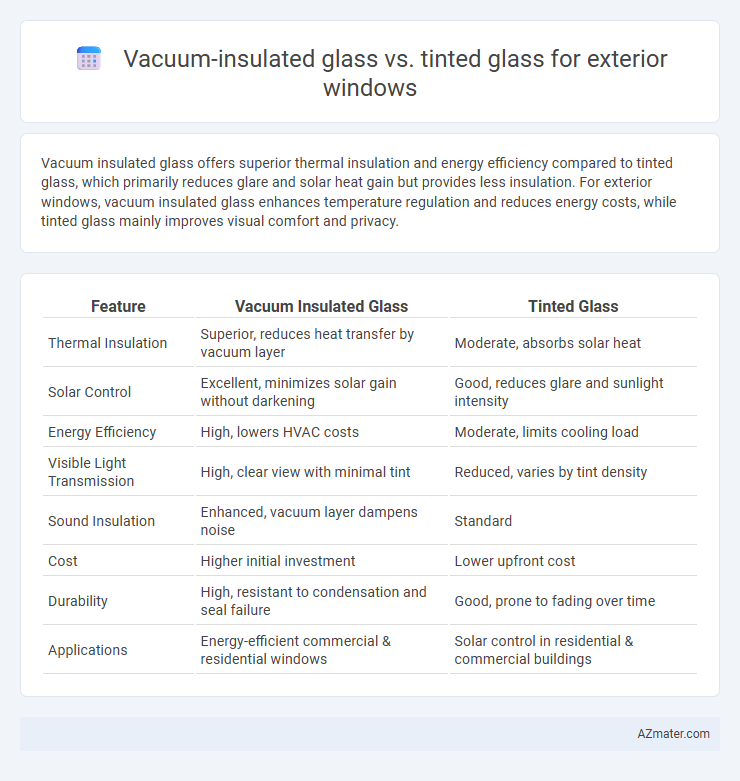
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to tinted glass, which primarily reduces glare and solar heat gain but provides less insulation. For exterior windows, vacuum insulated glass enhances temperature regulation and reduces energy costs, while tinted glass mainly improves visual comfort and privacy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Superior, reduces heat transfer by vacuum layer | Moderate, absorbs solar heat |
| Solar Control | Excellent, minimizes solar gain without darkening | Good, reduces glare and sunlight intensity |
| Energy Efficiency | High, lowers HVAC costs | Moderate, limits cooling load |
| Visible Light Transmission | High, clear view with minimal tint | Reduced, varies by tint density |
| Sound Insulation | Enhanced, vacuum layer dampens noise | Standard |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Durability | High, resistant to condensation and seal failure | Good, prone to fading over time |
| Applications | Energy-efficient commercial & residential windows | Solar control in residential & commercial buildings |
Introduction to Exterior Window Glass Options
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by creating a near-vacuum space between glass panes, significantly reducing heat transfer for enhanced energy efficiency in exterior windows. Tinted glass minimizes solar heat gain and glare by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, helping regulate indoor temperature and improve comfort. Both options enhance window performance, with vacuum insulated glass prioritizing insulation and tinted glass focusing on solar control for exterior applications.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer that significantly reduces heat transfer, enhancing thermal insulation for exterior windows. This technology improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, outperforming traditional tinted glass which primarily reduces solar heat through color and coatings. VIG's superior insulation properties make it a preferred choice for sustainable building designs aiming to reduce energy consumption and improve indoor comfort.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass for exterior windows is designed with a color-added coating that reduces solar heat gain and glare while enhancing privacy and aesthetic appeal. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which focuses on thermal insulation through a sealed air gap, tinted glass primarily blocks UV rays and controls light transmission without providing significant insulation. This makes tinted glass ideal for reducing cooling loads and improving comfort in sunny climates where heat and glare are major concerns.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance compared to tinted glass by minimizing heat transfer through a near-vacuum layer that drastically reduces conduction and convection. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting infrared radiation but does not significantly improve insulation against conductive heat loss. As a result, VIG provides better energy efficiency and indoor temperature stability, especially in extreme climates, whereas tinted glass mainly enhances shading and glare control.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer, leading to significant energy savings on heating and cooling compared to tinted glass, which primarily reduces solar heat gain but provides less overall insulation. The advanced vacuum technology in vacuum insulated glass reduces energy consumption by up to 50%, enhancing building energy efficiency and lowering utility bills. Although vacuum insulated glass has a higher upfront cost than tinted glass, its long-term energy savings and improved indoor comfort deliver greater cost savings over the product's lifespan.
Noise Reduction Capabilities
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior noise reduction for exterior windows by using a vacuum layer that eliminates sound transmission between glass panes, significantly outperforming traditional tinted glass. Tinted glass primarily reduces glare and solar heat gain but provides minimal sound insulation compared to vacuum insulated units. For optimal exterior noise mitigation, vacuum insulated glass is the preferred choice due to its advanced acoustic buffering properties.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Vacuum insulated glass offers a sleek, modern appearance with ultra-thin profiles that enhance exterior window aesthetics while maintaining superior thermal performance. Tinted glass provides versatile design options through a range of color tints and light transmission levels, allowing customization of building facade tones and glare reduction. Combining vacuum insulated glass with selective tints can maximize design flexibility, balancing aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency in exterior window applications.
UV Protection and Fading Prevention
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior UV protection by significantly reducing harmful ultraviolet rays, which helps prevent interior fading and material deterioration. Tinted glass partially blocks UV radiation but is less effective than vacuum insulated glass in minimizing heat transfer and long-term fading of furnishings. Choosing vacuum insulated glass enhances energy efficiency and preserves interior aesthetics by maintaining lower UV penetration and better insulation performance.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability with enhanced resistance to thermal stress, preventing fogging and reducing condensation over time, making it a low-maintenance option for exterior windows. Tinted glass provides UV protection and glare reduction but may degrade faster under harsh weather conditions, requiring more frequent cleaning to maintain its appearance and performance. For long-term durability and minimal upkeep, vacuum insulated glass is the preferred choice in exterior window applications.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Building
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings seeking to reduce heating and cooling costs. Tinted glass primarily reduces solar heat gain and glare, enhancing occupant comfort in sunny climates but with less impact on overall insulation. Selecting the best option depends on climate conditions, energy performance goals, and aesthetic preferences, with vacuum insulated glass favored for maximizing energy savings and tinted glass for managing light and heat exposure.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Tinted glass for Exterior window
 azmater.com
azmater.com