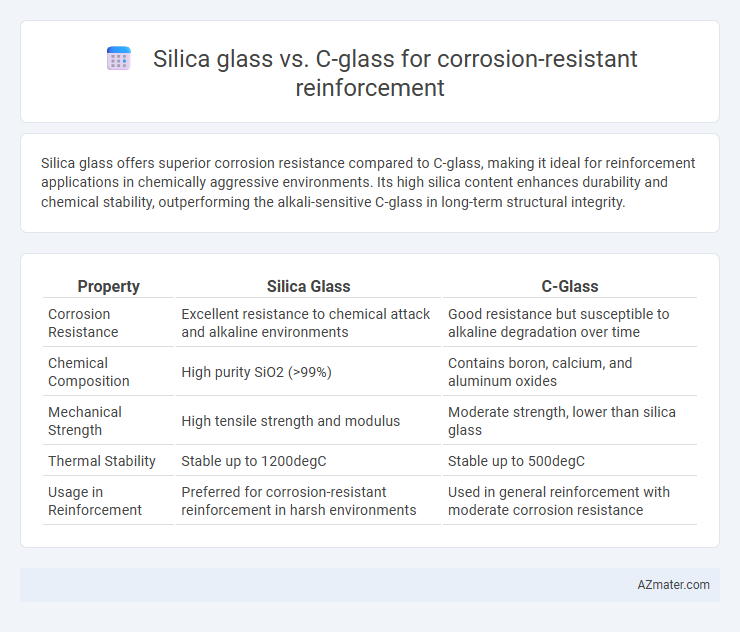
Silica glass offers superior corrosion resistance compared to C-glass, making it ideal for reinforcement applications in chemically aggressive environments. Its high silica content enhances durability and chemical stability, outperforming the alkali-sensitive C-glass in long-term structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | C-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to chemical attack and alkaline environments | Good resistance but susceptible to alkaline degradation over time |
| Chemical Composition | High purity SiO2 (>99%) | Contains boron, calcium, and aluminum oxides |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and modulus | Moderate strength, lower than silica glass |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 1200degC | Stable up to 500degC |
| Usage in Reinforcement | Preferred for corrosion-resistant reinforcement in harsh environments | Used in general reinforcement with moderate corrosion resistance |
Introduction to Corrosion-Resistant Reinforcements
Silica glass and C-glass are two prominent materials used for corrosion-resistant reinforcements in concrete structures, with silica glass offering superior chemical stability and high resistance to alkaline environments. C-glass, known for its cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties, provides moderate resistance to corrosion but lacks the durability of silica glass under aggressive chemical exposures. The choice between silica glass and C-glass significantly impacts the longevity and maintenance requirements of reinforcement in infrastructure exposed to corrosive conditions.
Overview of Silica Glass Reinforcement
Silica glass reinforcement offers superior corrosion resistance due to its high silicon dioxide content, which provides excellent chemical stability in aggressive environments. The material exhibits low permeability and exceptional durability, making it ideal for reinforcing structures exposed to acid, alkali, and marine conditions. Compared to C-glass, silica glass delivers enhanced mechanical strength and longevity in corrosive applications, reducing maintenance costs and extending service life.
Characteristics of C-Glass Reinforcement
C-glass reinforcement is highly favored in corrosion-resistant applications due to its excellent chemical stability and resistance to alkalis, acids, and moisture, outperforming silica glass in harsh environments. Its composition typically includes calcium oxide and boron oxide, which enhance its durability and maintain structural integrity under prolonged exposure to corrosive substances. C-glass also offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for reinforcing concrete structures subject to aggressive chemical attacks.
Chemical Composition Differences
Silica glass reinforcement primarily consists of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) with minimal impurities, offering superior chemical durability and resistance to alkaline environments. In contrast, C-glass incorporates calcium oxide (CaO) and boron oxide (B2O3) in addition to silica, which enhances chemical resistance but may reduce overall durability in highly aggressive corrosive settings. The distinct chemical compositions influence their performance, with silica glass providing enhanced corrosion resistance in concrete reinforcement applications where alkaline and chloride exposure is critical.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Silica glass exhibits higher tensile strength and superior thermal stability compared to C-glass, making it more resistant to mechanical degradation in corrosive environments. C-glass offers good chemical durability but generally possesses lower modulus of elasticity and tensile strength than silica glass, resulting in reduced stiffness and mechanical performance under stress. For corrosion-resistant reinforcement, silica glass is preferred when mechanical resilience and long-term structural integrity are critical.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Silica glass exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to C-glass, making it ideal for reinforcement applications in highly alkaline environments such as concrete. The high silica content in silica glass enhances its chemical durability and reduces susceptibility to hydroxide ion attack, thus extending the lifespan of reinforced structures. In contrast, C-glass contains lower silica and higher boron and aluminum oxides, which are less effective in preventing corrosion, especially in chloride-rich or acidic conditions.
Durability in Harsh Environments
Silica glass offers superior chemical stability and significantly higher resistance to alkaline environments compared to C-glass, making it ideal for corrosion-resistant reinforcement in harsh conditions. Its low alkali content and enhanced durability extend the lifespan of structures exposed to aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, outperforming C-glass in long-term performance. While C-glass provides moderate corrosion resistance, its susceptibility to degradation under high pH and chloride exposure limits its effectiveness in extremely harsh environments.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Silica glass offers superior chemical resistance and high thermal stability, making it ideal for construction applications requiring durable, corrosion-resistant reinforcement in harsh environments such as chemical plants and offshore structures. C-glass, with its excellent alkali resistance and electrical insulating properties, is commonly used in industrial applications like pipelines, storage tanks, and reinforced concrete exposed to mildly corrosive conditions. Both materials enhance structural integrity by preventing degradation caused by moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, but Silica glass is preferred for extreme corrosive environments due to its higher purity and resistance.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Silica glass offers superior corrosion resistance for reinforcement applications but comes at a higher cost due to its complex manufacturing process and limited raw material availability. C-glass provides a more cost-effective alternative with widely available raw materials, making it suitable for large-scale projects despite slightly lower corrosion resistance. The choice between silica glass and C-glass hinges on balancing upfront material expenses against long-term durability requirements and supply chain reliability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Reinforcement Material
Silica glass and C-glass both offer corrosion resistance for reinforcement applications, but silica glass provides superior chemical stability and enhanced durability in aggressive environments. C-glass, while cost-effective and resistant to alkalis, may not perform as well under prolonged exposure to highly corrosive agents. Selecting silica glass reinforcement ensures longer service life and improved structural integrity in demanding corrosion-resistant conditions.
Infographic: Silica glass vs C-glass for Corrosion-resistant reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com