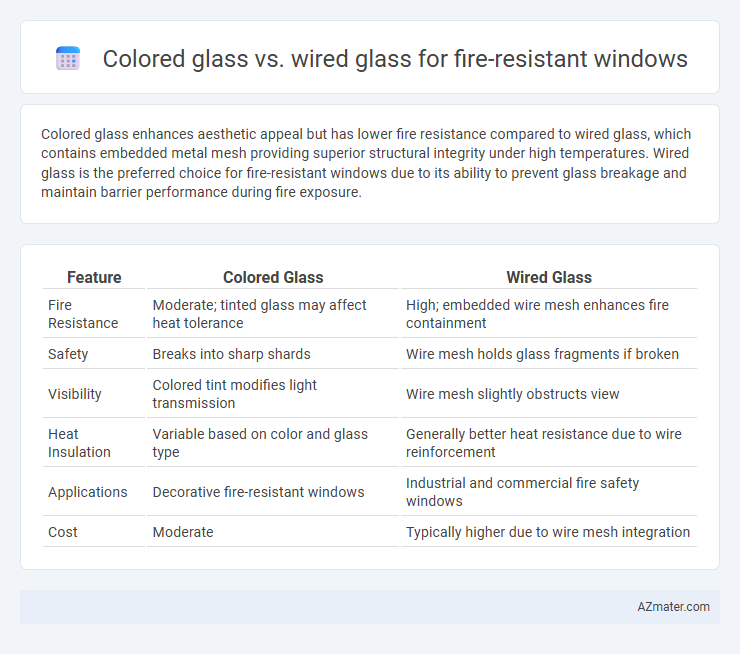
Colored glass enhances aesthetic appeal but has lower fire resistance compared to wired glass, which contains embedded metal mesh providing superior structural integrity under high temperatures. Wired glass is the preferred choice for fire-resistant windows due to its ability to prevent glass breakage and maintain barrier performance during fire exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate; tinted glass may affect heat tolerance | High; embedded wire mesh enhances fire containment |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp shards | Wire mesh holds glass fragments if broken |
| Visibility | Colored tint modifies light transmission | Wire mesh slightly obstructs view |
| Heat Insulation | Variable based on color and glass type | Generally better heat resistance due to wire reinforcement |
| Applications | Decorative fire-resistant windows | Industrial and commercial fire safety windows |
| Cost | Moderate | Typically higher due to wire mesh integration |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Windows
Fire-resistant windows are designed to prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, ensuring enhanced safety and structural integrity. Colored glass offers aesthetic appeal while maintaining heat resistance, whereas wired glass contains embedded steel mesh to hold the glass together under thermal stress. Choice between colored glass and wired glass depends on balancing fire protection standards with design preferences and visibility needs.
What Is Colored Glass?
Colored glass for fire-resistant windows incorporates metal oxides or other colorants during manufacturing to achieve specific hues while maintaining fire-resistance properties, enhancing aesthetic appeal without compromising safety. Unlike wired glass, which includes a metal mesh to hold shards during breakage, colored glass relies on its chemical composition to withstand high temperatures and inhibit flame spread. Its ability to combine visual design with fire protection makes colored glass a versatile option for architectural applications requiring both safety and style.
What Is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of fire-resistant glass embedded with a metal mesh that holds the glass fragments together during exposure to heat and flames, preventing shattering and maintaining structural integrity. Compared to colored glass, wired glass offers enhanced safety by reducing the risk of breakage and providing a reliable barrier against fire spread while still allowing light transmission. Its fire-resistant properties make wired glass a preferred choice in fire-rated windows for commercial and industrial applications.
Fire-Resistance Properties: Colored vs Wired Glass
Colored glass offers moderate fire resistance by absorbing and diffusing heat, reducing glare while maintaining visibility during a fire, but it may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as wired glass. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, provides superior fire resistance by holding the glass intact under intense heat and preventing shattering, thereby maintaining a barrier to flames and smoke. For fire-resistant windows, wired glass is typically preferred for its enhanced ability to maintain structural integrity and safety during fire exposure.
Safety and Impact Resistance Comparison
Colored glass offers moderate impact resistance and enhances visibility during fire emergencies, while wired glass excels in fire resistance by preventing glass shattering and providing structural integrity under heat. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that holds the glass fragments together, significantly improving safety by reducing the risk of injury from flying shards. Although wired glass is more effective in fire containment and impact resistance, colored glass can be specially treated to meet certain fire safety standards while offering aesthetic benefits.
Design and Aesthetic Considerations
Colored glass for fire-resistant windows enhances design versatility by offering a wide palette of hues that complement architectural styles and interior themes, creating unique visual appeal. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh, providing a textured, industrial aesthetic that prioritizes safety but limits color options and smoothness. Design choices must balance aesthetic desires with fire safety standards, as wired glass often suits utilitarian environments, while colored glass appeals to creative and decorative applications.
Thermal Performance and Insulation
Colored glass for fire-resistant windows offers enhanced solar control by reducing heat gain through its tinted properties, improving thermal performance in both residential and commercial settings. Wired glass, while providing structural integrity during fire exposure, generally exhibits poorer insulation values due to its wire mesh, which can create thermal bridging and reduce overall energy efficiency. Selecting colored glass with advanced fire-resistant coatings delivers superior thermal insulation, minimizing heat transfer and maintaining safer indoor temperatures compared to traditional wired glass installations.
Cost and Installation Factors
Colored glass for fire-resistant windows generally costs more due to specialized manufacturing processes and pigment integration, while wired glass offers a more budget-friendly option with simpler production. Installation of colored glass requires precise handling to preserve its aesthetic qualities, often demanding skilled labor, whereas wired glass is easier to install due to its standard thickness and reinforced wire mesh. Cost efficiency favors wired glass in large projects, but colored glass provides added design value that may justify higher installation expenses.
Maintenance Requirements and Durability
Colored glass for fire-resistant windows generally requires less frequent maintenance due to its smooth surface and resistance to staining and corrosion, while wired glass demands more regular inspections and cleaning because the embedded wire mesh can accumulate dirt and rust over time. In terms of durability, colored glass often offers superior long-term resilience against thermal stress and environmental factors, whereas wired glass may be more prone to chipping and corrosion around the wire mesh, potentially compromising its fire resistance and structural integrity. Choosing colored glass reduces upkeep costs and ensures sustained performance in fire safety applications.
Which Glass Is Best for Fire-Resistant Windows?
Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, is traditionally favored for fire-resistant windows due to its ability to maintain structural integrity under high temperatures, preventing fire spread. Colored glass offers aesthetic appeal but generally lacks the same level of fire performance and heat resistance required for safety certifications. For optimal fire resistance, wired glass remains the superior choice, meeting stringent building code requirements and ensuring reliable fire protection.
Infographic: Colored glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant window
 azmater.com
azmater.com