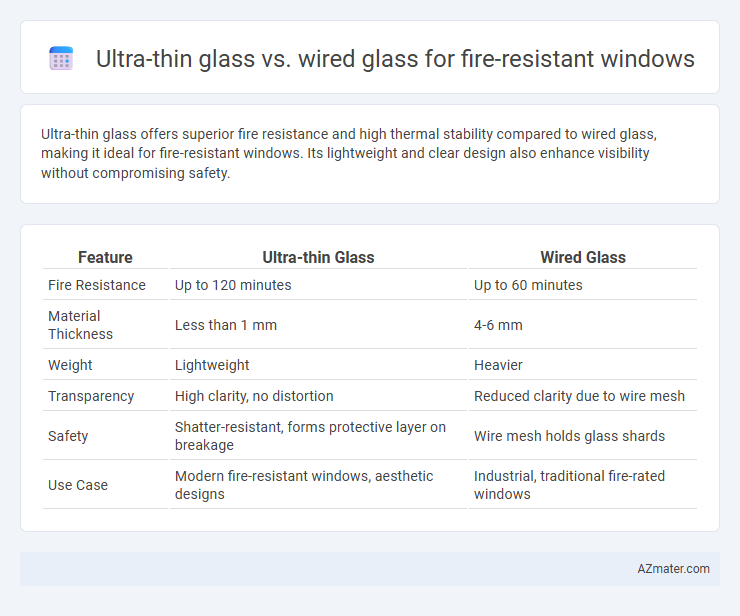
Ultra-thin glass offers superior fire resistance and high thermal stability compared to wired glass, making it ideal for fire-resistant windows. Its lightweight and clear design also enhance visibility without compromising safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-thin Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Up to 120 minutes | Up to 60 minutes |
| Material Thickness | Less than 1 mm | 4-6 mm |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Transparency | High clarity, no distortion | Reduced clarity due to wire mesh |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant, forms protective layer on breakage | Wire mesh holds glass shards |
| Use Case | Modern fire-resistant windows, aesthetic designs | Industrial, traditional fire-rated windows |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Window Technologies
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced transparency and lightweight properties while maintaining fire-resistant capabilities, making it ideal for modern architectural designs. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh to prevent shattering and provides a robust barrier against heat and flames. Both technologies address different safety and aesthetic needs in fire-resistant window applications, with ultra-thin glass emphasizing sleekness and wired glass ensuring structural resilience.
What is Ultra-Thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass is a specialized fire-resistant material characterized by its minimal thickness, typically less than 0.5 mm, allowing for enhanced heat resistance and flexibility compared to traditional wired glass. This type of glass incorporates advanced manufacturing techniques to maintain structural integrity under high temperatures while providing superior clarity and lightweight properties. Ultra-thin glass outperforms wired glass in thermal insulation and impact resistance, making it an innovative choice for fire-resistant window applications.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of fire-resistant window glass embedded with a metal wire mesh, which reinforces the glass and prevents it from shattering during a fire. This wire mesh helps contain flames and smoke while maintaining some structural integrity under high temperatures, meeting fire safety standards in many commercial buildings. However, wired glass tends to be heavier and less optically clear than ultra-thin glass alternatives, which offer improved aesthetics and lighter weight without compromising fire resistance.
Fire Resistance Capabilities: Ultra-Thin Glass vs Wired Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers high-temperature resistance up to 1,000degF (538degC) and rapid heat dissipation, making it effective for fire-resistant windows in modern architecture. Wired glass, traditionally rated for fire resistance around 45 to 90 minutes, prevents glass shattering by maintaining structural integrity through embedded wire mesh but may allow higher heat transfer. Ultra-thin glass provides superior thermal insulation and clarity while wired glass emphasizes fire containment by reducing glass fragmentation during fire exposure.
Safety and Impact Resistance Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers superior impact resistance and enhanced safety due to its flexibility and ability to absorb shock without shattering, making it ideal for fire-resistant windows in high-risk environments. Wired glass, while fire-resistant, is more brittle and prone to breakage under impact, posing safety risks from sharp glass fragments. In fire safety applications, ultra-thin glass provides a safer, more durable solution by combining fire resistance with increased strength and impact absorption.
Thermal Performance and Insulation
Ultra-thin glass offers superior thermal performance with higher insulation values and lower thermal conductivity compared to wired glass, effectively reducing heat transfer during a fire. Wired glass, embedded with wire mesh, provides mechanical strength but has lower insulation properties, allowing more heat to pass through, which compromises thermal resistance. Choosing ultra-thin glass enhances energy efficiency and fire safety by maintaining temperature stability and minimizing heat penetration in fire-resistant window applications.
Aesthetic Considerations and Design Flexibility
Ultra-thin glass offers superior aesthetic appeal with its sleek, minimalistic profile and enhanced clarity, allowing for greater natural light transmission and unobstructed views in fire-resistant window applications. Wired glass, while traditionally valued for its fire resistance and security, presents a more industrial look due to embedded wire mesh, which can limit design options and visual openness. Designers seeking modern, elegant solutions frequently prefer ultra-thin glass for its flexibility in custom shapes and seamless integration into contemporary architectural styles.
Cost and Installation Factors
Ultra-thin glass offers a modern, lightweight option for fire-resistant windows with higher upfront costs but simplified installation due to its reduced weight and flexibility. Wired glass, typically more affordable, involves more complex installation processes because of its heavier, reinforced structure and specialized mounting requirements. Choosing between the two hinges on budget constraints and installation capabilities, with ultra-thin glass favored for cost-effectiveness in labor and wired glass chosen for traditional robustness at lower material prices.
Compliance with Fire Safety Standards
Ultra-thin glass meets stringent fire safety standards like NFPA 257 and ASTM E119 due to its exceptional thermal resistance and integrity during fire exposure. Wired glass complies with these standards by maintaining a wire mesh that prevents glass fragmentation, enhancing fire containment. Both types are approved for fire-resistant windows but differ in optical clarity and safety performance under impact.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Building
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity, lightweight properties, and enhanced flexibility, making it an ideal choice for modern fire-resistant windows in high-rise buildings where design aesthetics and space-saving are crucial. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, provides robust heat resistance and fire containment, making it suitable for industrial settings and areas with stringent fire safety regulations. Selecting between ultra-thin glass and wired glass depends on factors such as building code requirements, thermal performance, structural demands, and architectural design priorities to ensure optimal fire protection and safety compliance.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant window
 azmater.com
azmater.com