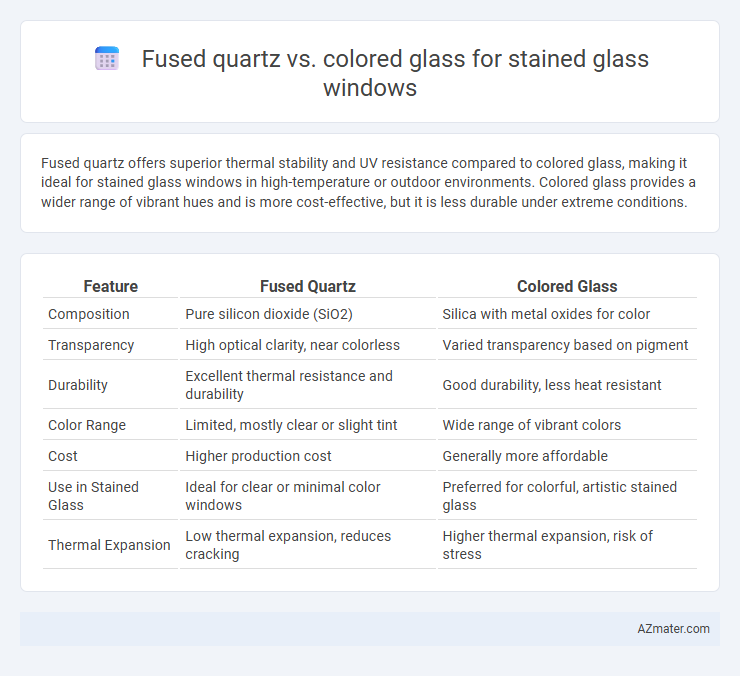
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and UV resistance compared to colored glass, making it ideal for stained glass windows in high-temperature or outdoor environments. Colored glass provides a wider range of vibrant hues and is more cost-effective, but it is less durable under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fused Quartz | Colored Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Silica with metal oxides for color |
| Transparency | High optical clarity, near colorless | Varied transparency based on pigment |
| Durability | Excellent thermal resistance and durability | Good durability, less heat resistant |
| Color Range | Limited, mostly clear or slight tint | Wide range of vibrant colors |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally more affordable |
| Use in Stained Glass | Ideal for clear or minimal color windows | Preferred for colorful, artistic stained glass |
| Thermal Expansion | Low thermal expansion, reduces cracking | Higher thermal expansion, risk of stress |
Introduction to Fused Quartz and Colored Glass
Fused quartz is a high-purity, silicon dioxide material renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and superior clarity, making it ideal for precision stained glass applications. Colored glass, composed of silica combined with various metal oxides and additives, offers a wide spectrum of vibrant hues and opacity levels, essential for artistic expression in stained glass windows. The choice between fused quartz and colored glass depends on the desired optical properties, durability, and aesthetic effects in stained glass window construction.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Fused quartz is composed primarily of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with minimal impurities, offering high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, while colored glass typically contains silica mixed with metal oxides like cobalt, chromium, or selenium to produce vibrant hues. The manufacturing process of fused quartz involves melting high-purity quartz crystals at temperatures above 1700degC, followed by controlled cooling to achieve a uniform, non-crystalline structure; in contrast, colored glass is made by melting raw materials with colorants at lower temperatures (approximately 1400-1600degC), then shaping and annealing to lock in the pigmentation. These compositional and processing differences result in fused quartz providing superior durability and optical clarity, whereas colored glass allows for a broader palette of saturated colors but with varying degrees of durability.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity and higher light transmission compared to colored glass, making it ideal for stained glass windows requiring maximum brightness and color fidelity. The low impurity levels and minimal internal stress in fused quartz result in less light scattering, enhancing visual sharpness and vividness of the colors. Colored glass, while available in numerous hues, typically exhibits lower transparency and can slightly distort light due to its chemical additives and manufacturing process.
Coloration: Techniques and Longevity
Fused quartz offers superior color purity and translucency for stained glass windows due to its high silica content and minimal impurities, enabling vibrant, long-lasting hues that resist fading under UV exposure. Colored glass, often formulated with metal oxides and additives, allows diverse coloration techniques such as pot-metal or flashed glass, but these colors may degrade over time depending on environmental conditions and glass quality. The longevity of coloration in fused quartz surpasses traditional colored glass, making it a preferred choice for installations requiring durable, stable visual effects.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Fused quartz exhibits superior strength and durability compared to colored glass, with a high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it ideal for stained glass windows exposed to variable climates. Colored glass, while visually vibrant, is more prone to cracking and fading over time due to its lower melting point and weaker structural integrity. The enhanced molecular structure of fused quartz ensures longevity and maintains clarity, outperforming traditional colored glass in long-term stability.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Fused quartz exhibits superior thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures exceeding 1,650degC without deformation, making it ideal for stained glass windows exposed to intense heat or rapid temperature fluctuations. Colored glass typically has lower thermal thresholds, around 600-800degC, and is more prone to stress fractures under thermal shock. Chemically, fused quartz is highly inert and resistant to most acids and alkalis, ensuring long-lasting durability, whereas colored glass can suffer from chemical degradation and color fading over time due to less robust chemical stability.
Artistic Possibilities and Design Flexibility
Fused quartz offers superior clarity and thermal stability, enabling intricate designs with precise color layering and sharp detail for stained glass windows. Colored glass provides a richer palette with naturally occurring hues and textures, enhancing artistic expression through varied translucency and tone. Both materials expand creative potential, but fused quartz allows for greater control over optical effects while colored glass delivers traditional vibrancy and depth.
Cost and Availability
Fused quartz, known for its superior thermal stability and clarity, typically comes at a higher cost and is less readily available than colored glass, making it a premium choice for stained glass windows. Colored glass offers a wide variety of hues and is generally more accessible and affordable due to established manufacturing processes and widespread distribution. The cost-effectiveness and availability of colored glass make it the preferred material for most traditional stained glass projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fused quartz offers superior environmental benefits over colored glass for stained glass windows due to its high durability and recyclability, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Its production emits fewer greenhouse gases as it requires less energy-intensive processes compared to colored glass manufacturing, which often involves heavy metal pigmentation and higher energy consumption. Choosing fused quartz supports sustainability goals by minimizing waste and lowering the overall carbon footprint associated with stained glass installations.
Choosing the Right Material for Stained Glass Windows
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and resistance to UV degradation compared to colored glass, making it ideal for stained glass windows exposed to harsh sunlight and temperature fluctuations. Colored glass provides a broader palette of vibrant hues and is generally more cost-effective, suitable for traditional and decorative projects where energy efficiency and longevity are less critical. Selecting between fused quartz and colored glass depends on the desired balance between durability, color vibrancy, and budget constraints for the stained glass installation.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Colored glass for Stained glass window
 azmater.com
azmater.com