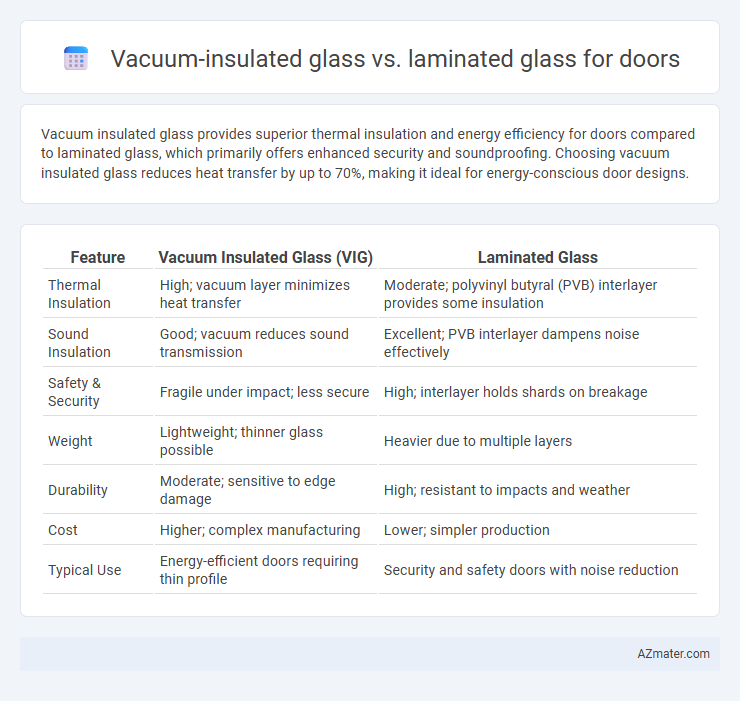
Vacuum insulated glass provides superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for doors compared to laminated glass, which primarily offers enhanced security and soundproofing. Choosing vacuum insulated glass reduces heat transfer by up to 70%, making it ideal for energy-conscious door designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High; vacuum layer minimizes heat transfer | Moderate; polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer provides some insulation |
| Sound Insulation | Good; vacuum reduces sound transmission | Excellent; PVB interlayer dampens noise effectively |
| Safety & Security | Fragile under impact; less secure | High; interlayer holds shards on breakage |
| Weight | Lightweight; thinner glass possible | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Durability | Moderate; sensitive to edge damage | High; resistant to impacts and weather |
| Cost | Higher; complex manufacturing | Lower; simpler production |
| Typical Use | Energy-efficient doors requiring thin profile | Security and safety doors with noise reduction |
Introduction to Vacuum Insulated Glass and Laminated Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) features two glass panes separated by a vacuum space, drastically reducing heat transfer and enhancing thermal insulation for doors. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing increased safety, sound insulation, and UV protection. Both types improve door performance, with VIG focusing on energy efficiency and laminated glass emphasizing impact resistance and security.
Core Differences Between Vacuum Insulated and Laminated Glass
Vacuum insulated glass consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer, providing superior thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer significantly compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass comprises layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, offering enhanced safety and impact resistance but lower insulation properties. The core difference lies in vacuum insulated glass's energy efficiency for temperature control, while laminated glass primarily improves security and soundproofing in doors.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance for doors compared to laminated glass by significantly reducing heat transfer through its vacuum layer, which minimizes conduction and convection. Laminated glass primarily improves safety and sound insulation but has higher thermal conductivity due to its solid interlayer, resulting in less effective insulation. Choosing VIG enhances energy efficiency by maintaining interior temperatures and reducing heating and cooling costs.
Sound Insulation Capabilities
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior sound insulation for doors by eliminating air gaps, significantly reducing noise transmission compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass also provides effective soundproofing through its interlayer that dampens sound vibrations but may not match the noise reduction levels of vacuum insulated units. For optimal acoustic performance in doors, vacuum insulated glass is preferred in environments with high noise pollution.
Safety and Security Features
Vacuum insulated glass offers enhanced impact resistance and superior thermal insulation, making it a secure choice for doors against break-ins and extreme weather. Laminated glass contains a durable interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, preventing injury and unauthorized entry. Both glazing options provide robust safety and security, with laminated glass excelling in shatter protection and vacuum insulated glass in structural strength and energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency for Doors
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation due to its low heat transfer properties, significantly reducing energy loss compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass provides moderate energy efficiency by blocking ultraviolet rays and enhancing durability but lacks the advanced insulation features of vacuum insulated glass. For door applications prioritizing energy savings, vacuum insulated glass delivers exceptional performance by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and minimizing heating and cooling costs.
Durability and Longevity
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability for doors by resisting condensation, thermal stress, and impact due to its airtight vacuum layer between glass panes. Laminated glass excels in safety with its interlayer holding shards in place upon breakage, enhancing impact resistance but may degrade over time from UV exposure. For long-term performance, vacuum insulated glass maintains clarity and structural integrity longer, while laminated glass prioritizes safety at potential cost to lasting durability.
Aesthetic and Design Options
Vacuum insulated glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with its slim profile and minimal frame visibility, providing maximum natural light and a clean, elegant look for doors. Laminated glass excels in design versatility, allowing for decorative interlayers, tinted colors, and patterns that enhance door style while providing safety benefits. Both options accommodate custom sizes and shapes, but vacuum insulated glass prioritizes transparency and thermal efficiency, whereas laminated glass emphasizes creative design and visual customization.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Vacuum insulated glass typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to laminated glass due to advanced manufacturing and superior thermal performance, but it offers significant energy savings that enhance long-term return on investment (ROI). Laminated glass, while more affordable initially, provides safety benefits and moderate insulation, making it cost-effective for projects prioritizing durability and security over energy efficiency. Evaluating project-specific factors such as climate, energy prices, and maintenance costs is crucial for optimizing ROI when choosing between vacuum insulated and laminated glass for doors.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type in Doors
Vacuum insulated glass is ideal for exterior doors in climates requiring superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency, reducing heat transfer and condensation. Laminated glass excels in doors needing enhanced safety and security features, as its interlayer holds shards together upon impact, making it suitable for entry and patio doors in high-traffic areas. Both glass types provide soundproofing benefits, but vacuum insulated glass is preferred where insulation performance is paramount, while laminated glass is best for safety and durability applications.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Laminated glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com