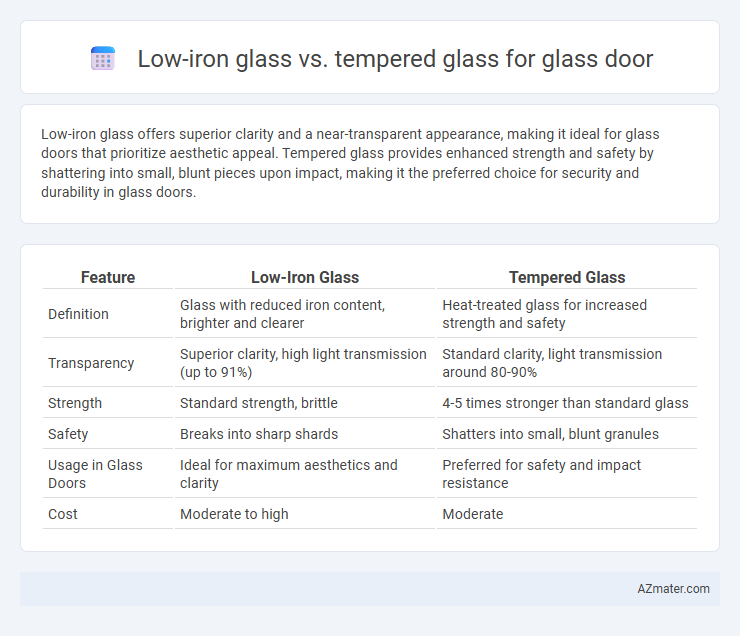
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and a near-transparent appearance, making it ideal for glass doors that prioritize aesthetic appeal. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, making it the preferred choice for security and durability in glass doors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with reduced iron content, brighter and clearer | Heat-treated glass for increased strength and safety |
| Transparency | Superior clarity, high light transmission (up to 91%) | Standard clarity, light transmission around 80-90% |
| Strength | Standard strength, brittle | 4-5 times stronger than standard glass |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp shards | Shatters into small, blunt granules |
| Usage in Glass Doors | Ideal for maximum aesthetics and clarity | Preferred for safety and impact resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Low-Iron Glass and Tempered Glass
Low-iron glass, known for its enhanced clarity and minimal green tint, provides superior transparency ideal for modern glass doors requiring a clean, crisp appearance. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its strength and safety, making it resistant to impact and thermal stress, which is critical for door applications. Combining low-iron glass with tempering technology offers a robust, visually appealing solution that maximizes both durability and aesthetic quality in glass door installations.
Key Differences between Low-Iron and Tempered Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and minimal green tint, making it ideal for glass doors where aesthetic transparency is a priority. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety through heat treatment, ensuring it shatters into small, blunt pieces upon impact. While low-iron glass emphasizes visual purity, tempered glass focuses on durability and impact resistance, making the choice dependent on the required balance between appearance and safety.
Visual Clarity and Color: Low-Iron vs Tempered Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior visual clarity and a clearer, more true-to-color appearance compared to tempered glass due to its reduced iron content, which minimizes the greenish tint commonly found in standard glass. Tempered glass, while stronger and more impact-resistant, typically exhibits a slight greenish hue that can affect color accuracy and transparency. For glass doors where aesthetics and color fidelity are paramount, low-iron glass is the preferred choice over tempered glass.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal but has similar strength properties to standard annealed glass, making it less resistant to impact compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that enhances its strength, making it up to four to five times stronger than low-iron annealed glass and significantly more resistant to breakage and thermal stress. In terms of durability for glass doors, tempered glass provides greater safety and longevity, especially in high-traffic or high-impact environments, whereas low-iron glass is preferred where optical clarity is prioritized over strength.
Safety Features of Each Glass Type
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and strength but is more prone to shattering under impact compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its strength by up to four times and, when broken, shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk. For glass doors prioritizing safety, tempered glass is often preferred due to its enhanced impact resistance and safer breakage patterns.
Cost Analysis: Low-Iron Glass vs Tempered Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs 20-50% more than tempered glass due to its high clarity and reduced green tint, enhancing aesthetic appeal in glass doors. Tempered glass, known for its strength and safety compliance, offers a more budget-friendly option with prices generally lower by up to half compared to low-iron glass. Evaluating long-term investment, tempered glass provides durability advantages, while low-iron glass justifies higher upfront costs for premium transparency and design elegance.
Energy Efficiency and Light Transmission
Low-iron glass offers superior light transmission due to its reduced green tint, enhancing natural daylight and improving energy efficiency by decreasing the need for artificial lighting. Tempered glass, while stronger and safer, typically contains standard iron levels that slightly diminish light passage, potentially increasing reliance on supplemental lighting. Combining low-iron glass with tempering technology can optimize both energy efficiency and safety for glass doors.
Applications of Low-Iron and Tempered Glass in Doors
Low-iron glass offers exceptional clarity and color neutrality, making it ideal for glass doors in luxury retail stores, high-end residential properties, and modern office entrances where aesthetic appeal is paramount. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety, suited for commercial buildings, sliding glass doors, and public access points requiring impact resistance and compliance with safety regulations. Combining low-iron and tempered glass in doors ensures both superior transparency and durability, optimizing performance in high-traffic architectural applications.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Low-iron glass for glass doors offers enhanced clarity and aesthetic appeal but requires regular cleaning to prevent visible smudges and water spots due to its high transparency. Tempered glass, known for its durability and resistance to impact, has a longer lifespan with lower maintenance needs, as it is less prone to scratches and damage. Proper maintenance of tempered glass involves periodic inspection for chips or cracks to ensure safety, while low-iron glass demands careful cleaning techniques to preserve its pristine appearance over time.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Doors
Low-iron glass offers exceptional clarity and true color visibility, making it ideal for glass doors where aesthetic appeal and natural light transmission are priorities. Tempered glass provides superior strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, making it the best choice for doors requiring enhanced durability and security. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing the need for visual clarity with safety considerations in your specific door application.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Tempered glass for Glass door
 azmater.com
azmater.com