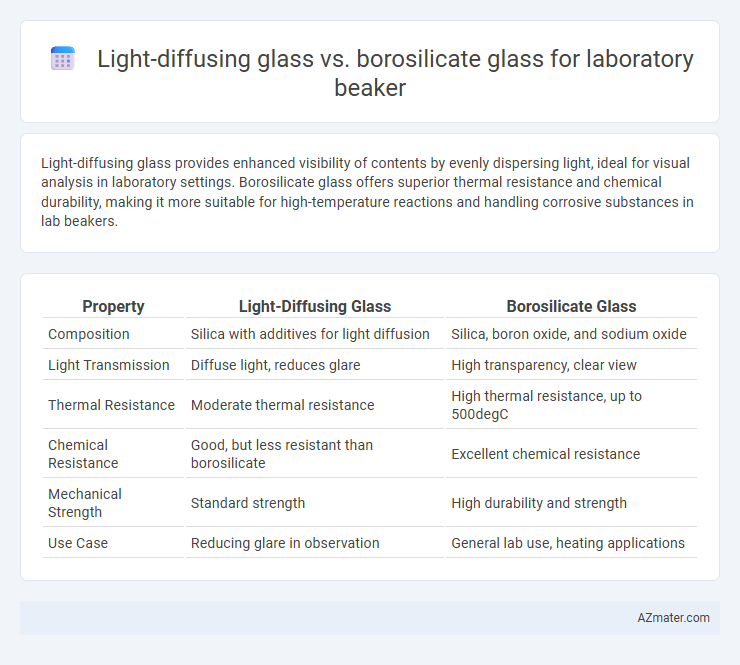
Light-diffusing glass provides enhanced visibility of contents by evenly dispersing light, ideal for visual analysis in laboratory settings. Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it more suitable for high-temperature reactions and handling corrosive substances in lab beakers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Light-Diffusing Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica with additives for light diffusion | Silica, boron oxide, and sodium oxide |
| Light Transmission | Diffuse light, reduces glare | High transparency, clear view |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate thermal resistance | High thermal resistance, up to 500degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but less resistant than borosilicate | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Standard strength | High durability and strength |
| Use Case | Reducing glare in observation | General lab use, heating applications |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Laboratory beakers are commonly made from borosilicate glass due to its exceptional thermal resistance, chemical durability, and low thermal expansion, ensuring high precision and safety in experiments. Light-diffusing glass, while less prevalent, is utilized in specialized applications requiring uniform light distribution and reduced glare, benefiting optical measurements and photochemical reactions. Selecting the appropriate glass material depends on the experimental needs, balancing thermal stability and optical properties within laboratory workflows.
Understanding Light-Diffusing Glass
Light-diffusing glass in laboratory beakers enhances uniform illumination by scattering light evenly, reducing glare and hotspots during experiments that require precise optical measurements. This glass type, often treated or coated to diffuse light, contrasts with borosilicate glass, known for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability but lacking inherent light-diffusing properties. Selecting light-diffusing glass over borosilicate is crucial for applications demanding consistent light distribution to improve observational accuracy and data reliability under varied lighting conditions.
Properties of Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional thermal resistance with a low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it ideal for laboratory beakers subjected to rapid temperature changes. Its high chemical durability ensures minimal reaction with acidic or alkaline substances, maintaining sample purity during experiments. The material's mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock outperform light-diffusing glass, providing greater longevity and reliability in rigorous lab environments.
Thermal Resistance: Light-Diffusing vs Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance with a high tolerance to rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for laboratory beakers exposed to extreme heat or sudden cooling. Light-diffusing glass, while enhancing visibility and minimizing glare, generally exhibits lower thermal resistance and increased susceptibility to thermal shock compared to borosilicate glass. Laboratories requiring reliable heat durability and resistance to thermal stress typically prefer borosilicate glass for its proven performance under demanding thermal conditions.
Chemical Durability in Laboratory Settings
Light-diffusing glass for laboratory beakers offers moderate chemical resistance, suitable for general applications but may degrade when exposed to strong acids or alkalis. Borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical durability, resisting corrosion and thermal shock from harsh chemicals like nitric acid and sodium hydroxide, making it ideal for demanding laboratory conditions. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion ensures longevity and reliability in chemical experiments requiring repetitive heating and cooling cycles.
Optical Clarity and Diffusion Characteristics
Light-diffusing glass for laboratory beakers offers enhanced opacity by scattering light, reducing glare and making contents less visible, which is ideal for reactions requiring light sensitivity. Borosilicate glass provides superior optical clarity with minimal light distortion, allowing precise observation of chemical processes due to its high transparency and low thermal expansion. The choice depends on whether optical clarity or controlled light diffusion is more critical for the experimental application.
Mechanical Strength and Impact Resistance
Light-diffusing glass offers enhanced impact resistance due to its microstructured surface that disperses stress more evenly, reducing the likelihood of cracks under sudden force. Borosilicate glass is renowned for its superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, making it highly durable for laboratory beakers subjected to rapid temperature changes. While borosilicate excels in withstanding harsh chemical and thermal environments, light-diffusing glass provides improved durability against physical impact without compromising optical clarity.
Applications in Scientific Research
Light-diffusing glass in laboratory beakers enhances optical clarity by scattering light evenly, making it ideal for experiments requiring uniform illumination and accurate spectrophotometric measurements. Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it suitable for heating reactions, corrosive chemicals, and high-temperature sterilization in scientific research. Selecting between these glasses depends on the specific application needs, with light-diffusing glass favored in optical studies and borosilicate preferred for thermal and chemical robustness.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Light-diffusing glass laboratory beakers typically cost more due to specialized manufacturing processes and limited suppliers, resulting in lower availability compared to borosilicate glass options. Borosilicate glass beakers are widely available and affordable, benefiting from mass production and strong demand in laboratories worldwide. The cost-effectiveness and ready accessibility of borosilicate glass make it the preferred choice for most laboratory applications requiring glassware.
Choosing the Best Glass for Laboratory Beakers
Light-diffusing glass offers superior optical clarity and even light distribution, ideal for experiments requiring precise visual observation, while borosilicate glass is renowned for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it the preferred choice for harsh laboratory conditions. Borosilicate glass withstands rapid temperature changes and chemical corrosion, ensuring long-term durability and safety during heating or reactive experiments. Selecting between these glasses depends on the specific laboratory application needs, with borosilicate glass commonly favored for general-purpose beakers and light-diffusing glass chosen for specialized optical requirements.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory beaker
 azmater.com
azmater.com