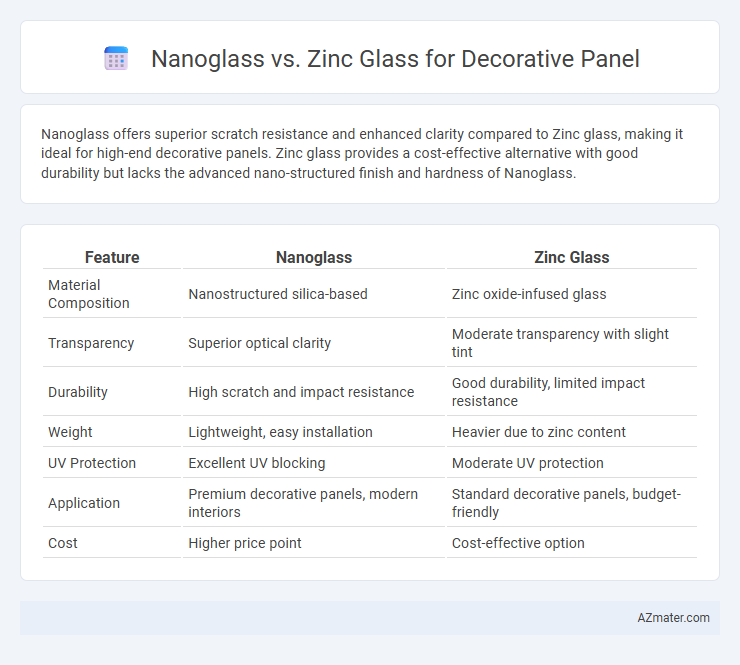
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced clarity compared to Zinc glass, making it ideal for high-end decorative panels. Zinc glass provides a cost-effective alternative with good durability but lacks the advanced nano-structured finish and hardness of Nanoglass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanoglass | Zinc Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Nanostructured silica-based | Zinc oxide-infused glass |
| Transparency | Superior optical clarity | Moderate transparency with slight tint |
| Durability | High scratch and impact resistance | Good durability, limited impact resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy installation | Heavier due to zinc content |
| UV Protection | Excellent UV blocking | Moderate UV protection |
| Application | Premium decorative panels, modern interiors | Standard decorative panels, budget-friendly |
| Cost | Higher price point | Cost-effective option |
Introduction to Decorative Glass Panels
Decorative glass panels enhance interior design by combining aesthetics with functionality, offering durability, clarity, and customization. Nanoglass features nanotechnology-based coatings that improve scratch resistance, UV protection, and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Zinc glass incorporates zinc oxide for enhanced strength and thermal stability, providing unique metallic finishes and increased durability in decorative applications.
What is Nanoglass?
Nanoglass is an advanced decorative panel material produced using nanotechnology to enhance glass properties such as increased strength, scratch resistance, and clarity. Unlike traditional zinc glass, which contains zinc oxide for durability, nanoglass incorporates nanoscale coatings or particles that significantly improve surface hardness and UV resistance. These enhancements make nanoglass ideal for decorative applications requiring both aesthetic appeal and long-lasting performance.
What is Zinc Glass?
Zinc glass is a type of decorative panel material made by incorporating zinc oxide into the glass matrix, enhancing durability and providing a smooth, high-gloss finish ideal for modern interiors. Compared to nanoglass, zinc glass offers superior resistance to scratches and chemical corrosion, making it suitable for high-traffic areas. Its excellent light transmission and color stability maintain vibrant aesthetics over time, distinguishing it from conventional and nanostructured glass panels.
Nanoglass vs Zinc Glass: Composition & Manufacturing
Nanoglass for decorative panels is composed of ultra-fine silica nanoparticles that create a smooth, durable surface with enhanced clarity and scratch resistance, manufactured through a sol-gel process that allows precise control over thickness and texture. Zinc glass incorporates zinc oxide into the glass matrix, increasing durability and UV resistance, produced via traditional glass melting and casting methods that integrate zinc compounds for improved strength and aesthetic qualities. The manufacturing of nanoglass prioritizes nanoscale particle dispersion for superior optical properties, whereas zinc glass relies on chemical additives within the molten glass to achieve enhanced mechanical and environmental performance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Comparing Visual Qualities
Nanoglass offers superior clarity and a more reflective surface, enhancing the brightness and depth of decorative panels compared to traditional zinc glass. Zinc glass presents a slightly muted, vintage aesthetic with softer tones and a matte finish, suitable for rustic or industrial designs. The choice between nanoglass and zinc glass depends on whether a modern, glossy look or a subtler, textured appearance is desired for the decorative panel.
Durability and Strength: Nanoglass vs Zinc Glass
Nanoglass exhibits superior durability and strength compared to zinc glass, making it ideal for high-impact decorative panels in commercial and residential spaces. Its advanced molecular structure significantly enhances resistance to scratches, cracks, and thermal stress, outperforming zinc glass under heavy usage conditions. Zinc glass, while offering moderate strength and corrosion resistance, is more prone to surface wear and mechanical damage over time, limiting its lifespan in demanding applications.
Maintenance & Cleaning: Which is Easier?
Nanoglass surfaces offer superior resistance to stains and scratches compared to zinc glass, making maintenance and cleaning simpler and less time-consuming. Zinc glass requires specialized cleaning agents to avoid surface degradation, while nanoglass can be effectively cleaned with standard, mild detergents without compromising its finish. The durability of nanoglass reduces the frequency of deep cleaning and preserves its aesthetic appeal for longer periods.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Decorative Panels
Nanoglass panels exhibit higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing techniques but offer long-term savings through durability and scratch resistance, reducing replacement frequency. Zinc glass panels present a more affordable upfront investment, suited for projects with strict budget constraints, though they may incur additional maintenance costs over time. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including installation, upkeep, and replacement, is essential for accurate budgeting in decorative panel selection.
Environmental Impact & Sustainability
Nanoglass decorative panels offer superior environmental benefits due to their energy-efficient manufacturing process and higher recyclability compared to traditional Zinc glass panels. Zinc glass production typically involves higher carbon emissions and less sustainable sourcing of raw materials, negatively impacting overall ecological footprints. Choosing Nanoglass supports sustainable architecture by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting closed-loop material usage in decorative panel applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Decorative Panels
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced clarity, making it ideal for high-traffic decorative panels requiring durability and ultra-clear aesthetics. Zinc glass, known for its unique light diffusion and metallic properties, provides a distinctive reflective finish suitable for artistic or modern interior designs. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing durability, visual impact, and specific environmental conditions of the installation site.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Zinc glass for Decorative panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com