superhydrophobic glass offers self-cleaning properties that reduce maintenance costs and maintain optimal light transmission, indirectly supporting energy efficiency by minimizing the need for artificial lighting and cleaning-related energy consumption. Solar control glass directly improves building energy performance by reflecting or absorbing solar radiation, reducing cooling loads and lowering air conditioning energy usage in facades. While superhydrophobic glass enhances durability and clarity, solar control glass delivers more significant and measurable reductions in HVAC energy demand through its specialized coatings and spectral management.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Superhydrophobic glass significantly reduces maintenance needs by repelling water, dirt, and pollutants, leading to less frequent cleaning and better preservation of clarity over time. In contrast, solar control glass requires regular maintenance to prevent accumulation of dust and grime that can diminish its energy efficiency and light transmission. Longevity of superhydrophobic coatings may vary depending on environmental exposure, while solar control glass typically maintains its performance longer with proper upkeep.
Aesthetic Implications for Building Designs
Superhydrophobic glass offers sleek, self-cleaning surfaces with minimal water spotting, enhancing facade clarity and maintaining a pristine, modern aesthetic over time. Solar control glass contributes to energy efficiency by reducing glare and heat gain, which supports the use of larger glass panels without compromising occupant comfort, thus enabling bold, light-filled designs. Combining these materials can optimize both visual appeal and functional performance, creating facades that are strikingly transparent and energy-smart.
Suitability for Different Climate Zones
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior water repellency and self-cleaning properties ideal for humid and rainy climates, reducing maintenance and preventing mold growth on facades. Solar control glass excels in hot and sunny regions by reflecting infrared radiation and reducing heat gain, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Selecting the appropriate glass depends on climate-specific requirements, with superhydrophobic glass favored in wet environments and solar control glass preferred in areas with intense solar exposure.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Superhydrophobic glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced nanocoating technologies that enhance water repellency and self-cleaning properties, reducing maintenance expenses for facades. Solar control glass offers moderate upfront investment but provides substantial energy savings by minimizing heat gain and reducing HVAC loads, leading to faster return on investment in climates with high solar exposure. Analyzing total lifecycle costs reveals that while superhydrophobic glass reduces cleaning frequency, solar control glass often delivers superior ROI through energy efficiency benefits in commercial facade applications.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Your Facade Project
Superhydrophobic glass offers self-cleaning properties by repelling water and dirt, reducing maintenance costs and preserving facade clarity in polluted or rainy environments. Solar control glass enhances energy efficiency by reflecting infrared radiation, minimizing heat gain, and improving indoor comfort in sunny climates with high cooling demands. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing environmental factors, maintenance considerations, and energy performance goals to optimize facade durability and building sustainability.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Solar control glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com