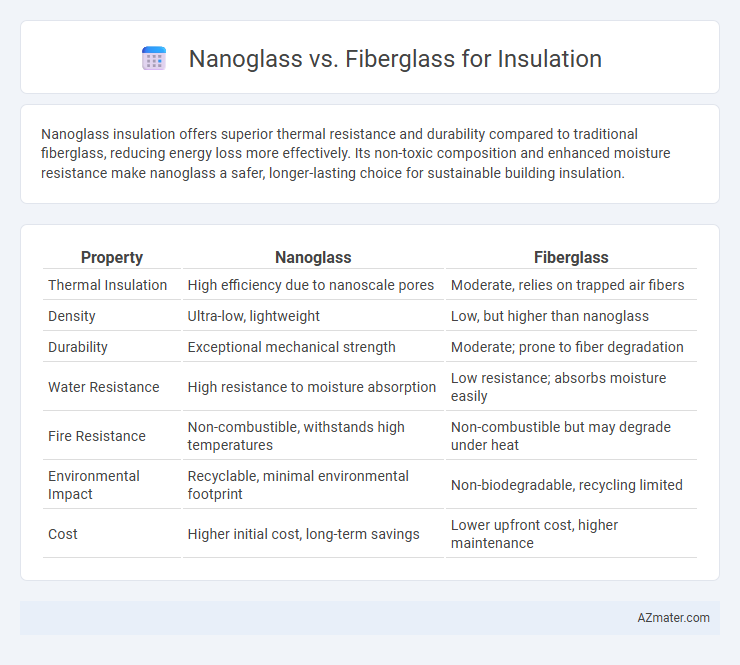
Nanoglass insulation offers superior thermal resistance and durability compared to traditional fiberglass, reducing energy loss more effectively. Its non-toxic composition and enhanced moisture resistance make nanoglass a safer, longer-lasting choice for sustainable building insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanoglass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High efficiency due to nanoscale pores | Moderate, relies on trapped air fibers |
| Density | Ultra-low, lightweight | Low, but higher than nanoglass |
| Durability | Exceptional mechanical strength | Moderate; prone to fiber degradation |
| Water Resistance | High resistance to moisture absorption | Low resistance; absorbs moisture easily |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, withstands high temperatures | Non-combustible but may degrade under heat |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, minimal environmental footprint | Non-biodegradable, recycling limited |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term savings | Lower upfront cost, higher maintenance |
Understanding Nanoglass and Fiberglass Insulation
Nanoglass insulation utilizes nanotechnology to create ultra-thin, transparent, and highly efficient thermal barriers, offering superior insulation performance and energy savings compared to traditional materials. Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers woven into a mat, providing effective thermal resistance and soundproofing but often requires thicker layers for comparable efficiency. Understanding the structural differences highlights nanoglass's advantage in space-saving and enhanced thermal conductivity while fiberglass remains a cost-effective, widely available solution for general insulation needs.
Thermal Efficiency: Nanoglass vs Fiberglass
Nanoglass insulation offers superior thermal efficiency compared to traditional fiberglass due to its nanoscale silica structure, which significantly reduces heat transfer. The lower thermal conductivity of nanoglass results in enhanced energy savings and improved temperature regulation within buildings. Fiberglass, while cost-effective, typically exhibits higher thermal conductivity, leading to less efficient insulation performance over time.
Energy Savings and Environmental Impact
Nanoglass insulation offers superior thermal resistance compared to traditional fiberglass, significantly reducing energy consumption by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Its advanced nanostructure enhances insulation efficiency, leading to lower heating and cooling costs over time. Nanoglass is also environmentally friendly, composed of recyclable materials with a smaller carbon footprint during production, making it a sustainable alternative to fiberglass insulation.
Soundproofing Capabilities Compared
Nanoglass insulation offers superior soundproofing capabilities compared to traditional fiberglass, effectively reducing noise transmission through enhanced density and unique microstructure. Fiberglass insulation, while widely used for thermal resistance, provides moderate acoustic dampening due to its fibrous composition but often requires greater thickness for comparable soundproofing performance. Nanoglass materials excel in high-frequency noise attenuation, making them ideal for environments demanding advanced sound control such as recording studios and urban housing.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Nanoglass insulation offers superior moisture resistance compared to fiberglass due to its non-porous, hydrophobic properties, effectively preventing water absorption and mold growth. Fiberglass insulation, while cost-effective, tends to retain moisture, leading to reduced thermal efficiency and potential structural damage over time. The enhanced durability of nanoglass makes it a more resilient choice for insulation in humid or wet environments, ensuring long-term performance and energy savings.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Nanoglass insulation offers a lightweight, flexible material that can easily conform to irregular spaces, making installation faster and more precise compared to traditional fiberglass batts. Fiberglass, while widely used, often requires careful handling due to its rigid panels and potential for fiber shedding, which can complicate the installation process and reduce flexibility in tight or unusual spaces. The superior adaptability of nanoglass reduces labor time and improves overall energy efficiency by minimizing gaps and thermal bridging.
Health and Safety Considerations
Nanoglass insulation offers superior health and safety benefits compared to traditional fiberglass, as it contains fewer airborne fibers that can irritate the respiratory system. Unlike fiberglass, which is known to cause skin irritation and potential long-term respiratory issues due to inhalation of glass particles, nanoglass is engineered to minimize particulate release, reducing occupational hazards during installation and maintenance. The non-toxic, chemically stable composition of nanoglass also ensures safer indoor air quality and lowers the risk of allergic reactions or chemical sensitivities common with some fiberglass products.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Nanoglass insulation generally demands a higher initial investment compared to fiberglass due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior material properties. Despite the upfront cost, nanoglass offers enhanced thermal resistance and durability, resulting in significant energy savings and lower maintenance expenses over time. Fiberglass remains a cost-effective solution for budget-conscious projects, but nanoglass delivers better long-term value through improved insulation efficiency and lifespan.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Buildings
Nanoglass insulation offers superior thermal resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to traditional fiberglass, making it highly efficient for both residential and commercial buildings. Its eco-friendly properties and lightweight structure enable easier installation and enhanced space utilization in tight architectural designs. Fiberglass remains popular for its cost-effectiveness and proven performance in large-scale projects, but nanoglass's advanced durability and resistance to moisture make it ideal for energy-efficient and sustainable building applications.
Choosing the Right Insulation Material for Your Project
Nanoglass insulation offers exceptional thermal resistance and durability by utilizing nanoscale glass fibers, providing superior energy efficiency compared to traditional fiberglass. Fiberglass remains popular due to its affordability and ease of installation, making it suitable for a wide range of applications where cost-effectiveness is a priority. Selecting the right insulation depends on project requirements, budget constraints, and desired thermal performance, with nanoglass ideal for high-performance needs and fiberglass for standard insulation tasks.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com