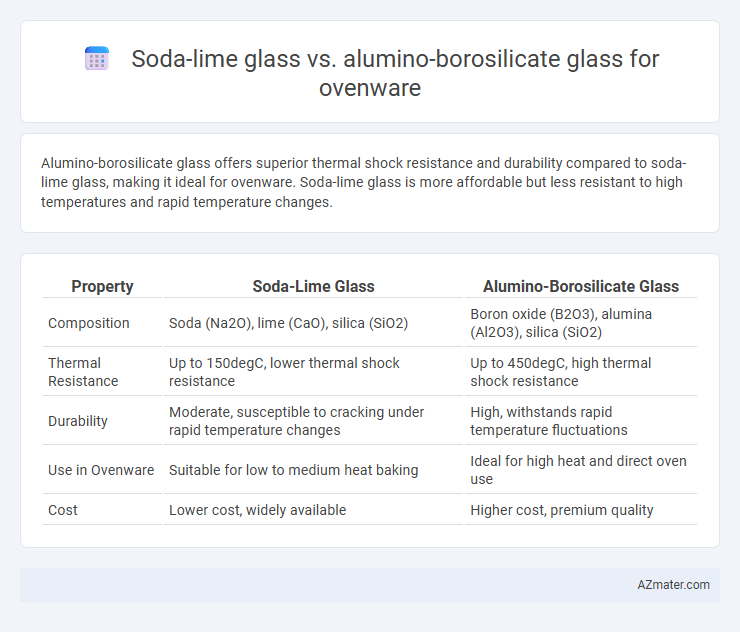
Alumino-borosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to soda-lime glass, making it ideal for ovenware. Soda-lime glass is more affordable but less resistant to high temperatures and rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Soda-Lime Glass | Alumino-Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Soda (Na2O), lime (CaO), silica (SiO2) | Boron oxide (B2O3), alumina (Al2O3), silica (SiO2) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC, lower thermal shock resistance | Up to 450degC, high thermal shock resistance |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to cracking under rapid temperature changes | High, withstands rapid temperature fluctuations |
| Use in Ovenware | Suitable for low to medium heat baking | Ideal for high heat and direct oven use |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, premium quality |
Introduction to Ovenware Glass Types
Soda-lime glass, commonly used in ovenware, offers affordability and good thermal shock resistance but has lower mechanical strength compared to alumino-borosilicate glass. Alumino-borosilicate glass features superior thermal stability, chemical durability, and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature oven applications. Understanding the composition differences between these glass types helps optimize performance and safety in cookware design.
Composition of Soda-lime Glass
Soda-lime glass, primarily composed of about 70-75% silica (SiO2), 12-15% soda (Na2O), and 10-15% lime (CaO), offers moderate thermal resistance but lower durability compared to alumino-borosilicate glass used in ovenware. The presence of soda lowers the melting point, making soda-lime glass easier to manufacture while lime enhances chemical durability and thermal stability to some extent. Its lower thermal shock resistance and higher thermal expansion coefficient make soda-lime glass less suitable for high-temperature ovenware applications than alumino-borosilicate variants.
Composition of Alumino-borosilicate Glass
Alumino-borosilicate glass used in ovenware contains silica (SiO2), boron oxide (B2O3), alumina (Al2O3), and alkali oxides, providing superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength compared to soda-lime glass, which primarily consists of silica, soda (Na2O), and lime (CaO). The incorporation of alumina in alumino-borosilicate glass significantly enhances durability and reduces thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking applications. Soda-lime glass lacks the boron and alumina components, resulting in lower thermal resistance and higher susceptibility to cracking under rapid temperature changes.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Alumino-borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to soda-lime glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 450degC without cracking, making it ideal for ovenware subjected to sudden heat shifts. Soda-lime glass typically tolerates temperatures up to 250degC and is prone to thermal shock, limiting its use in high-temperature oven applications. The enhanced durability of alumino-borosilicate glass results from its low thermal expansion coefficient, ensuring reliable performance during intense cooking processes.
Durability and Strength
Alumino-borosilicate glass offers superior durability and strength compared to soda-lime glass, making it highly suitable for ovenware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Its enhanced thermal shock resistance reduces the risk of cracking or shattering during oven use, while soda-lime glass is more prone to breakage under thermal stress. The structural composition of alumino-borosilicate glass provides a more robust and long-lasting option for cookware designed for high-heat applications.
Heat Shock Performance
Alumino-borosilicate glass exhibits superior heat shock resistance compared to soda-lime glass, making it the preferred choice for ovenware subjected to rapid temperature changes. The thermal expansion coefficient of alumino-borosilicate glass is significantly lower, typically around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, whereas soda-lime glass ranges from 8.5 to 9.0 x 10^-6 /degC, resulting in greater durability under thermal stress. This enhanced heat shock performance reduces the risk of cracking or shattering during sudden heating or cooling, ensuring safer and longer-lasting ovenware.
Chemical Stability and Reactivity
Alumino-borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical stability and lower reactivity compared to soda-lime glass, making it more resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion in ovenware applications. Soda-lime glass, while cost-effective, is more prone to leaching and chemical interaction with acidic or alkaline foods due to its higher sodium oxide content. This increased chemical durability of alumino-borosilicate glass ensures enhanced safety and longevity in cookware exposed to high temperatures and varying pH environments.
Safety Considerations in Oven Use
Soda-lime glass, commonly used in ovenware, has a lower thermal shock resistance compared to alumino-borosilicate glass, posing a higher risk of cracking or shattering under rapid temperature changes. Alumino-borosilicate glass offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it safer for high-temperature oven use and reducing the risk of breakage. When selecting ovenware, alumino-borosilicate glass is preferred for enhanced safety due to its ability to withstand sudden temperature fluctuations without compromising structural integrity.
Cost and Availability
Soda-lime glass is more cost-effective and widely available for ovenware applications due to its simpler manufacturing process and abundance of raw materials. Alumino-borosilicate glass, despite higher strength and thermal resistance, typically incurs greater production costs and is less commonly stocked by retailers. Choosing soda-lime glass reduces upfront expenses and ensures easier procurement, while alumino-borosilicate glass is preferred in specialized, high-temperature environments where durability justifies the premium price.
Which Glass is Best for Ovenware?
Alumino-borosilicate glass is the best choice for ovenware due to its superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to soda-lime glass. This type of glass withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for baking and roasting applications. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable, is prone to breakage under high heat and sudden temperature fluctuations, limiting its performance in ovenware.
Infographic: Soda-lime glass vs Alumino-borosilicate glass for Ovenware
 azmater.com
azmater.com