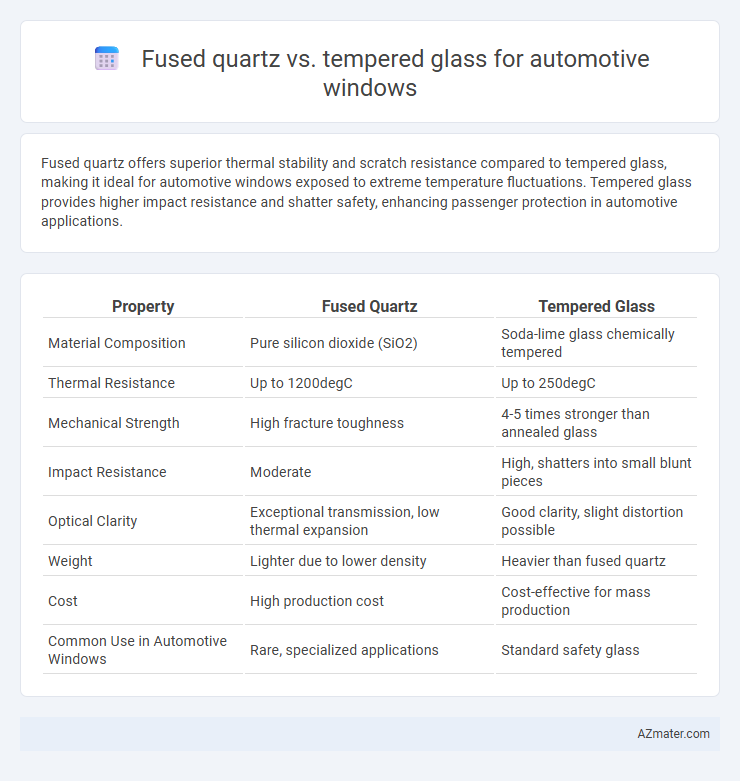
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and scratch resistance compared to tempered glass, making it ideal for automotive windows exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations. Tempered glass provides higher impact resistance and shatter safety, enhancing passenger protection in automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Soda-lime glass chemically tempered |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 250degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High fracture toughness | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High, shatters into small blunt pieces |
| Optical Clarity | Exceptional transmission, low thermal expansion | Good clarity, slight distortion possible |
| Weight | Lighter due to lower density | Heavier than fused quartz |
| Cost | High production cost | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Common Use in Automotive Windows | Rare, specialized applications | Standard safety glass |
Introduction to Automotive Window Materials
Fused quartz and tempered glass serve distinct roles in automotive window materials, with fused quartz offering superior thermal resistance and optical clarity, ideal for high-temperature applications and precision visibility. Tempered glass, known for its enhanced strength and safety features, undergoes controlled thermal processing to prevent shattering, making it the standard choice for vehicle side and rear windows. Both materials contribute to automotive safety and performance, but tempered glass dominates in cost-effectiveness and impact resistance for everyday automotive use.
Composition of Fused Quartz vs Tempered Glass
Fused quartz is composed primarily of nearly pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), providing exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature automotive window applications. Tempered glass, on the other hand, consists of soda-lime silica glass that undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatment, resulting in increased strength and safety by inducing compressive stresses on the surface. The distinct compositions of fused quartz and tempered glass influence their performance characteristics, with fused quartz offering superior optical clarity and thermal resistance compared to the mechanically strengthened, impact-resistant tempered glass used commonly in automotive windows.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Fused quartz offers superior mechanical strength due to its high resistance to thermal shock and low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it less prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass is engineered through a heat-treatment process that increases its impact resistance and safety, shattering into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, which enhances occupant protection. While fused quartz excels in durability under extreme thermal conditions, tempered glass provides better everyday impact resistance and cost-effectiveness for automotive window applications.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity with minimal light distortion and a high transmission rate of approximately 92%, making it ideal for automotive windows that demand precise visibility. In contrast, tempered glass typically transmits around 80-90% of visible light but may exhibit slight optical imperfections due to its manufacturing process. High light transmission and low refractive index variations in fused quartz contribute to enhanced driver safety and comfort by reducing glare and ensuring true color visibility.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Fused quartz exhibits superior thermal resistance and temperature tolerance compared to tempered glass, enduring temperatures up to 1200degC without deformation, making it ideal for automotive windows exposed to extreme heat. Tempered glass typically withstands temperatures up to 250degC to 300degC before losing strength or warping, limiting its use in high-temperature conditions. The low thermal expansion coefficient of fused quartz minimizes stress and cracking during rapid temperature changes, enhancing durability in automotive applications requiring thermal stability.
Impact Resistance and Safety Features
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and higher resistance to thermal shock, but tempered glass excels in impact resistance, shattering into small, less dangerous fragments upon breakage for enhanced automotive safety. Tempered glass's controlled fracture patterns reduce injury risk during collisions, making it the preferred choice for automotive windows. Impact resistance standards like ANSI Z26.1 emphasize tempered glass's reliability in protecting occupants from debris and impacts while maintaining structural integrity.
Weight Differences and Fuel Efficiency
Fused quartz offers significantly lower density compared to tempered glass, resulting in lighter automotive windows that reduce overall vehicle weight. This weight reduction directly enhances fuel efficiency by decreasing the energy required for acceleration and maintaining speed. Lighter windows also contribute to improved vehicle handling and lower emissions, supporting environmentally friendly automotive performance.
Cost Analysis: Fused Quartz vs Tempered Glass
Fused quartz is significantly more expensive than tempered glass due to higher raw material costs and complex manufacturing processes, making it less economical for large-scale automotive window production. Tempered glass offers a cost-effective solution with mass production capabilities and established supply chains, reducing per-unit expenses significantly. Lower initial investment and repair costs favor tempered glass in budget-constrained automotive applications despite fused quartz's superior thermal and mechanical properties.
Application Suitability in Automotive Design
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal resistance and optical clarity, making it suitable for automotive windows exposed to extreme temperature variations and high-performance environments. Tempered glass provides superior impact resistance and safety by shattering into small, less harmful pieces, which is essential for passenger protection and regulatory compliance in standard automotive designs. The choice between fused quartz and tempered glass hinges on specific application requirements, such as durability, safety standards, and thermal stability within the automotive window system.
Future Trends and Innovations in Automotive Windows
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and scratch resistance, making it a prime candidate for next-generation automotive windows designed to enhance durability and optical clarity. Innovations in tempered glass focus on integrating smart technologies such as self-tinting and embedded sensors for improved safety and energy efficiency. Future trends emphasize the development of hybrid materials combining fused quartz and tempered glass properties to optimize performance and reduce vehicle weight.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Tempered glass for Automotive window
 azmater.com
azmater.com