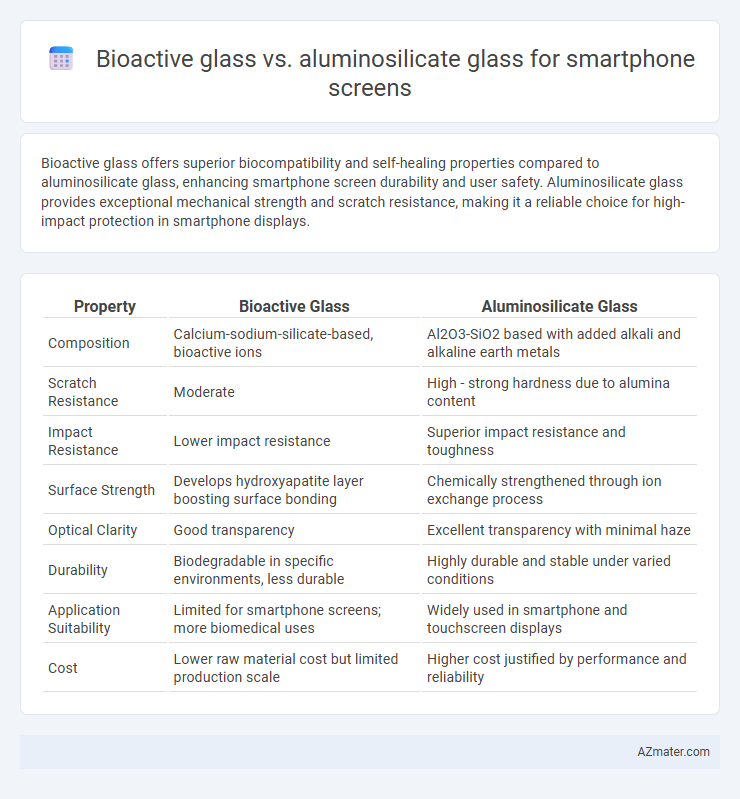
Bioactive glass offers superior biocompatibility and self-healing properties compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing smartphone screen durability and user safety. Aluminosilicate glass provides exceptional mechanical strength and scratch resistance, making it a reliable choice for high-impact protection in smartphone displays.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioactive Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium-sodium-silicate-based, bioactive ions | Al2O3-SiO2 based with added alkali and alkaline earth metals |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High - strong hardness due to alumina content |
| Impact Resistance | Lower impact resistance | Superior impact resistance and toughness |
| Surface Strength | Develops hydroxyapatite layer boosting surface bonding | Chemically strengthened through ion exchange process |
| Optical Clarity | Good transparency | Excellent transparency with minimal haze |
| Durability | Biodegradable in specific environments, less durable | Highly durable and stable under varied conditions |
| Application Suitability | Limited for smartphone screens; more biomedical uses | Widely used in smartphone and touchscreen displays |
| Cost | Lower raw material cost but limited production scale | Higher cost justified by performance and reliability |
Introduction to Smartphone Screen Materials
Bioactive glass offers enhanced biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties compared to traditional aluminosilicate glass, which is widely used for smartphone screens due to its high strength and durability. Aluminosilicate glass, formed by aluminum oxide and silica, provides excellent scratch resistance and impact protection critical for everyday mobile device use. Bioactive glass integration could improve user safety by reducing microbial contamination while maintaining essential mechanical properties.
What is Bioactive Glass?
Bioactive glass is a specialized material known for its remarkable ability to bond with biological tissues, primarily composed of silica, calcium oxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, which differentiates it from aluminosilicate glass used in smartphone screens. This glass type promotes healing and regeneration by releasing ions that interact with the environment, making it highly valued in biomedical applications rather than in typical display protection. While aluminosilicate glass offers superior scratch resistance and mechanical strength for smartphone screens, bioactive glass's unique chemical properties are more suited for medical fields, limiting its practicality in consumer electronics.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a durable, chemically strengthened material commonly used in smartphone screens due to its high resistance to scratches and impact. Composed primarily of silica and alumina, this glass offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to traditional soda-lime glass. Its enhanced durability makes it a preferred choice for protecting displays in modern smartphones.
Mechanical Strength: A Comparative Analysis
Bioactive glass exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it highly resistant to scratches and impacts on smartphone screens. Its unique composition enhances fracture toughness and hardness, outperforming the traditional aluminosilicate glass widely used in current devices. This increased mechanical resilience contributes to improved durability and longer lifespan of smartphone displays under everyday stress conditions.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Bioactive glass offers enhanced bioactivity but generally lacks the hardness and durability provided by aluminosilicate glass, which is widely used in smartphone screens for superior scratch resistance and impact durability. Aluminosilicate glass, strengthened through ion-exchange processes, demonstrates higher resistance to scratches and mechanical shocks, making it ideal for daily smartphone use. The inherent structural composition of aluminosilicate glass provides a balance of toughness and flexibility, resulting in fewer cracks and better overall impact absorption compared to bioactive glass.
Durability and Longevity
Bioactive glass exhibits superior resistance to chemical degradation and physical wear compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing smartphone screen durability. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in Gorilla Glass, offers excellent scratch resistance and impact strength but may be more prone to micro-crack formation under extreme conditions. The longer lifespan of bioactive glass stems from its ability to self-heal minor surface damage and maintain structural integrity over prolonged use, making it a promising material for next-generation smartphone screens.
Optical Clarity and Touch Sensitivity
Bioactive glass exhibits superior optical clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass, delivering higher light transmittance and reduced haze, which enhances display brightness and color accuracy in smartphone screens. The material's optimized surface chemistry also improves touch sensitivity by enabling more precise capacitive response and faster signal detection. In contrast, aluminosilicate glass, while durable, often has slightly lower transmittance and marginally reduced touch responsiveness due to its denser microstructure.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Bioactive glass for smartphone screens generally incurs higher production costs due to its complex synthesis involving biocompatible compounds and specialized processing techniques. In contrast, aluminosilicate glass benefits from well-established manufacturing methods, such as tempering and chemical strengthening, resulting in lower costs and widespread commercial availability. Manufacturing scalability favors aluminosilicate glass, making it the more cost-effective choice for mass-produced smartphone displays.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass offers enhanced environmental benefits compared to aluminosilicate glass due to its potential for biodegradability and recyclability, reducing long-term waste in smartphone screens. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and scratch-resistant, involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes and limited recycling options, leading to a higher carbon footprint. Incorporating bioactive glass in smartphone screens promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental pollution and supporting circular economy practices within the electronics industry.
Future Prospects in Smartphone Screen Technology
Bioactive glass offers promising future prospects in smartphone screen technology due to its self-healing properties and enhanced biocompatibility, potentially increasing screen durability and user safety. Aluminosilicate glass remains the industry standard with superior hardness and scratch resistance but may face limitations in flexibility and impact absorption compared to bioactive alternatives. Advances in nanotechnology could integrate bioactive glass components into hybrid screens, creating more resilient, sustainable, and multifunctional smartphone displays.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com