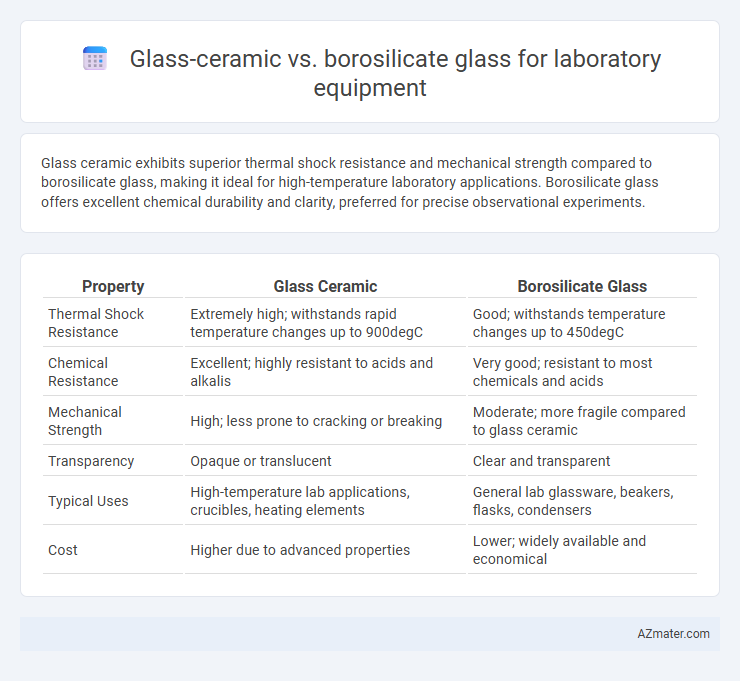
Glass ceramic exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to borosilicate glass, making it ideal for high-temperature laboratory applications. Borosilicate glass offers excellent chemical durability and clarity, preferred for precise observational experiments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Extremely high; withstands rapid temperature changes up to 900degC | Good; withstands temperature changes up to 450degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent; highly resistant to acids and alkalis | Very good; resistant to most chemicals and acids |
| Mechanical Strength | High; less prone to cracking or breaking | Moderate; more fragile compared to glass ceramic |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Typical Uses | High-temperature lab applications, crucibles, heating elements | General lab glassware, beakers, flasks, condensers |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced properties | Lower; widely available and economical |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Glass ceramic and borosilicate glass are essential materials in laboratory glassware, prized for their thermal resistance and chemical durability. Borosilicate glass features a low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, ideal for test tubes, beakers, and flasks. Glass ceramics offer superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, often used in applications requiring extreme temperature resistance and structural integrity.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a material formed through controlled crystallization of certain glass compositions, resulting in a composite that combines the transparency of glass with the strength and thermal stability of ceramics. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is primarily a type of glass with boron trioxide to enhance thermal resistance, glass ceramics exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress, making them ideal for high-performance laboratory equipment. These properties ensure glass ceramic labware withstands rapid temperature changes and heavy-duty usage better than borosilicate alternatives.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of laboratory glassware made from silica and boron trioxide, renowned for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability. It maintains structural integrity under rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for high-heat laboratory processes. Glass ceramic, while also heat-resistant, differs by offering greater mechanical strength and lower thermal expansion, but borosilicate remains the preferred choice for precise chemical experiments due to its proven resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock.
Thermal Resistance: Glass Ceramic vs Borosilicate
Glass ceramic exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to borosilicate glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 1200degC without cracking, whereas borosilicate glass typically endures thermal shocks up to 450degC. The low coefficient of thermal expansion in glass ceramic minimizes stress during heating and cooling cycles, making it ideal for high-temperature laboratory applications. Borosilicate glass, while durable and resistant to moderate thermal variations, is more prone to thermal shock under extreme temperature fluctuations.
Chemical Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Glass ceramic exhibits superior chemical durability and corrosion resistance compared to borosilicate glass, making it more resistant to acids, alkalis, and thermal shock in laboratory environments. Borosilicate glass offers good resistance to thermal stress and chemical attack but can degrade over time when exposed to highly corrosive substances. Laboratories handling aggressive chemicals often prefer glass ceramic to ensure longevity and maintain the integrity of sensitive experiments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Glass ceramic laboratory equipment exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to borosilicate glass, offering enhanced resistance to thermal shock and impact. Borosilicate glass provides good chemical durability and moderate mechanical strength but is more prone to breakage under sudden temperature changes. The durability of glass ceramics makes them the preferred choice for applications requiring high thermal cycling and mechanical stress tolerance.
Transparency and Optical Properties
Glass ceramic shows lower transparency compared to borosilicate glass, with its microcrystalline structure diffusing light and reducing clarity. Borosilicate glass offers superior optical properties, maintaining high transparency and minimal light distortion, making it ideal for precise visual observations in laboratory settings. Its low thermal expansion also helps preserve optical clarity under temperature changes, unlike glass ceramic which may exhibit slight opacification.
Cost and Availability
Glass ceramic laboratory equipment typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and limited suppliers, making it less widely available than borosilicate glass. Borosilicate glass is more cost-effective and commonly accessible from numerous manufacturers, catering to a broad range of laboratory needs. The widespread availability of borosilicate glass often makes it the preferred choice for budget-conscious laboratories requiring durable glassware.
Typical Laboratory Applications
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature applications such as crucibles, heating elements, and fusion processes in laboratory settings. Borosilicate glass is commonly used for chemical glassware like beakers, flasks, and condensers due to its excellent chemical durability and ability to withstand moderate thermal stress. Both materials cater to distinct laboratory applications, with glass ceramic preferred for extreme thermal environments and borosilicate glass favored for everyday chemical experiments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Lab
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature laboratory applications requiring rapid temperature changes. Borosilicate glass provides excellent chemical durability and transparency, suitable for general-purpose labware and precise visual monitoring. Selecting the optimal material depends on the specific thermal and chemical demands of your experiments to ensure durability and safety.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com